miRNA Profiling to Distinguish Bodily Fluids
advertisement

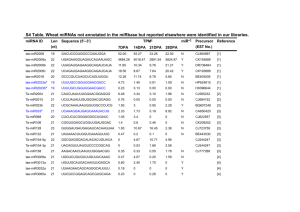
miRNA Profiling to Distinguish Bodily Fluids Rachel Markert (http://4.bp.blogspot.com/XQlCMNOapwI/TjZo_XTWemI/AAAAAAAABVI/yPhPQyjOqDY/s1600/blood.jpg) (http://3.bp.blogspot.com/_hVwPMMFDypI/TDNojHnNzlI/AAAAAAAAAJI/AGLt4p6EyRc/s1600 /Forensics+front.jpg) Purpose of Experiment • Use miRNA in forensic applications by recovering miRNA from samples obtained for forensics and identifying the bodily fluid it came from. • Prove that miRNA assaying can be cheaper, easier, and overall capable in forensic labs. (http://www.kenoshapolice.com/UserFiles/image/crime%20scene.jpg) Forensic Background • Forensic investigations often involve body fluids, such as blood and saliva • These fluids contain mRNAs and more stable miRNAs • Fluids can connect suspects to crime scenes or victims and miRNAs is easier and faster than other methods (http://www.leelofland.com/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2011/07/New-Picture-67.jpg) Micro-RNA Background • • • • Small noncoding RNA Used in cellular processes, posttranslational miRNA regulation used for controlling gene expression. Binds to mRNA (http://cnx.org/content/m36053/latest/mirna.png) Experiment: Step 1 • Fluids were obtained through buccal swabs for saliva and vacutainer tubes for blood. • The microarray method used fluids from 4 females and 1 male • Verification by PCR used samples from 3 females and 2 males • Aged blood was made from one sample over one year (http://www.dnares.in/images/header/buccal-swab-collection.jpg) (http://anotherstudentdoctor.files.wordpress.com/2010/09/vacutainer.jpg) Experiment: Step 2 • • • • Extraction of RNA from all samples Enriched for miRNAs with kits Buffer used to remove erythrocytes from blood RNA concentration was found using RNA integrity number (RIN) from fluorometer and bioanalyzer Experiment: Step 3 • Microarrays were used • Probes were created as reverse complements of miRNAs from known human sequences • Positive results for blood and saliva were selected for from respective arrays http://www.biolab.cn/uploads/1/Image/20090606110818709.gif Experiment: Step 4 • RT-PCR was done on each selected sample for both blood and saliva • From before, miRNA was extracted again • cDNA was created by reverse transcriptase after polyadenylation by poly (A) polymerase • Oligo-dT primers were used to tag the 5’ end for quantitative PCR Courts et al. (2011) TABLE 1—Body-fluid identification assay panels. Body-Fluid ⁄ Task Blood Saliva Normalization Assay Name Sequence References miR-126 miR-150 miR-451 miR-200c miR-203 miR-205 RNU6b UCGUACCGUGAGUAAUAAUGCG UCUCCCAACCCUUGUACCAGUG AAACCGUUACCAUUACUGAGUU UAAUACUGCCGGGUAAUGAUGGA GUGAAAUGUUUAGGACCACUAG UCCUUCAUUCCACCGGAGUCUG CTGCGCAAGGATGACACGCAAATTCGTG AAGCGTTCCATATTTTT (4,13) (4,13) (4,14,15) (4,16–18) (4,19,20) (4,18,19,21) (22,23 Experiment: Step 5 • Mathematical equations were carried out for hierarchical clustering S (t ) var(t ) g var(t , i) i 1 Var(t) is sample variance Var (t,i) is variance in group i, calculated already Normalization for qPCR Ct Ct (miRNA) Ct ( RNU 6b) C Ct (miRNAbody fluid 1) Ct (miRNAbody fluid 2) Courts et al. (2011) Courts et al. (2011) Courts et al. (2011) FIG. 4—qPCR validation of candidate miRNAs for blood and saliva. Upper panel: relative expression of blood candidate miRNAs in blood compared to saliva, for which expression has been arbitrarily set to 0; Central panel: relative expression of blood candidate miRNAs in aged blood compared to saliva for which expression has been arbitrarily set to 0; Lower panel: relative expression of saliva candidate miRNAs in saliva compared to blood for which expression has been arbitrarily set to 0. FIG. 5—Expression of candidate miRNAs in different kinds of tissue. Upper panel: Normalized median expression of the three blood-miRNAs (miR-126, miR-150, miR-451) in blood, saliva, liver, muscle and brain Lower panel: Normalized median expression of the three saliva-miRNAs (miR-200c, miR-203, miR-205) in blood, saliva, liver, muscle and brain. Results • As seen previously, 3 candidates from both blood and saliva contained specific miRNAs • Aged blood also resulted in miRNA assay, proving that miRNA could withstand some degradation • A mixed sample of blood and saliva resulted in distinguishing between the two types of samples Future Applications • Hopefully, widespread use in forensic labs • Standardization of the procedure for validation and optimal processes for distinction • More research into other body fluids, such as semen, vaginal secretions, and menstrual blood • Use especially in rape cases http://www.fresnosheriff.org/images/Forensic-Lab-Technologist.jpg References • Courts, C; Madea, B. “Specific micro-RNA signatures for the detection of saliva and blood in forensic body-fluid identification.” J Forensic Sci. v.56 no. 6 p. 1464-1470. 2011. • Landgraf , P; Rusu , M; Sheridan , R; et al. “A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing.” Cell. v. 129 no. 7 p. 1401–14. 2007.