USH 1 Topic 8.1-8.3 Notes
advertisement

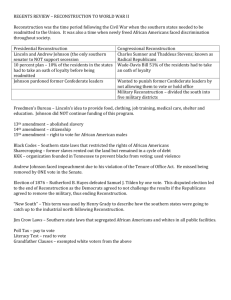
Topic 8.1-8.3 Reconstruction 1865-1877 “Reconstruction Plans” 1.1-1.4, 9.1 Atlanta Destruction (Present) The Reconstruction Battle Begins: Richmond in Ruin: (Below) T. Stephens: (Right) Reconstruction – The rebuilding after the Civil War. Lincoln wanted a moderate policy that would reconcile the South with the Union instead of punishing it for treason. – Amnesty – pardon The South would gain 15 seats in the House of Representatives. Thaddeus Stevens – A radical Republican who did not want to reconcile with the South. – “revolutionize Southern institutions, habits, and manners.” The Reconstruction Battle Begins Radical Republicans – A group of Republicans who opposed Lincoln’s plan to bring the South back into the Union. Wade-Davis Bill – Wanted to prevent Confederate leaders from returning to power after the war. – Wanted the Republican Party to become powerful in the South. – Wanted the federal government to help African Americans gain political equality by guaranteeing their right to vote in the South. Moderate Republicans Wanted to go “easy” on south Prevent future war *Lincoln’s Ten Percent Plan – “Malice toward none” The Reconstruction Battle Begins Freedmen - Freed African Americans. Freedmen’s Bureau – Bureau established by Congress to help freed African Americans adjust to their new freedom. Some believed the freedmen should be given confiscated Confederate land, while others felt it went against an individuals property rights. – Congress refused to support land confiscation. – Anti-freedmen cartoon (below) – http://www.latinamericanstudies.org/freed mans-bureau.htm Johnson Takes Office Andrew Johnson: Did Black Codes – a series of laws passed by Southern legislatures, which severely limited African Americans’ rights in the South. Civil Rights Act – 1866 law that granted citizenship to all persons born in the United States except Native Americans. Overturned in 1875 Fourteenth Amendment – Amendment to the Constitution that granted citizenship to all persons born or naturalized in the United States. not support 14th Amendment Radicals dislike him Tenure of Office Act: Radical Repub. Law to “set-up” Johnson for removal: Said that a President could not fire anyone w/o Congress approval Edwin Stanton: Sec. of War fired by Johnson Johnson impeached: put on trial for crime of breaking tenure of office act He avoided removal by ONE vote! Republicans Dominate Government (Topic 8.2) Anti-carpet bagger cartoon (Below): Which political party would have supported this cartoon? Which symbol is a clue? Carpetbagger – Name given to Northern whites who moved to the South after the war and supported Republicans. – Many had moved to the South to educate whites and African Americans. Scalawag – Name given by former Confederates to Southern whites who supported Republican Reconstruction of the South. Segregation and Integration SegregationSeparation of the races Integration- Combining the races Republican Rule in the South Thousands of African Americans took part in governing the South. Most of the first elected were educated in the South. Joseph Rainey – First African American elected to the House of Representatives. (Left) Hiram Revels – African American elected to the Senate. Even though African Americans took part in the government, they did not control it. Southern Resistance In 1870 and 1871 Congress passed three Enforcement Acts. – One act made it a federal crime to interfere with a citizens right to vote. The second act placed federal elections under the supervision of federal marshals. Ku Klux Klan Act – Law that outlawed the activities of the Ku Klux Klan. Life During Reconstruction Tenant Farmers – Farmers who paid rent for the land they farmed. Sharecroppers – Farmers who paid a share of their crops to cover their rent and the equipment they needed. Furnishing Merchant – Country stores and local suppliers who provided sharecroppers with their supplies. Reconstruction’s Impact Topic 8.3 The Civil War The Return of Amendments Southern Political Power 13th- Abolished Slavery 14th- Citizenship rights Redeemers- Unite white southerners to for former slaves regain political power (anyone born or naturalized in U.S.) Republicans- Lost popularity in South 15th- Voting Rights for after a series of African-American men Civil Rights Act of 1875- Africanscandals-Whisky Americans could ride public transit Scandal Election of 1876 Republican: Rutherford Compromise of 1877 B. Hayes ***Hayes agreed to Democrat: Samuel pull Union troops out of Tilden south if allowed to serve as President ***Hayes lost popular vote but won electoral Many early gains for college African-Americans were lost over time De Jure SegregationUpheld by Law 1896: Plessy v. Ferguson “Separate but Equal” #36. Popular votes? #37. Electoral votes? Women’s Suffrage • Susan B. Anthony: Felt betrayed when 14th/15th Amendments did not include women- 1872: Broke law by voting illegally in New York • Elizabeth Cady Stanton: National Women’s Suffrage Association NWSA Jim Crow Laws • Jim Crow- Segregation Laws • States’ Governments Limit Voting Rights • Poll tax: people had to pay to register to vote (Georgia $12) • Literacy tests: “Understanding” Tests • Had to own property • Grandfather clause: In Louisiana this clause allowed any man to vote if he had an ancestor on the voting rolls in 1867, which made former slaves, and their decendants ineligible to vote • 1894: 130,000 Black Registered Voters in Louisiana • 1904: 1,300 Black Registered Voters Jim Crow and Limited Opportunity African Americans Oppose Injustices Ida B. Wells: –Memphis Free Speech –Anti-lynching »Said it was greed not just racial prejudice that led to the brutal acts and violence –Mob destroyed printing press of Memphis Free Speech and drove Ida from town The “Early” Civil Rights Movement – A Call for Compromise • Booker T. Washington: proposed that African Americans concentrate on education and economic gains rather than deal with politics • Atlanta Compromise: Booker T. Washington wanted the African American population to postpone the fight for Civil Rights until they were prepared to full equality. – A Voice of the Future • W.E.B. Du Bois – The Souls of Black Folk – Promoting and protecting the voting rights of African Americans was the only way to reach equality. Booker T. Washington, W.E.B. Dubois, Ida B. Wells