The Presidency
advertisement

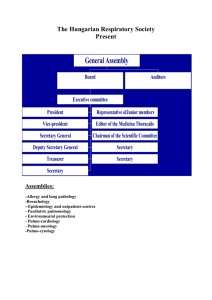
The Presidency Power to Enforce the Laws Learning Target: EB 1.1 – I can identify the requirements of the presidency, the purpose of the Executive Branch of government, and the main roles of the President of the United States in modern day democracy. Global Studies/Civics Brahe, Cornell, Wimberly Presidential Roles • The President has eight major roles: 1. Chief Executive – “Leader of the Free World” 2. Chief Diplomat – meets with foreign nations 3. Chief of State – presides over ceremonial events 4. Chief of Party – leads/unites political party 5. Commander in Chief – in charge of troops 6. Chief Legislator – suggests legislation 7. Judicial Leader – can grant pardons/amnesty 8. Chief Citizen Formal Qualifications Be a “natural born citizen.” Is it possible for a person born abroad to be President? Yes! Has it ever happened? No. http://www.americancitizenship.org/ Be at least 35 years old. Ronald Reagan was the oldest President at age 69. Most Presidents served in their 50’s. Have lived in the United States for at least 14 years. The President’s Term • Four Year Term • Term Limit? – Until 1951, the Constitution placed no limit on the number of terms a President might serve. George Washington began the “two-term tradition” which became an unwritten rule. – Franklin D. Roosevelt felt the need to break the “two-term tradition as the USA headed into World War II in 1940. Congress passed the 22nd amendment put a cap on how many terms(2) and years (10) a president could serve. Pay and Benefits of the President $400,000 salary (including a $50,000 a-year-expense account.) A 132 room mansion (The White House). Camp David – the resort hideaway in the Catoctin Mountains in Maryland. The finest medical, dental, and other health care available. Transportation: A fleet of limos Air Force One Cars, including “Cadillac One: the Car that thinks it’s a Tank”… A Few Powers of the President • Executive Order: a rule or order issued by the president which has the force of law (examples: FDR’s internment of Japanese-Americans during WWII, Truman’s desegregation of units in the army, pardoning Vietnam War draft dodgers, etc.) • Pardon: crime is forgiven and person is freed (or not charged) • Amnesty: similar to a pardon, but often for a larger group • Reprieve: convicted criminal’s sentence is delayed Presidential Succession • • • 1 Vice President of the United States Joe Biden (D) 2 Speaker of the House John Boehner (R) 3 President pro tempore of the Senate Orrin Hatch (R) (Leaders of the 15 Executive Departments, in order of creation) • • • • • • 4 Secretary of State John Kerry (D) – in charge of foreign policy (our relations with other nations) 5 Secretary of the Treasury 6 Secretary of Defense 7 Attorney General – Loretta Lynch (Dept. of Justice) 8 Secretary of the Interior 9 Secretary of Agriculture 10 Secretary of Commerce 11 Secretary of Labor 12 Secretary of Health and Human Services 13 Secretary of Housing and Urban Development 14 Secretary of Transportation 15 Secretary of Energy 16 Secretary of Education 17 Secretary of Veterans Affairs 18 Secretary of Homeland Security President’s Cabinet Advisors to the President – 15 departmental secretaries, Vice President, plus: • • • • • • • White House Chief of Staff Environmental Protection Agency Acting Administrator Office of Management & Budget United States Trade Representative Ambassador United States Ambassador to the United Nations Ambassador Council of Economic Advisers Chairman Small Business Administration Administrator The Cabinet are people who are appointed by the President and Confirmed by the Senate to assist the president with the duties involved in running the Executive Branch. State of the Union Address • U.S. Constitution: The President “shall • Technological changes— State of from time to time give to the Congress the Union is now a forum for the Information of the State of the Union, President to speak directly to the and recommend to their Consideration American people such measures as he shall judge necessary and expedient.” Article II, Section 3, Clause 1. • The constitutionally mandated presidential address has gone through a few name changes: – 1790 to 1946 = Annual Message – Since 1947 = State of the Union • After 1913, Woodrow Wilson revived the practice of presenting the message to Congress (joint session – both Houses) in person • Allows President to rally support for his agenda – First radio broadcast: President Calvin Coolidge, 1923 – First television broadcast: President Harry Truman, 1947 – First televised evening delivery: President Lyndon Johnson, 1965 – First live webcast on Internet: President George W. Bush, 2002


![August 20, 1986 SG/94/86 D-08 From: The Secretary General [*] To](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007822023_2-1a5272e9a5af1caa9930908b70495ac3-300x300.png)