Fiscal policy
advertisement

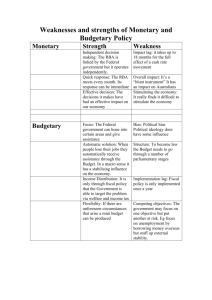
APPLICATIONS: ECONOMIC POLICY IN THE SHORT-PERIOD academic year 2015/16 Introduction to Economics Augusto Ninni ECONOMIC POLICY IN THE SHORT-PERIOD What are the objectives of economic policy? How can the Government and Central Bank affect the equilibrium of the economic system in the shortperiod? How does economic policy operate? What are its effects? ECONOMIC POLICY IN THE SHORT-PERIOD Objectives and instruments of economic policy in the short period Effects of fiscal policy Effects of monetary policy Liquidity trap THE OBJECTIVES OF ECONOMIC POLICY In the short-period economic policy is implemented in order to affect the level of GDP (Y). Main objective: ↑ Y in case of recession. Let’s assume that we observe a decrease in autonomous consumption (e.g., ↓ C0) -> Previous analysis shows that this cause ↓ Y. Economic policy is implemented to avoid ↓ Y. In these cases the interventions are called “expansionary policies”. THE OBJECTIVES OF ECONOMIC POLICY In some cases, however, the objective of economic policy is just the opposite: ↓ Y (to slow down growth). Explanation: under certain circumstances too rapid growth may generate inflation. In these cases the interventions are called “restrictive policies” The Instruments of economic policy Economic policy can impact on the short-period equilibrium in different ways: • Government -> through Public expenditure (G) and taxes (T) -> Fiscal policy • Central Bank -> through Money supply (MS/P) or analogous instruments -> Monetary policy The effects of fiscal policy 1) Increase of taxes ( ↑T) To study the effects of ↑ T we use the IS-LM model: T appears in the IS -> IS shift leftwards T des not appear in the LM -> LM doesn’t move We start from equilibrium E: ↑T -> IS shifts leftward i LM E iE iE’ IS E’ IS’ Y E’ YE Effects: E -> E’ ; YE -> YE’ -> Y and iE-> iE’ -> i Y The effects of fiscal policy Explanation ↓Y : • Increase of taxes ( ↑ T) -> • Decrease of disposable income (↓ YD) -> • Decrease of consumption (↓ C) -> • Decrease of aggregate demand (↓ Z) -> • Decrease of production (↓ Y) • + effects of multiplier The effects of fiscal policy Explanation ↓ i : • Decrease of production (↓ Y) -> • Decrease of money demand (↓ MD) -> • (Given MS) Reduction of interest rate (↓ i) The effects of fiscal policy Effects on the other components of aggregate demand a) Consumption -> C = C (Y-T) + ↑ T impacts on consumption through the income ↑ T -> ↓ YD -> ↓ C -> Y… -> ↓ YD -> ↓ C (multiplier) The increase of taxes reduces consumption. The effects of fiscal policy b) Investment -> I = I(Y,i) +↑ T has two counteracting effects: ↑ T -> ↓ Y -> ↓ sales -> ↓ I ↑ T -> ↓ i -> ↓ financial cost -> ↑ I Total effect is ambiguous (I can increase or decrease) The prevailing effect depends on the shape of the IS and LM curves The effects of fiscal policy 2) Increase of public expenditure (↑ G) IS-LM: G appears in the IS -> IS shifts rightward G does not appear in the LM -> LM doesn’t shift We start from equilibrium E: ↑ G -> IS shifts rightward i LM E’ iE’ iE E IS’ IS YE Y E’ Effects: E -> E’; YE -> YE’ -> Y and iE -> iE’ -> i Y The effects of fiscal policy Explanation of ↑ Y : • Increase of public expenditure (↑ G) -> • Increase of aggregate demand (↑ Z) -> • Increase of production (↑ Y) -> • + effects of multiplier Explanation of ↑ i -> ↑ MD but money supply is constant. Effects on other components of aggregate demand -> C and ambiguous effect on I -> analogous to the preceding case. The effects of fiscal policy We examined: • T -> Y -> Restrictive fiscal policy Note: analogous effects obtain for G • G -> Y -> Expansionary fiscal policy Note: analogous effects obtain for T The effects of fiscal policy It is important to consider that fiscal policy impacts on the public budget: Public deficit = G – T It follows that: Expansionary Restrictive fiscal policy (↑ G or ↓ T) -> ↑ Public deficit; fiscal policy (↓ G or ↑ T) -> ↓ Public deficit; In practice restrictive fiscal policy is often implemented to balance the public budget. The effects of monetary policy Increase of money supply (↑ MS/P) IS-LM: MS/P doesn’t appear in the IS -> IS doesn’t move; MS/P appears in the LM -> LM shifts downward. We start from eq. E: ↑ MS/P -> LM shifts downward i LM E iE iE’ YE E’ LM’ IS Y E’ Effects: E -> E’; iE -> iE’ -> i and YE -> YE’ -> Y Y The effects of monetary policy Explanation ↓ i : • Increase of money supply ( ↑ MS/P ) -> • Decrease of interest rate (↓ i) Explanation ↑ Y : • Decrease of interest rate (↓ i) -> • Increase of investments (↑ I) -> • Increase of aggregate demand (↑ Z) -> • Increase of production (↑ Y) -> • + Effects of multiplier The effects of monetary policy