File historical figures and research methods exam
advertisement

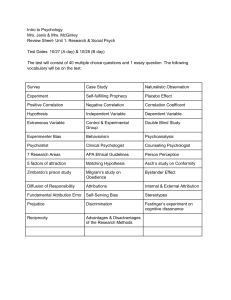
Historical Introduction and Research Method Exam 1. Psychology is defined as: a. the science of behavior and consequences. b. the scientific study of behavior and mental processes. c. the study of behavior and mental processes. d. the study of behavior. 2. The 1st psychological laboratory was established by: a. Wilhelm Wundt. b. Sigmund Freud. c. John Locke. d. B.F. Skinner. e. William James 3. William James studied behavior based on how it was adaptive. He was heavily influenced by _____. a. Charles Darwin b. Francis Bacon c. John Locke d. Sigmund Freud e. Sigmund Freud 4. This psychologist stated that as humans we need genuineness, acceptance and empathy for us to grow. a. Sigmund Freud b. Wilhelm Wundt c. John Watson d. William James e. Carl Rodgers 5. This psychologist used the method of introspection in his “research” to describe conscious experiences, such as the basic elements of an apple. a. b. c. d. e. Carl Rodgers John Watson Sigmund Freud Wilhelm Wundt William James 6. 1st American psychologist and functionalist rote the first general text book on psychology called Principles of Psychology (1890) a. Sigmund Freud b. Wilhelm Wundt c. John Watson d. William James e. Carl Rodgers 7. __________________ said our personality is based on three structures, id, ego, and superego.. a. Abraham Maslow b. B.F. Skinner c. Carl Rodgers d. Sigmund Freud e. William James Historical Introduction and Research Method Exam 8. This behavioral researcher used classical conditioning to change behaviors. He is well known for his Little Albert experiment. a. Carl Rodgers b. John Watson c. Sigmund Freud d. Wilhelm Wundt e. William James 9. This researcher was considered the Mac Daddy of Operant Conditioning. He was a nurture guy through and through. a. Carl Rodgers b. John Watson c. Wilhelm Wundt d. B.F. Skinner e. William James 10. This psychologist studies the structure and function of the brain as they relate to specific psychological processes and behaviors. a. Clinical Psychologist b. Educational Psychologist c. Evolutionary Psychologist d. Neuropsychologist. e. School Psychologist 11. The study of the psychological adaptations of humans to the changing physical and social environment, and behavioral differences among individuals. a. Developmental Psychologist b. Educational Psychologist c. Evolutionary Psychologist d. Neuropsychologist. e. School Psychologist 12. This psychologist focuses studies physical, cognitive and social changes throughout the lifespan a. Evolutionary Psychologist b. Developmental Psychologist c. School Psychologist d. Educational Psychologist e. Neuropsychologist. Historical Introduction and Research Method Exam 13. They focus on the diagnosis and treatment of children’s learning issues. a. Developmental Psychologist b. Educational Psychologist c. Evolutionary Psychologist d. Neuropsychologist. e. School Psychologist 14. Observing subjects in their natural setting without getting involved is called. a. survey. b. naturalistic observation. c. participant observation. d. correlation. e. case study 15. “As more ice cream is eaten, more people are murdered” is a wonderful example of: a. Case study b. Correlation c. Experiment d. Naturalistic Observation e. Survey 16. An act or operation for the purpose of discovering something unknown or of testing a hypothesis or theory is called a(n): a. Case study b. Correlation c. Experiment d. Naturalistic Observation e. Survey 17. Repeating a research study to see whether the first finding can be repeated with other subjects and circumstances usually with different subjects in different situations is called: a. Replication b. Survey c. Scientific Method d. Participant Observation e. Hawthorne Effect Historical Introduction and Research Method Exam 18. A hypothesis is a(n): a. passion to explore and understand without misleading or being mislead b. process of linking facts to deeper principles. c. set of principles that explains newly discovered facts. d. testable prediction that gives direction to research. e. way to organize facts. 