Sarcophagus of the spouses Etruscan c. 520 BCE Terracotta
advertisement

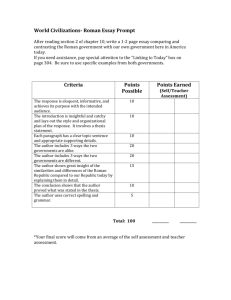
Sarcophagus of the spouses Etruscan c. 520 BCE Terracotta Sarcophagus of married couple, ashes inside Once held objects in hands, possibly egg to symbolize fertility Temple of Minerva and sculpture of Apollo of Veii (Veii, near Rome, Italy) Master Sculptor Vulca Etruscan c.510 – 500 BCE Wood, Mudbrick or Tufa (volcanic rock) Temple made of mud brick and wood Very little architecture survives, models from descriptions by Vitruvius Tomb of the Triclinium Tarquinia, Italy Etruscan c. 480-470 BCE House of the Vetti Pompeii, Italy Imperial Roman c. 2nd C BCE rebuilt 62-79 CE Plan Atrium Frescoes Terra Cotta sculpture Tufa (limestone) and Fresco Cut Stone & Fresco Tomb House of 2 brothers Freedmen who made money as merchants Reclining while eating, banquet couch Man has protective gesture around woman And woman is feeding him…Symbolic of high standing women had in Etruscan society Influences of Greek architecture in the columns and capitals. Etruscan variation on Greek Capitals, called Tuscan order. Men painted darker than women Named after an ancient Banqueting couples Roman dining table, recline, eating in appearing in fresco ancient manner Large reception area, Peristyle garden in rear atrium - open to sky, has a catch basin called Axial symmetry allows impluvium in the someone entering to center. see all the way through to peristyle garden No Exterior windows Alexander Mosaic from the House of Faun, Pompeii Republican Roman c. 100 BCE Mosaic Roman floor mosaic based on an original Greek Mural painting found at Pompeii Alexander at left, young, brave, assured of success. Darius in center right on chariot, horrified, surrendering victory Complex interweaving of figures Head of a Roman patrician Republican Roman c. 75-50 BCE Marble Bust of a man Depicted as elderly Influence of Greek Extremely realistic face Helenistic art Called a veristic Full of experience and portrait wisdom – desired traits Deep crevices in face Augustus of Prima Porta Imperial Roman Early 1st c. CE Marble Idealized view of the Roman Emeror Contrapposto Confusion between god Barefoot indicates he is and man, sense of on divine ground divine rule Back not carved, placed Breastplate indicates against a wall he is a warrior, judges Right hand held in robes show him as a Roman orator pose civic ruler Colosseum (Flavian Ampitheater) Rome, Italy Imperial Roman 70-80 CE Stone & Concrete Wild, dangerous spectacles – gladiator combat, animal hunts, not used in religious prosecution Forum of Trajan Rome, Italy Apollodorus of Damascus Forum & Markets 106-112 CE Column of Trajan – 113 CE Brick & Concrete Architecture Marble (Column) Law Courts held here, Apses for judges 50,000 spectators Concrete core Real name is Flavian Ampitheater 76 entrances & exits circle the façade Interplay of barrel vaults, groin vaults, & arches Much of the marble was removed in the Middle Ages Nave is spacious and wide Columns “lighten” in order as the go up each level: Tuscan, Ionic, Corinthian, flattened Corinthian Façade has engaged columns Top level has small brackets used to hold flagstaffs, anchors for a retractable canvas roof to protect crowd on hot days Paid for by Trajan’s spoils taken from defeat of the Dacians Pantheon Imperial Roman 118-125 CE Concrete with Stone facing Dedicated to the gods 2 Pediments, one deeply recessed behind the other. Built to contain a perfect sphere, influenced by Greek mathematical ideas Ludovisi Battle Sarcophagus Late Imperial Roman c. 250 CE Marble Battle sarcophagus Very crowded surface: Horror Vacui Confusion of battle Oculus acts as light source & air Height =width Hemisphere Triumph of concrete construction Niches for statues of gods When it was made, it was the largest dome in the world and it would be hunreds of years before architects built a dome of a similar size Roman army slaughters barbarians Roman general has no helmet/invincible Rome at war throughout 3rd Century