Literary Elements
advertisement

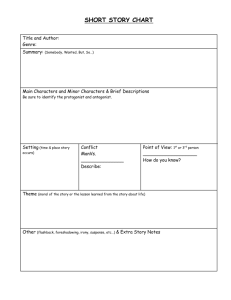
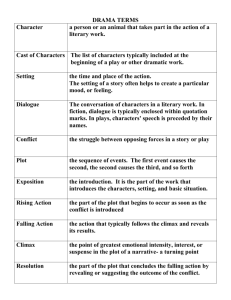
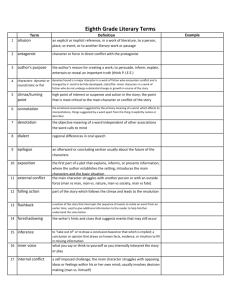
Literary Elements Part 1 Conflict, Plot, Antagonist, and Protagonist, Conflict The problem or struggle in a story that triggers the action. There are 5 basic types of conflict. Types of Conflict Man v. Man Man v. Self Man v. Society Man v. Fate (God) Man v. Nature Internal Conflict Any struggle or problem that is going on within the character. Man v. Self External Conflict Any struggle or problem that involves the character and any other person, thing or unknown force. – Man v. Man – Man v. Nature – Man v. Society – Man v. God (Fate) Plot The action or sequence of events in a story. It is usually a series of related events that build up on one another as the story develops. Plot Line Climax (Crisis, turning point, point of no return) Falling Action Exposition Resolution Exposition – The background or situation surrounding the story. Rising action - the series of struggles that builds a story toward a climax. Climax – the most intense point in a story. Falling action – part of the story that works out decisions reached during the climax. Resolution – is part of the story in which the problem is solved. Antagonist and Protagonist Protagonist - Main character Antagonist - The person or thing working against the protagonist Antagonist Protagonist Literary Devices Part 2 Theme, Irony, Suspense, Allusion Characterization, etc. Theme The statement about life the author is trying to get across in a story. – In most cases the theme will be implied rather than directly told. In The Most Dangerous Game by Richard Connell, the theme was “the hunter becomes the hunted.” Allusion A reference to a literary, mythological, or historical person, place, or thing. -- Martin Luther King Jr. alluded to the Gettysburg address in starting his “I have a dream” speech by saying “Five score years ago…”. --This referenced Abraham Lincoln’s “Four score and seven years ago.” (Gettysburg address.) Foreshadowing • The use in a literary work of clues that suggest events that will happen later in a story. • --In Romeo and Juliet, both main characters state early on that they would rather die than live apart. Epiphany • An event in which the essential nature of something-a person, situation, object- is suddenly understood in a new way. --Think of an “ah ha!” moment, or visually, a light bulb going above your head going on. Detail • Facts revealed by the author or that support the attitude or tone of the work. • --A detail gives more information. For example, a detail about Killeen is that it is the location of Fort Hood. Archetype • A type of character, action, or situation that occurs over and over in literature. • --An archetype can at times be considered a generalization or stereotype. “The princess must always be rescued by a prince.” Motif • A main idea in a literary work. A pattern or strand of imagery or symbolism in literature. • --A motif is different from a theme in that it happens over and over in a story. Imagery • The words used to represent persons, objects, feelings, by appealing to the five senses. • --Ex. Her face is a garden. • --He laughed like a hyena. Point of view • The view or perspective from which a story is told. • The author is not the one telling the story, but the narrator. This can be 1st, 2nd, 3rd person point of view. Setting • The time and place of the story. • --The setting of Batman is Gotham City in the future. • --The setting can change throughout the story. Irony Is using a word or phrase to mean the exact opposite of its literal or normal meaning. There are three kinds of irony: Dramatic irony, in which the reader or the audience sees a character’s mistakes, but the character does not. Verbal irony, in which the writer says one thing and means another: “The best substitute for experience is being thirteen” Situational irony, in which there is a great difference between the purpose of an action and the result. Suspense The uncertainty or anxiety we feel about what is going to happen next in a story. The Grip of Suspense When we feel suspense, we feel as if we are hanging in midair, like those characters in a movie who cling by their fingertips to cliffs, their feet kicking out into space. That’s suspense – and that’s why stories like The Interlopers by Saki are called cliffhangers. Characterization Is the method an author uses to reveal characters and their personalities. There are two types of characterization Direct Characterization – In which a writer tells us directly what a character is like or what their motives are. Indirect Characterization – In which a writer shows us a character but allows us to interpret for ourselves the kind of person we are meeting. •Speech •Appearance •Private thoughts •Actions and •How others in the story feel about them. Literary Elements Part 3 Symbolism, Tone, and Mood Symbolism Person, place, thing, or event that stands both for itself and for something beyond itself. A form of figurative language that is identified with something else Public symbols are symbols that are widely recognized and accepted Universal Examples Symbolism, A long history… Symbolism, Literary Example Symbolism •Why would the eagle be chosen as a symbol of the United States? •What metaphors exist within the symbol of the eagle when comparing it to a nation? Symbolism • Strength of an eagle’s wings… • Sharp eyes… • Largeness of the bird… • Why do you think our forefathers chose the eagle over Benjamin Franklin’s proposed turkey? Tone Tone is the attitude that an author takes toward the audience, the subject, or the character. Tone is conveyed through the author's words and details. Mood Mood is the emotions that you feel while you are reading. Some literature makes you feel sad, others joyful, still others, angry. How does the following passage from O. Henry's short story, After Twenty Years, make you feel? Literary Elements Part 4 Figures of speech Simile • A comparison of two different things or ideas through the use of the words LIKE or AS. • --He was as tall as a tree. • --She was sick like a dog. Metaphor • A comparison of two unlike things NOT using like or as. • -- This homework is a breeze. • --He showered her with gifts. Personification • A personification is when nonhuman objects are given human characteristics. • --The sun winked at me. Pun • A play on words that are identical or similar in sound but mean two completely different things. • Shakespeare used puns often in his work. • Mercutio: “Nay, gentle Romeo, we must have you dance.” Romeo: “Not I, believe me. You have dancing shoes with nimble soles; I have a soul of lead so stakes me to the ground I cannot move.” More examples of puns • Every oven in the restaurant was broken. The patrons got a raw deal. • Did you hear about the guy whose whole left side was cut off? He's all right now. Paradox • When two elements of a statement contradict one another. It seems impossible, but may show hidden truths. • A teenager told me, “All teenagers are liars.” Oxymoron • A form of paradox that combines a pair of opposite terms into one single unusual expression. ---Pretty ugly. ----Freezer burn. ----Great depression. Idiom • A phrase or expression that has a different meaning that its literal meaning. • -- Call it a day: stop work for the day. • "It's late and you've accomplished a lot. Why don't you call it a day? Hyperbole • An outrageous exaggeration. ---This is the best day ever!!! ---My sister wears so much makeup, she weighs 50 pounds more after she puts it on. --- My teacher is so old, she taught cave men how to start a fire. The End