19. An explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes and predicts observations a. inferential reasoning. b. correlation coefficient. c. hypothesis d. theory e. conclusion 20. The following is an example of an operational definition: a. he is stressed and doesn’t adjust to his environment. b. he engages in academic time by attending to material and task, making the appropriate response (yes or no), and asking for assistance in an appropriate manner (“Could you please help me on this?”). c. she shows empathy and can understand the other person’s feelings. d. all of the above. e. none of the above. 21. A mistaken belief that two factors or events are related when they are not is called: a. an illusory correlation. b. correlation coefficient. c. false consensus effect. d. hindsight bias. e. overconfidence. 22. Which of the following correlation coefficients reflects the weakest correlation? a. -.04 b. -.065 c. +.35 d. +.63 e. +1.10 23. Consistently, we find low self-esteem is often related with high levels of depression. This means: a. depression causes low self-esteem. b. low self-esteem and depression are caused by a third factor. c. low self-esteem causes depression. d. they are correlated but this does not prove causation. e. they prove causation due to their strength of relationship. 24. In order to prove a cause-and-effect relationship, we must use: a. naturalistic observation. b. the experimental method. c. surveys. d. correlation coefficients. e. longitudinal studies Historical Introduction and Research Method Exam 25. Dr. Kno’ wants to investigate if aggressive behavior in children is increased if they play violent videogames. In this instance, the independent variable is: a. video games b. aggressive behavior. c. Kno’s investigation d. violent videogames e. a placebo. 26. When you try to put universal principles from this example, what type of research are you attempting? a. Case Study b. Survey c. Naturalistic Observation d. Correlation e. Experiment 27. Neither the researcher nor the subjects knew whether or not they received the drug studied or a placebo. This is an example of: a. a double-blind study. b. a single blind study. c. dependent variables d. independent variables. e. placebo effects. 28. This describes the strength between two variables. a. central tendency b. frequency distribution c. scatterplot d. correlation coefficient e. mean Historical Introduction and Research Method Exam 29. Let’s say your hypothesis is that chocolate can cause violent behavior. What should you do questions about your hypothesis so others know what you are trying to research? a. Create an dependent variable b. Create an independent variable c. Identify any confounding variable d. Operationally define these terms e. Randomly assign your subjects first clear up any 30. Joan had not been able to get pregnant for years so she and her husband decided to adopt. Six months after the adoption, Joan became pregnant. This proves: a. coincidences which confirm a belief are believed to be meaningful. b. if you try hard to have a child, you are less likely to due to stress. c. she must have become remarried. d. the belief that infertile couples are more likely to have a child after adoption. 31. If you want to study how to “spit hot fire”, come to Knowles class.” is an example of: a. Naturalistic observation b. Participant observation c. Case Study d. Reactivity e. Observer bias 32. Any research that observes, records and does not talk about relationships, it just describes it is called: a. illusory correlation. b. experimental research c. descriptive research d. correlational research e. replication 33. Most common type of study in psychology. It measures correlation, it is cheap and fast, but has a low-response rate would be known as a. a survey. b. a correlation. c. a case study. d. a naturalistic observation. e. a experiment. Historical Introduction and Research Method Exam _________________________________________________ 34. Giving human traits non-human organisms and artifacts, such as “EARRRLLLL!!!!!” Weaver Baseball, copy machines, and computers is called: a. Reactivity b. Observer bias c. Hawthorne effect d. Anthropomorphizing e. Barnum Effect _________________________________________________ 35. The mere presence of an observer can alter the situation—people behave differently is fondly known as a. Reactivity b. Observer bias c. Hawthorne