File
advertisement

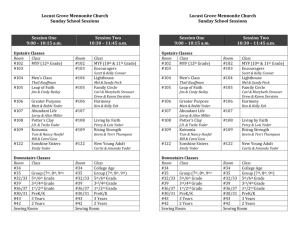
Unit 2 Review Chp. 18-19 and Current Supreme Court Cases Free Exercise Case discussed in-class: Reynolds v USA, Gobitis & Barnette Still need to know: Wisconsin v Yoder (1972) Reynolds v USA (1879) Principle: if the practice of your faith VIOLATES a federal law, your practice must stop. [Gov’t wins!] Gobitis & Barnette Gobitis Principle: if intent of law is secular and important (patriotism), then Faith needs to yield. [Gov wins!] Barnette: if the intent of the law (secular and important) can be met another way; then law must yield. [Faith wins!] Wisconsin v Yoder (1972) Basic Facts: Yoder (Amish man) pulled son out of school at the end of 8th grade. New WI law required students to stay until 16 ys old. Yoder said staying in modern school and learning modern info went against his faith and violated his son’s free exercise clause. Wisconsin v Yoder (1972) Ruling for YODER! Principle: if the practice of your faith MEETS the INTENT of the law, then the LAW must change [win for Faith!] Grant Cert? A parochial school received government funds to send three teachers to AP programs. A citizen of the district claimed this action violated the Free Establishment clause of the 1st Amendment. The lower court sided with the school. The Circuit Court reversed the ruling. This action reinterpreted the Lemon Test created by the Supreme Court in the 1960’s. The school has requested a writ of cert. YES – Grant cert! Importance – Amendment issue, broad impact on religious schools. Some conflict & new precedence trying to be set Match the Case with the Issue 4th Amendment Marbury v. Madison (1803) Judicial Review Reynolds v. United States Free Exercise Clause Lemon v. Kurtzman (1979) Establishment Clause Kyllo v US(2001) Match the Case with the Issue 4th Amendment Marbury v. Madison Judicial Review Reynolds v. United States Free Exercise Clause Lemon v Kurztman (1979) Establishment Clause Kyllo v US (2001) How does one become a Supreme Court Justices? S. Court Justices A lifetime of experience and good reputation Nominated by the President Confirmed by the Senate On FOR LIFE Example(s) of protected Free Exercise Refusing to say the Pledge of Allegiance Not stopping at red lights because you are singing praise songs in your car Requiring all students in a public school to be silent while proctor prays before the SAT Muslim student wearing a head covering to school Free Exercise Winners • Refusing to say the Pledge of Allegiance • Muslim student wearing a head covering to school Explain the Difference Between… Loose Constructionist vs. Strict constructionist Explain the Difference Between… Loose Constructionist vs. Strict constructionist General: A philosophy of Constitutional interpretation Loose constructionist = interpret the Constitution based on the intent of the Framers within the context of today, more open Strict constructionist = interpret the Constitution based on the letter of the law; if it’s directly stated in the Constitution than it’s not a power of the federal government Put in the right order Opinion read in public Certiorari granted Oral arguments Briefs written and submitted Trial court File for Writ of Certiorari Conference Held Correct Order Trial Court File for Writ of Certiorari Certiorari Granted Write and submit briefs Oral arguments Conference Opinions read in public Matching the case with the issue Free Speech Free Establishment Free Exercise Clause Lemon v Kurtzman Gobitas (1940) and Barnette (1943 ) decisions Wisconsin v. Yoder (1972) Everson v Board of Education Snyder v Phelps (2011) Matching the case with the issue Free Speech Free Establishment Free Exercise Clause Lemon v Kurtzman Gobitas (1940) and Barnette (1943 ) decisions Wisconsin v. Yoder (1972) Everson v Board of Education Snyder v Phelps (2011) How does Congress check the Supreme Court? Congress’ check on S. Court Senate confirms the nominations Senate holds the impeachment trial Congress sets the salary Congress sets the size of judicial districts Congress writes the laws Pass new amendments When does the Supreme Court have original jurisdiction? Original Jurisdiction State vs. State issue: State is suing another state Another nation is the one of the litigants Match the facts with the case FACTS Amish and Education Pledge of Allegiance and 7th Day Adventists Busing to Parochial Schools Mormons and Polygamy CASE Gobitis (1940) & Barnette (1943) Reynolds v US (1879) Wisconsin v Yoder (1972) Everson v Board of Education(1979) Match the facts with the case FACTS Amish and Education Pledge of Allegiance and 7th Day Adventists Busing to Parochial Schools Mormons and Polygamy CASE Gobitis (1940) & Barnette (1943) Reynolds v US (1879) Wisconsin v Yoder (1972) Everson v Board of Education (1979) Name the S. Court Justices Supreme Court Justices BACK ROW: (left to right) Maria Sotomayor, Stephen Breyer, Samuel Alito, Elena Kegan FRONT ROW: (Left to Right) Clarence Thomas, Antonin Scalia, Chief Justice John Roberts, Anthony Kennedy, Ruth Bader Ginsberg