Sports & Entertainment Marketing II
advertisement

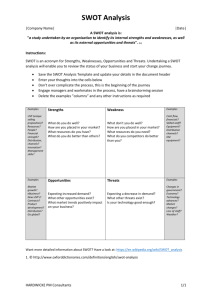
4.05B Employ marketing-information to develop a marketing plan What is SWOT? SWOT is an anagram that stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. A SWOT analysis looks at each of these factors in your business, in an organized fashion. A SWOT analysis is an important part of the strategic-planning process because it helps you to focus on the key issues that you must pay attention to when formulating your next marketing move. Smart marketers know that the best strategy is one that emphasizes their companies’ strengths, minimizes their companies’ weaknesses, capitalizes on good opportunities, and avoids external threats. Conducting a SWOT analysis is the first step in the process of formulating that strategy. Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats Strength Any resource or capability your business has that can help you gain a competitive advantage in your industry Weakness Any limitation or shortcoming your business has that can keep you from achieving your objectives Opportunity Any favorable situation in the environment surrounding your business Threat Any unfavorable situation in the environment surrounding your business Why SWOT? Running a successful business is an impossible task unless you are committed to doing some smart strategic planning. You must be able to prioritize as well as to look at your business with the proper perspective—not getting too confident because of your strengths, but also not losing heart because of your weaknesses. It’s also important to be able to recognize the opportunities you should pursue and the threats you should stay away from. Benefits of Conducting a SWOT Analysis Becoming aware of issues that you hadn’t thought of before Having a “filter” for a great deal of information Gaining new insights about your business environment by applying SWOT to a competitor’s company Who Should Be Involved in SWOT? People who can help with your SWOT analysis: Top executives in the business Owners of the business Employees at every level of the business Suppliers Customers When to Conduct a SWOT Conducting a SWOT analysis can benefit any business, any time. SWOT is a relatively quick way to get to “the heart of the matter” when it comes to your business’s strategic plan. When you have a limited amount of time available to make a decision, a simple SWOT analysis can help you organize vital information in a way that makes your top priorities more clear How to Conduct a SWOT Analysis Conducting a SWOT analysis involves the following: Determine the goals and objectives of your SWOT analysis. Define the scope of the SWOT analysis. Interview key contributors (e.g., the business’s top executives, owners, employees, suppliers, customers, etc.). Determine your business’s strengths. Strengths are internal organizational factors—under your control. Ask yourself and your interviewees: ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ What are our advantages? What do we do well (what is our expertise)? What are our assets? What resources do we have access to? Where are we making money? Examples of strengths: ○ A product or service that you offer that no one else in your area does ○ A convenient location ○ Strong brand recognition ○ The skills and talents of your staff Identify your business’s weaknesses. Weaknesses are internal organization factors— under your control. Ask yourself and your interviewees: ○ What can we improve? ○ What resources do we lack? ○ Where are we losing money? ○ What are our competitors doing better than we are? Examples of weaknesses: ○ Lack of expertise or experience ○ Bad reputation among the public ○ Poor communication among staff members ○ Weak brand name Determine the opportunities available to your business. Opportunities are external environmental factors—out of your control. Conduct environmental scanning to collect information about the environment surrounding your business. Ask yourself and your interviewees: ○ What are the newest technological breakthroughs? ○ What new needs of customers can we meet? ○ What economic trends are beneficial to us? ○ What niches have our competitors missed? Examples of opportunities: ○ A new software development ○ An improved mechanical process ○ A corporate merger ○ Failure of another company Determine the threats facing your business. Threats are external environmental factors—out of your control. Threats are also determined by using environmental scanning. Ask yourself and your interviewees: ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ What obstacles do we face? What is our competition doing? What economic trends are harmful to us? Where are we vulnerable? Do we have money problems? Examples of threats: ○ New competition moving into your area ○ A new tax that your business owes the government ○ A new law that your business must follow ○ Bad debt or cash-flow problems ○ A new trend sweeping the public SWOT Data Organize the data that you have collected. Take a look at the data you’ve collected for each category. ○ What information seems to stick out? ○ Did a certain strength, weakness, opportunity, or threat get mentioned repeatedly? Be Careful! SWOT is subjective. Different people can have very different perspectives on the exact same issues. SWOT analysis deals in large part with opinion, so there isn’t necessarily a right and a wrong in each case. Live in the present. A SWOT analysis is meant to be an evaluation of where your business is right now, not where you were in the past or where you hope to be in the future. If you’re not realistic about the present state of your company, SWOT will be ineffective. You must be specific. There’s no room to be vague or ambiguous in a SWOT analysis. Unless you are specific, your SWOT matrix will not be useful for strategic planning.