Effects on the other components of aggregate demand. a) Consumption -> C = C (Y-T) + ↑ MS/P -> ↑ Y -> ↑ YD -> ↑ C The increase of money supply increases consumption The effects of monetary policy b) Investments -> I = I(Y,i) +↑ MS/P has two effect that go in the same direction: • • ↑ MS/P -> ↓ i -> > ↑ I ↑ MS/P -> ↑ Y -> ↑ sales -> ↑ I The increase of money supply increases investments. The effects of monetary policy We examined: ↑ MS/P -> ↑ Y -> Expansionary monetary policy The opposite effect on Y obtain for ↓ MS/P -> Restrictive monetary policy The latter kind of policy produces opposite effects also on i, C and I THE POLICY MIX So far we examined the effects of fiscal policy and monetary policy in isolation. What happens if the fiscal policy and monetary policy are used jointly? When is this the case? Is it possible to pursue different objectives of economic policy at the same time? POLICY MIX: DEFINITION Policy mix: Joint implementation of different policies (mainly fiscal and monetary policies) in order to pursue different economic objectives with greater efficacy. POLICY MIX: DEFINITION In terms of instruments the policy mix jointly exploits the tools of fiscal and monetary policies (e.g., G and MS) (IMPORTANT: not G and T). In terms of objectives the mix: • Allows one to pursue one single objective with greater efficacy; • Allows one to pursue more than one objective at the same time. EXAMPLE: REDUCTION OF PUBLIC DEFICIT WITHOUT RECESSION Public deficit = Difference between public expenditure and taxes (G-T) If an economy has a deficit taxes are not sufficient to cover public expenditure (G>T) In this case part of the public expenditure is financed through debts (e.g. Bond, Bot, Btp, ecc.). Public deficit -> Bonds emission -> Public debt. EXAMPLE: REDUCTION OF PUBLIC DEFICIT WITHOUT RECESSION If public deficit remains for long time, public debt grows over time. If the public debt grows too much, there is the risk that it cannot be paid back (Mexico, Argentina… Italy) -> financial instability For this reason the the economies with high public deficit should try to reduce it. To reduce public deficit -> ↓ (G-T) -> ↓ G or ↑ T (restrictive fiscal policy) EXAMPLE: REDUCTION OF PUBLIC DEFICIT WITHOUT RECESSION Problem: restrictive fiscal policy -> ↓ Y Through the policy mix one can: reduce public deficit -> ↓ (G-T) without ↓ YE Two joint objectives -> two instruments -> policy mix Let’s examine the effects of the mix. We start from point E: ↓ Deficit -> ↓ G or ↑ T -> IS shifts leftward Restrictive fiscal policy in isolation -> ↓ Y i LM E E’ IS IS’ Y E’ YE Y To avoid this we use the other available tool: ↑ MS/P (expansionary monetary policy)-> LM shifts rightward Total effect: E -> E’’ -> Y does not change. LM i LM’ E’ E IS E’’ IS’ Y E’ YE Y A mix of restrictive fiscal policy (↑T or ↓ G) and expansionary monetary policy (↑ MS/P) allows one to reduce the public deficit without causing a recession. LM i LM’ E’ E IS E’’ IS’ Y E’ YE Y EXAMPLE US A good example of policy mix is the one implemented by Clinton and Greenspan Premise: during the 80s large increase in US public deficit End 1992 (Clinton is elected) a large plan to reduce public deficit is launched Problem: Negative effects on GDP (↓Y) NB: A recession had occurred 1990-91 To avoid recession expansionary monetary policy EXAMPLE EU This is pretty much what has happened during the EU debt crisis Southern EU countries have large public debts (which undermine their trustfulness in financial market) This situation calls for restrictive fiscal policy In a period of recession such policies can create further damage To limit the recessive effect of restrictive fiscal policy the ECB is adopting expansionary monetary policies (in open markets) Liquidity trap We showed that the LM curve is increasing in i. Particular case: part of the curve is horizontal. i LM Horizontal part Y What is the effect of an expansionary monetary policy in this case? MS/P -> LM shifts rightward The equilibrium does not change i IS LM LM’ E YE Y Liquidity trap In this case an expansionary monetary policy has no effect on the equilibrium and Y does not change (policy is ineffective). This case is usually called liquidity trap. When does this happen? In general the shape of the LM depends on MD and therefore individual choices concerning the allocation of financial wealth. Liquidity trap A recent example of liquidity trap is the Japanese economy. The Japanese economy went through a long crisis (total growth 1998-2002 = -0,1% , negative growth in 1998, 2001 e 2002). The Central Bank implemented an expansionary monetary policy. After a short period of modest impacts a liquidity trap emerged and the policy stopped to produce effects.