Unit 3 Revised power points - Colorado Springs School District 11
advertisement

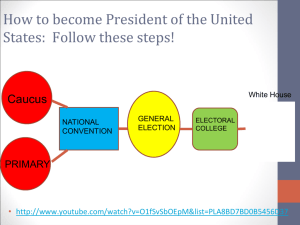
•Single Member Districts: House •State-Wide: Senate (2 per state) • Plurality House Senate Congress only Seats/districts •90% in the House win re-election •80% in the Senate win re-election •Permanent Congress? •Term limits? Why? Advantages of the Incumbent 1. Declare Iowa Jan 3 2. Primary and caucuses New Hampshire Jan 10 Utah last primary June 26 Proportional V Winner take all Presidential Primaries Jan. 3: Iowa caucuses Jan. 10: New Hampshire primary Jan. 21: South Carolina primary Jan. 31: Florida primary Feb. 4: Nevada caucuses; Maine caucuses begin Feb. 7: Colorado, Minnesota caucuses; Missouri primary* Feb. 28: Arizona, Michigan primaries March 3: Washington State caucuses March 6: Super Tuesday — Primaries or caucuses in Alaska, Georgia, Idaho, Massachusetts, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, Tennessee, Vermont, Virginia. Wyoming caucuses begin. March 10: Kansas caucuses March 13: Alabama, Mississippi primaries; Hawaii caucuses March 17: Missouri caucuses March 20: Illinois primary March 24: Louisiana primary April 3: District of Columbia, Maryland, Wisconsin primaries April 24: Connecticut, Delaware, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island primaries May 8: Indiana, North Carolina, West Virginia primaries May 15: Nebraska, Oregon primaries May 22: Arkansas, Kentucky primaries May 29: Texas primary June 5: California, Montana, New Jersey, New Mexico, South Dakota primaries June 26: Utah primary *Non-binding primary; Missouri delegates chosen at March 17 caucuses.Source: USA TODAY reporting Front loading I accept! Frontloading Winner take all •Can be elected w/only a plurality, rather than majority •Possibility of minority president: (1824, 1876, 1888, 2000) •Possibility of faithless electors •Small states proportionally overrepresented •Small states ridiculously overrepresented if goes to House •Inhibits development of 3rd Parties •Direct Elections •District system •Proportional system Would you prefer the Electoral College method of selecting a president over a direct national election? Why or why not? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Committee set up by corp, labor union, or interest group: Raises and spends money for political reasons •Must have 50 volunteer members •Give to at least 5 federal candidates •Register with govtfollow guidelines Trying to stop big money from swaying elections • Federal Elections Commission: Enforce •Must disclose amounts over $100.00 •Matching funds program: must qualify (President only) •Hard money limit: $1000.00 per individual •PAC hard money limit: $5000.00 •No Foreign contributions •Corps and UnionsPACs Where you get your money •Upheld limits on campaign contributions •Court struck down limits on campaign spending •Can spend as much on your own campaign—free speech •Limits ok for federal subsidy (matching funds) (Soft money and independent expenditure ads became a problem) •Bans soft money (unlimited) to national political parties (committees) by corps and unions. •Limits use of state soft money (party building activities) •Doubles hard money limits set from FECA •Restricted independent expenditures: 60 day & 30 day restrictions Struck down part of BCRA: •30/60 day limitations •Corporations are people •Corps and unions may give money directly to super pacs Independent expenditures: •Free speech •30/60 day restrictions are unconstitutional •Unlimited donations allowed to Super Pacs FECA 1971-1974 Buckley v. Valeo BCRA: McCain/Feingold 1976 2002 Huge increase in unlimited soft money contributions! •Created FEC •Disclose contributions>$100.00 •No foreign contributions •Individual: $1000.00 limit to candidate • 20K to national party committee, 5K to a PAC •PAC’s 5K/candidate •Matching funds program •Challenged it violated 1st Amend (speech) •Upheld limits •Free to spend as much on own campaign •Money is speech Created to stop soft money abuse Current status: •Banned unlimited soft money contributions to national parties •Increase in independent expenditures/527’s •Unions and Corps prohibited from any soft money donations •Citizens United •Doubled hard money limits •Super PACs •Starting to replace 527s •60-30 day restriction on electioneering (Issue advocacy ads/mention Candiate) If Unions and Corporations are banned from any soft money donations, how are they able to spend money in campaigns? Free Speech Corporations Do you favor campaign finance laws that restrict how much people can give to a candidate or political party? Why or why not? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ •Government policies •Diversity of population •Weakness of parties •Pluralist theory Labor unions Agricultural Business Professional Goal: to protest the status of its members and to convince govt. to take action PIRGs Goal: to bring about good policy for society as a whole Goal: to convince govt. to implement policies that are consistent with their philosophy (Grass-roots) Attempting to influence government: Most effective on narrow, technical issues that are not well publicized. Why? How to regulate interest groups? Provide information Influence govt. Testify at hearings Help write legislation •Fundraising Arm of Interest group: •Raise funds for favored candidates Growth: 6004100 Business PAC’s Corporations: 50% Professional associations: 15% Ideological organizations: 25% Labor unions: 10% Overrepresentation of upper classes Why? •1796-1824:Era of good feelings •1828-1856: 1st Dem Era: Jackson •1860-1892: 1st Rep Era: Civil War •1896-1928: 2nd Rep Era: East/West •1932-1964: 2nd Dem Era: New Deal •1968-present: Divided Govt. Era …Office of president controlled by one party with Congress controlled by the opposing party. 1968present Anyone can join No duties or dues Emphasis on election time Increased numbers of “Independents” Nat’l Convention National Committee State Committees Local Committees •Issue oriented: Free Soil, Prohibition •Centered around strong personality •Doctrinal: apply philosophy to a variety of issues Can sway the election Why we have a two party system! •Direct Primary elections •17th Amendment: Senators •Initiative, referendum, and recall •Help set national agenda •Rise of adversarial journalism •Journalists more liberal •Focus on profit People less informed •Personalize candidates •Mass public pays little attention to news •Selective attention •Selective perception •Other political socialization agents (Weakening influence on political parties) Focus on background of candidate Focus on image Talk shows and debates Focus on mistakes candidate makes Sound bites Convention coverage Focus on scandals