Weather and Climate Unit - Brandywine School District
advertisement

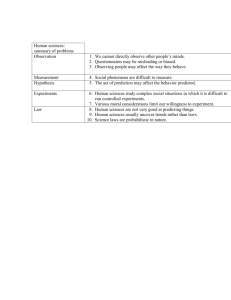
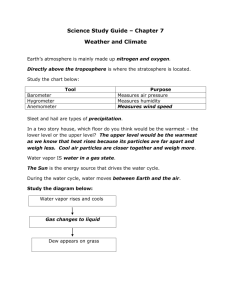
Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather The unequal heating and cooling of the Earth’s surface causes our weather and climate differences. Key Learning: What causes weather and climate differences? Unit Essential Question: Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather Concept: Predicting the Weather Lesson Essential Questions: 1. What factors influence the weather in the United States? 2. How do we use weather data to make short term weather predictions? 3. How can we use weather maps to make weather forecasts? You will be able to answer these questions by the end of Part 3 Vocabulary: High Pressure System Low Pressure System Air Mass Fronts/Frontal Boundary You should already know what these words mean. You will be able to use them in your responses and discussions throughout the unit Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather Homework Assignment # 8 In the Weather and Climate readings and assignments… Read pages 26-28 and complete the assignment on page 28 Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather Warm Up # 1: Now that you understand the ins and outs of weather, what are the important factors you must look at to describe the weather and to make future weather predictions? Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather Air Mass mT mP cT cP Where it forms Temperature Humidity Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather Type of Front Cold Front Warm Front Occluded Front Stationary Front How it forms Mass of cold air meets and replaces mass of warm air Mass of warm air overtakes cold air mass and moves over it Cold front overtakes a warm front Warm air mass meets cold air mass and no movement occurs Weather Violent storms followed by good weather Fast moving 2-5 hrs Rain and showers followed by hot, humid weather Slow moving-2 days Less extreme weather than cold or warm fronts Rain may fall for many days. Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather Warm Front: Mass of warm air overtakes cold air Clouds: cirrus are seen first, then cirrostratus, then altostratus, and finally nimbostratus. 7 things that happen as a warm front passes along the ground: 1. Temperature increases 2. Pressure decreases 3. Wind direction and speed change 4. Winds ahead of the warm front generally blow from east-southeast, while behind the front, winds shift and blow from south-southwest. 5. Moves northeastward 6. Movement is slow (about 2 days) 7. Weather you usually get with a warm front is steady rain and showers Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather Cold Front: Mass of cold air meets and replaces mass of warm air Clouds: First cumulus, then altocumulus, then finally cumulonimbus. 5 things that happen as a cold front passes along the ground 1. Temperature decreases 2. Pressure increases 3. Winds are from the north-northwest 4. Weather associated with a cold front is stormy. 5. Speed of a cold front: is 2-5 hours, stormy weather followed by cool dry conditions Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather You will now watch a demonstration on how fronts work. Pay attention to what happens to the hot water mass and the cold water mass. You will have to describe what happens (in terms of weather) after the demonstration. Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather Complete Summary # 1: Look at the satellite image of a pressure system/front moving west to east along the eastern United States. Complete the paragraph below. Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather Warm Up # 2: How are weather maps useful in determining weather forecasts? Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather Weather Maps Draw today’s weather map of the United States. Be sure to include any symbols you see. You should use color wherever possible! Then answer the questions. http://weather.unisys.com/index.php Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather Warm Up # 3: Draw a station model to represent the current weather conditions. Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather Analyzing Weather Data I have been collecting a month’s worth of weather data. Analyze that data by completing the questions and providing evidence from the weather log. Your group will then be responsible for drawing 4 days’ worth of station models. Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather Weather and Climate Unit Part 3: Predicting the Weather Complete Summary # 2: Look at the data for three different locations. Use the three sets of data to make a 24-hour forecast for each location. (Some hints are provided below) Location Wind Pressure Press. Direction (mb) Change Clouds Temp. (F) Change Rel. Hum. Change 1 S-SE 1020 1017 Cirrus to Altostratus 16 to 18 91 % to 98% 2 NW 1007 1011 Cumulonimbus Steady at 90% to to cumulus 10 79% 3 SWNW 1020 1020 Cumulus 12 to 13 84% to 76% Rising pressure brings better weather and fair skies. Falling pressure brings poor weather The closer the temperature and dew point, the greater the humidity and greater likelihood of precipitation The further apart the temperature and dew point, the drier the air and greater likelihood of fair weather Wind shifts to the east in Delaware often indicate upcoming rainy weather Clouds changing from high cirrus to lower clouds indicate warm fronts Clouds changing from cumulonimbus to cumulus indicate cold front weather