effect d. Anthropomorphizing e. Barnum Effect 36. Seeing what one expects to see such as Students at Coastal Academy are “bad”. I knew it would be that way. I saw children argue and threaten each other, curse frequently, and disrespect their teachers multiple times (never seen anyone do that at Glynn Academy) What would this be called? a. Anthropomorphizing b. Hindsight bias c. Observer bias d. Overconfidence e. Reactivity Historical Introduction and Research Method Exam 37. “The more you smile the less sad you are” is an example of: a. Operational definition b. Positive correlation c. Negative Correlation d. Observer bias e. Correlation coefficient 38. Which one of these is NOT part of four simple rules for ethics? a. NO harm b. Full Disclosure c. Confidentiality d. Publishing results e. Debriefing Let’s look at the salaries of the employees at Dunder Mifflen Paper in Scranton for 39-41: $20,000-Pam $25,000- Kevin $25,000- Angela $90,000 - Peter $90,000- Andy $200,000- Dwight $200,000- Jim $200,000- Lois $300,000- Michael 39. What is the median salary? 40. What is the mean salary is about? 41. What is the mode salary? a. $25,000 b. $90,000 c. $127,000 d. $200,000 e. $300,000 Historical Introduction and Research Method Exam 42. “Shocking” people when they answer a question wrong a. Landis’ Facial Expressions Experiment b. Monster Study c. Deindividuation d. Obedience to Authority (Stanley Milgram) e. Attachment Studies f. (a and b) Tuskegee Syphilis Study g. (a and c) Stanford Prison Experiment (Zimbardo) 43. In this experiment, subjects were shown a live rat and given instructions to behead it a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Landis’ Facial Expressions Experiment Monster Study Deindividuation Obedience to Authority (Stanley Milgram) Attachment Studies (a and b) Tuskegee Syphilis Study (a and c) Stanford Prison Experiment (Zimbardo) 44. Mary Tudor and Wendell Johnson conducted a study at an Iowa orphanage, and screened normally fluent children. Six children were chosen who were normal speakers and trained them to stutter a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Landis’ Facial Expressions Experiment Monster Study Deindividuation Obedience to Authority (Stanley Milgram) Attachment Studies (a and b) Tuskegee Syphilis Study (a and c) Stanford Prison Experiment (Zimbardo) 45. Let’s see what happens to venereal disease when you don’t treat it? a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Landis’ Facial Expressions Experiment Monster Study Deindividuation Obedience to Authority (Stanley Milgram) Attachment Studies (a and b) Tuskegee Syphilis Study (a and c) Stanford Prison Experiment (Zimbardo) 46. This study explored at how people play roles given to them. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Landis’ Facial Expressions Experiment Monster Study Deindividuation Obedience to Authority (Stanley Milgram) Attachment Studies (a and b) Tuskegee Syphilis Study (a and c) Stanford Prison Experiment (Zimbardo) Historical Introduction and Research Method Exam 47. As part of one experiment, people get swept up in a group and lose sense of self and feel anonymous and aroused. This is called. a. Landis’ Facial Expressions Experiment b. Monster Study c. Deindividuation d. Obedience to Authority (Stanley Milgram) e. Attachment Studies f. (a and b) Tuskegee Syphilis Study g. (a and c) Stanford Prison Experiment (Zimbardo) 48. This experiment showed that infants bond with surrogate mothers because of bodily contact and not because of nourishment. a. Landis’ Facial Expressions Experiment b. Monster Study c. Deindividuation d. Obedience to Authority (Stanley Milgram) e. Attachment Studies f. (a and b) Tuskegee Syphilis Study g. (a and c) Stanford Prison Experiment (Zimbardo) 49. This type of statistics reduces lots of data into a simpler summary, such as Coach Knowles winning % as a coach. a. Correlation b. Inferential c. Inscription d. Descriptive e. Experimental. 50. An example of this type of statistics would be as follows: Of 350 randomly selected people in the town of Brunswick, Ga, 175 people had the last name Knowles. With that knowledge, 50% of all people living in Georgia have the last name Knowles." a. Correlation b. Inferential c. Inscription d. Descriptive e. Experimental.