THE ROARING TWENTIES
advertisement

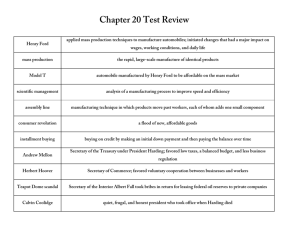
Do Now: Roaring 20’s Vocabulary Quiz 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Normalcy Speculation Buy on margin Installment buying Laissez faire Great Migration Demographics Per capital income Harlem Renaissance fundamentalism A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. Average income per person What is usual/normal Risk-taking for profit Hands off approach to economy Period of African American artistic expression wave of immigrants to cities Statistics on population Christian religious movement Borrowing money to buy stocks Paying for an item over time THE ROARING TWENTIES CHAPTER OBJECTIVES: • • • • • • Red Scare Nativism Economic Boom & Bust Isolationism Changes in society Cultural Conflict The Red Scare The Russian Revolution: Installation of the Communist government Communism was openly hostile to American values and beliefs Schenck v. U.S. (1919): Government can limit free speech when there is a “clear & present danger” to the nation Palmer Raids: Government action to identify and root out groups who posed a threat to the nation Sacco & Vanzetti Trial • Gunmen robbed and killed a guard and paymaster at a shoe factory. • Two Italian immigrants were arrested in connection with the crime. • Both were carrying guns, one was the same model as the murder weapon. • Many suspected that they were accused because they were immigrants. • Ultimately, both men were convicted and electrocuted. Red Scares America The Republican Presidency Warren G. Harding Foreign Policy Isolationism: Avoid political and economic alliances with foreign nations Fordney-McCumber Tariff: raised rates on import tariffs. discouraged imports on items made by new American industries Disarmament: Nations voluntarily give up their Weapons or limit size. At the Washington Conference, Several major nations signed Treaties limiting the size of their Navies. President Harding Immigration Nativism: Grew stronger following World War I Immigrants might hold dangerous political ideas that may hurt our government Congress limited immigration through passage of the Quota system, limiting the number of immigrants entering the US from each foreign nation SCANDALS CORRUPTION TEAPOT DOME One official had stolen government funds Others took bribes for help in getting contracts approved or laws passed Harding regularly held Poker parties in the basement of the White House and served bootlegged alcohol Secretary of Interior, Albert Fall, secretly gave oil drilling rights on government land to 2 private companies in return for illegal payments and gifts No direct evidence that Harding knew or was involved in the scandal The Coolidge Presidency Laissez Faire Kellogg-Briand Pact “The business of the American people is business” The government should not interfere with the growth of business This policy fueled the economic boom of the 1920’s Some viewed the policy as a failure to take action Coolidge continued the isolationist policies of Harding Under the pact, 15 nations agreed not to use threat of war to settle difference. A good idea, but not realistic because it had no provision for enforcement A BUSINESS BOOM CAUSES OF THE CONSUMER ECONOMY: depends on a large amount of buying Installment plan: lets consumers make partial payments over a period of time Electric power: increased demand for new household appliances Assembly line: reduced the time to produce goods and increased that amount of goods available for purchase $$ Consumer Economy $$ Society in the 1920’s: Women • Flapper: young, bold, rebellious woman of the 20’s • Single women began working until marriage • Although women could vote, they seldom did and did not change politics Women…. HARLEM RENAISSANCE Harlem Renaissance: African American literary awakening; wrote about African American culture and heritage Lost Generation: group of writers who were lost in a greedy, materialistic world that lacked values CULTURE AND CONFLICT: PROHIBITION Bootleggers: suppliers of illegal alcohol Speakeasies: illegal bars Growth of organized crime: began as efficient organizations that controlled the distribution of alcohol. Later expanded into gambling, prostitution, and racketeering. Life of Organized Crime CULTURE & CONFLICT: RELIGION • Clash between traditionalists and fundamentalism challenged beliefs: – Science and technology in everyday life – Modern society caused people to question existence of God – Scholars cited contradictions in history and the bible SCOPES TRIAL: brought the conflict to Court over issue of teaching evolution in school CULTURE AND CONFLICT: RACIAL TENSIONS • The Great Migration caused tension in Northern cities between whites & blacks. • By 1924, KKK membership had grown to 4 million. • KKK was no longer a southern organization • In 1925, the violence diminished when the head of the Indiana Klan was imprisoned for life CULTURE & CONFLICT: FIGHTING DISCRIMINATION • NAACP: National Association for the Advancement of Colored People • Marcus Garvey: dreamed of a new homeland where African Americans can live in peace – UNIA: Universal Negro Improvement Association sought to build up African American self-respect and economic power – Urged African Americans to return to Africa