Evolution
advertisement

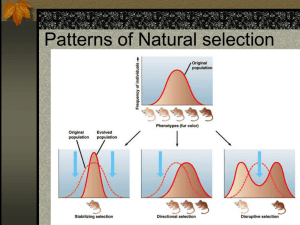
Evolution Genetic change in a population over time What are the 3 necessary ingredients for evolution? • Evolution is a natural phenomenon that will occur wherever suitable conditions exist • It’s a genetic change in a population over time • Is the example below macroevolution or microevolution? Evidences for Evolution • • • • Fossils: What is a fossil? Comparative Embryology Comparative Biochemistry Comparative Anatomy Fossil Evidence • Preservation in ice and acid • Preservation in amber • Preserved hard parts • Petrification • Molds and casts • Imprints Preservation in Ice & Acid • Organisms are kept from decaying in ice or strongly acidic conditions. • Why are bogs conducive to preservation and not decomposition? Preservation in Amber • Fossilized tree sap Preserved Hard Parts • Organic materials in hard parts of living things leech out and are replaced by minerals in the surrounding rock Petrification • Organic materials in tree tissue leech out and are replaced by minerals in the surrounding rock Molds & Casts • Molds impressions • Casts 3-D • Identify the 3 pictures as molds or casts. Imprints • Impressions or indentations in rock Stratification strata • What does the root word “strata”mean? • How fossils are formed • Becoming a Fossil Relative Dating estimating the age of something compared to something else Absolute Dating RadioMetric Dating Video: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/library/03/3/l_033_01.html • radioactive: decay of nuclei of unstable atoms half-life • uranium 238 = 4.5billion yrs uraniumlead • C14 up to 40,000yrs • C14C12 half life 5700 • If a piece of rock is found with a Lead:Uranium ratio of 7:1, how old is the rock? Comparative Embryology • "ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny" • each embryo has to repeat the adult stages of its biological predecessors • Haeckel was a fraud! Comparative Biochemistry • DNA sequence and protein molecules • What is the adjacent picture called? • What is the name of the process which generates it? Comparative Anatomy • Homologous structures • Analogous structures • Vestigial structures Homologous Structures • Similar in design, different in function • Divergent Evolution offspring of a common (similar) ancestor diverge b/c they are adapted by different environments Adaptive Radiation process by which ancestral species evolve into a number of diff species Analogous Structures similar in function different in design • offspring nonrelated (different) ancestors converge b/c they are adapted by similar environments • Speed and stealth in the water • Rolling for defense What is the name of this animal? • Echolocation for feeding in darkness (Oil bird and bat) • Convergent Evol. • result of geographic isolation and niches to be filled • process by which different species evolve similar structures or adaptations to similar (but diff) environments Parallel Evolution Divergent, Convergent & Parallel Evolution Make a Venn comparing the 3 types of evolution. 3 facts per group. • Hummingbird flowers • What kind of evolution do these flowers exhibit? Why? Co-Evolution • When two different organisms change in response to each other • How many bees are on the screen? Write your answer and then watch the videos. Evolution of Camouflage: Orchard Wasps Mimicry Will the REAL stinging insect please stand up! How many stinging insects on the screen? Mimicry only works if there are more _____________ Vestigial structures • a structure or organ that has no apparent use • if organisms use the minimal amount of E to survive,why would they use E to form a structure that has no use? Theories of Evolution • • • • • • • • • Empedocles Aristotle Linnaeus Lamarck Cuvier Lyell Wallace/Darwin Stanley/Gould Science influences society, which influences science. Lamarck & Acquired Characteristics • Acquired characteristics traits acquired during life can be passed to offspring • Theory of Use & Disuse what we use gets larger and what we don’t gradually disappears Natural Selection (Darwin & Wallace) • Overproduction • Struggle for existence/ Competition • Variation within a species • Survival of the fittest problem: how did variations arise? How does Evolution Really Work Overproduction • Thomas Malthus "Essay on Principles of Population" • geometric/expo nential progression (vs arithmetic) Gradualism vs Punctuated Equilibrium Permian Extinction Speciation Formation of a new species (group of organisms that can reproduce fertile offspring) needs: 1. Available niche 2. Genetic Isolation 3. Time Genetic Isolation Geographic/allopatric Isolation results from physical separation Ecological/sympatric Isolation: • Mechanical (post/pre zygotic) • Temporal • Ethological (behavioral) • Isolating Lacewing songs Directional Selection • Selection against one extreme • Fit to be ONE extreme Stabilizing Selection • Selection against both extremes • Fit to be AVERAGE Disruptive Selection • Selection against the average • It is fit to be BOTH extremes • Give a plausible example of each of the 2 types of speciation. • Give a plausible example of each of the 3 types of selection. • Making a Cladistic: Try the following activity: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/change/family/ Why Does Evolution Matter Now? • Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance • Biological Invaders How Did We Meet the GPS? SB5. Students will evaluate the role of natural selection in the development of the theory of evolution. a. Trace the history of the theory. b. Explain the history of life in terms of biodiversity, ancestry, and the rates of evolution. c. Explain how fossil and biochemical evidence support the theory. d. Relate natural selection to changes in organisms. e. Recognize the role of evolution to biological resistance (pesticide and antibiotic resistance). References • Absolute Dating: dig.anthro.niu.edu/anth102/ 01intro/1dating.html • PBS Evolution Library: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/library/index.html • Mimicry: http://www.morning-earth.org/Graphic-E/TransfMimic.html • NOVA: Homeobox Genes