Periodic Table: History, Organization & Properties | Chemistry
advertisement

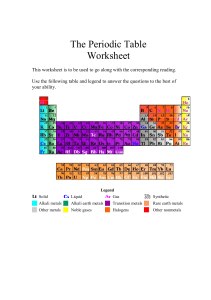
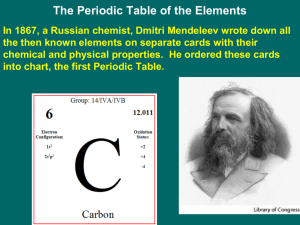
THE PERIODIC TABLE SCH3U1 Johann Wolfgang Dobereiner (1829) • Dobereiner organized known elements into triads based on their similar properties: Li – Na – K Ca – Sr – Ba S – Se - Te Cl –Br - I John Newlands (1865) • Ranked elements by atomic mass • Noted that elements with similar properties occurred every 8th element • Newlands called this pattern The Law of Octaves Dimitri Mendeleev (1869) • Known as the father of the periodic table • Assembled the first periodic table by atomic mass • Elements with similar properties were placed in columns • Left spaces for undiscovered elements and predicted their properties • The modern table is now arranged by increasing atomic number The Periodic Law “ The properties of the elements recur in a systematic pattern when the elements are arranged by atomic number.” Periods = horizontal rows Groups (Families) = vertical columns • contain elements with similar properties. . The Mendeleev Activity 1. Cut out and arrange the cards of the known elements into a crude representation of the Periodic Table. Hint: atomic mass always increases across a row and down a column! 2. Show me your table and get the unknown elements cards. 3. Place the unknown elements in the correct locations and identify the elements. 4. Complete the Periodic Table Layout sheet and answer the questions. Mendeleev’s Predictions • Mendeleev predicted the properties of the undiscovered element ekasilicon (germanium) very accurately: Property Ekasilicon (predicted 1869) Germanium (actual 1886) Atomic mass 72 72.32 Colour Dark grey Greyish-white Density (g/cm3) 5.5 5.47 Melting point (oC) High 947 Formula of Oxide EsO2 GeO2 Formula of Chloride EsCl4 GeCl4 Organization of the Modern Periodic Table Group Numbers transition metals inner transition metals Alternate Periodic Tables: Group 1: The Alkali Metals Elements: Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr Shared Physical Properties: • Soft solids at room temp. • Malleable • Ductile metallic • Good conductors of heat/electricity character Group 1: The Alkali Metals (continued) Elements: Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr Shared Chemical Properties: • Form soluble bases (alkali solutions) in water • Form oxides with formula X2O Group 2: The Alkaline Earth Metals Elements: Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra Shared Physical Properties: • solids at r.t. • Metallic character • Shared Chemical Properties: • Form insoluble bases in water • Form oxides with formula XO Group 17: The Halogens Elements: F, Cl, Br, I, At Shared Physical Properties: • Gas, liquid or solids at r.t. • Non-metallic Shared Chemical Properties: • React with metals to form solid salts (MX) • Form diatomic molecules (X2) Group 18: The Noble Gases Elements: He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn Shared Physical Properties: • Gases at r.t. • Non-metallic Shared Chemical Properties: • Very unreactive • Stable monoatomic atoms