The Geography of Greece
advertisement

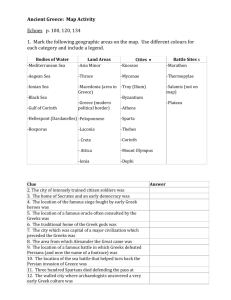
The Geography of Greece MAIN IDEAS • Rugged mountains divided Greece into many regions. • The sea linked the regions of Greece to each other and to foreign regions. Sea trade became common. • Trade helped the early Greeks develop a sophisticated culture. A. Landscape • Greek mainland is a peninsula—body of land with water on three sides – this peninsula sticks out into Mediterranean Sea - southern tip of Greece is a second peninsula called the Peloponnesus - an isthmus, a narrow strip of land, links the Peloponnesus to rest of Greece • Greece also includes thousands of islands • unlike Egypt, Greece has no major rivers • Mountains cover 70 to 80 % of Greece - mountains divide Greece into different regions - transportation was difficult - land was rocky and bad for farming (only 20-30% of land was farmland) - made it difficult to unite Greece under one government!!!!!!!!!! QUESTIONS 1. What is the name of the southern peninsula of Greece? 2. What percent of Greece is covered in mountains? 3. Name 4 ways mountains effected life in Greece. B. Climate • Mild, rainy winters and hot, dry summers (50 - 80 degrees) • mild climate encouraged outdoor events (sports, theater, festivals) C. Agriculture • over 50% of Greeks were farmers & herders – Farmed olives, grapes, barley, wheat – Fished in the Mediterranean Sea – Herded goats, sheep, donkeys • Being a landowner was a big deal –they could buy equipment and serve in the army; landowners were viewed as upper class • To get more farmland, Greeks founded colonies in places like Anatolia (Turkey) and Sicily QUESTIONS 1. What percent of Greeks were farmers? 2. Name two crops farmed in Greece. 3. Name two animals herded in Ancient Greece. 4. Do you think most people were landowners in Ancient Greece? Why or why not? D. Natural Resources • Greece did not have many natural resources like metals—had to be found elsewhere • Conquered other regions to get more resources and farmland • Had stone for building and plenty of good harbor sites - made money by trading and colonizing other lands QUESTION 1. Greeks did not have a lot of farmland or natural resources of their own. How did they get these things? Define: economy – agriculture culture peninsula Peloponnesus isthmus island - VOCAB