Short Story Elements
advertisement

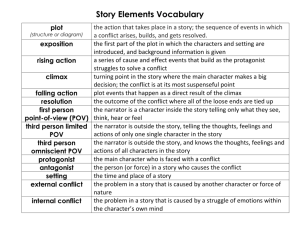
Short Story Elements Short Stories Develop Plot Characters Setting Narrator/Point of View Plot Plot is the series of related events in a story, each connected to the text. Plot tells us the beginning, middle, and end of the story. The sequence of events can be altered, such as in foreshadowing or flashback, to add interest Plot elements Exposition – the opening of a story, when characters and their conflicts are introduced. In “Most Dangerous Game,” the reader knows that something bad will happen on the island when Whitney and Rainsford discuss the name and the area. We also find out that Rainsford is a hunter who thinks that the animals they hunt have no feelings. We also know that they are on a boat in the dark. Plot elements Conflict – inner and outer conflict Outer conflict is between people or a person and a force of nature (man vs. man or man vs. weather) Inner conflict is inside a character’s head or heart (man vs. fear of heights, man vs. guilt) Examples of conflict In “Most Dangerous Game,” Rainsford had to battle Zaroff, Ivan and the dogs – this is an outer or external conflict. In the story, Rainsford had to battle his own ideas about hunting – this is an example of inner or internal conflict. Characters There are five main ways an author can develop a character Physical Appearances Actions Thoughts Language Other People’s Reactions Character Types Protagonist – main character who has a conflict Antagonist – person who opposes main character Round characters – described with many details and fully described Flat characters – not many details are offered about him or her Dynamic characters – people who change in the course of the story Static characters – people who never change in the story Characters Protagonist – Rainsford Antagonist – Zaroff Dynamic – Lizabeth Static – Ms. Lottie Round – Roger or Ms. Jones Flat – Lizabeth’s brother Setting Authors use sensory details to develop setting. Sights – busy street, elegant clothes Sounds – beeps, screams, barks Smells – turkey in the oven, locker room stench, fire Touch – soft couch, cold hallway Taste –popcorn and soda at the movies Five more elements of setting Geographical – rural town Regional - South Physical vs. mental – physical home Specific vs. universal - universal Time period – 1920s or 1930s From “A Christmas Memory” or “Marigolds” Narrator Third Person Omniscient – one who is not a character and uses third person pronouns (he, she, names, etc.) – like in “The Interlopers.” Third Person Limited – one who is not a character, but only gives the perspective of one character – like in “The Necklace.” First Person – the narrator is a character, but the perspective is unreliable because the character only gives readers his or her own ideas – like in Monster. Requirements You should have 20 entries 10 of these should tell what the elements mean – use your own words or those in the glossary. 10 of these should refer to a story that we have read You must finish your project by the end of class on Wednesday, so we can present information and review on Thursday. Your project is worth a test grade.