Political movements
advertisement

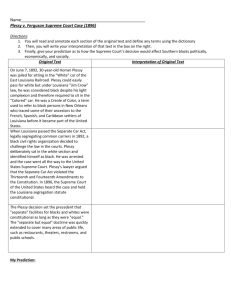
The student will evaluate key political, social, and economic changes that occurred in Georgia between 1877 and 1918. b. Analyze how rights were denied to AfricanAmericans through Jim Crow laws, Plessy v. Ferguson, disenfranchisement, and racial violence. c. Explain the roles of Booker T. Washington, W. E. B. DuBois, John and Lugenia Burns Hope, and Alonzo Herndon. Social and Political Changes in Georgia Jim Crow Laws- 1889 • A set of state laws allowing for public places to be legally segregated. • Examples included restaurants, trains, drinking fountains, bathrooms, schools and hospitals. • Segregation had been a social practice but was now legal under state laws. Inequality • Jim Crow laws were used to keep blacks from gaining the same opportunities as whites. • Most facilities while separate, were not equal. Homer Plessy Plessy vs. Ferguson- 1895 • Jim Crow laws made segregation legal. • African-Americans took their complaint to the U.S. Supreme Court. • The Court ruled that “separate but equal” was not unconstitutional as long as facilities were available for all Americans. • The East Louisiana Railroad Conductor who punched Homer Plessy's ticket asked if he was "white or colored." Plessy responded that he was "colored," but refused to move to the car designated for African-American travelers. Plessy was a member of the New Orleans' Citizens' Committee that organized challenges to segregation laws, and deliberately violated Louisiana's Separate Car Act of 1890 in order to force a legal confrontation over laws that abrogated the principles of the 13th and 14th Amendments. The Separate Car Act required railroad companies traveling within the state of Louisiana to provide separate travel accommodations for whites and African-Americans, preventing the races from co-mingling. Home Plessy had a single African-American grandparent, and looked white. He would not have been challenged as "colored" but for the Citizen's Committee pre-arranging his arrest with the East Louisiana Railroad Co. The railroad companies also wanted to overturn the law because they believed it was bad for business so the company agreed to help stage a confrontation. When the conductor walked through the "whites-only" car, he stopped to examine Plessy's first-class ticket, and asked whether the man was black or white. Plessy replied that he was black, but refused to remove himself to the African-American car. The Citizens' Committee had hired a private detective to ensure Plessy was detained; the detective took Plessy to the New Orleans' Parish jail. Disfranchisement • Means depriving a person of their citizenship. • In 1900 nearly 50% of all Georgians were black yet laws made it difficult for them to vote. • White political control led to violence against blacks if they tried to exercise their right to vote. Examples of Disfranchisement • Poll taxes were required to vote. • Literacy tests were given to prove a voter was worthy. • A “Grandfather clause” was passed stating that you could only vote if your grandfather was eligible to vote prior to 1866. • The White Primary laws only allowed whites to vote in the important primaries. Assignment Disfranchisement • Give three examples, what they were and why they were used. 1. Poll Tax: What: Why: 2. Literacy Test: What: Why: 3. Grandfather Clause: What: Why: Booker T. Washington • Born a slave but became an early leader for racial equality. • Began theTuskegee Institute in Alabama. • He delivered a speech promoting racial cooperation at the 1895 International Cotton Exposition that brought him national attention. Washington’s Ideas • Believed African-Americans needed to work their way up the social ladder. • He wanted blacks to focus on education and economic strength to gain respect and the right to demand equality. • He promoted vocational schools for blacks to learn basic skills for factory work. • He feared immigrants would replace black labor if they did not work within the system. W.E.B.Dubois • Writer and early leader for African-American rights. • Believed blacks deserved equal political, social, and economic rights. • Founding member of the NAACP. • Strongly disagreed with Booker T. Washington on how African-Americans should gain equal rights. Differences • DuBois wrote that Washington asked blacks to settle for slower change and lower expectations instead of pushing for the highest education and immediate equal rights. NAACP • National Association for the Advancement of Colored People. • In 1906, W.E.B. DuBois and others organized the NAACP to challenge racial inequalities. Changes in Georgia Terms Quiz Jim Crow Laws Lynching NAACP disfranchisement White Primary Grandfather Clause prejudice 19th Amendment discrimination Poll Tax 1. Being required to pay a fee before you could vote. 2. Murder by the hands of a mob, often by hanging. 3. An organization formed to fight discrimination. 4. To take away a person’s right to vote. 5. Unfair treatment or actions towards a person or group. 6. Hostility towards a person or group for no good reason. 7. Disallowing blacks to vote in elections that determined political candidates for the general election. 8. A set of rules meant to legally segregate blacks and whites. 9. A law that determined that you could only vote if your ancestors had voted before 1867. 10. A law giving women the right to vote. Alonzo Herndon • Learned to be a barber growing up as a slave. • He opened his own very successful barbershop in Atlanta after the Civil War called the Crystal Palace. • Herndon could not publically get his own hair cut at his barbershop. Atlanta Mutual Insurance Company • Herndon bought a small insurance company for $170 in 1905 and hired black college graduates to run his business. • Today it is worth over $100 million. John and Lugenia Burns Hope • Lugenia: Social worker who worked to improve poor AfricanAmerican neighborhoods. • John: African American educator. • A supporter of W.E.B DuBois and the NAACP. • President of Morehouse College in Atlanta. Things to know for your test 1. KNOW YOUR TERMS!!!!!!!!!! 2. Know the differences between Booker T Washington and W.E.B.DuBois and why they were different!!! (hint, hint, hint) 3. Understand what Jim Crow laws were and why they were passed. 4. Review and know the Supreme Court decision on the Plessy vs Ferguson case. 5. Review what disfranchisement was and know examples. 6. Know who Alonzo Herndon was and the businesses he owned. 7. Know John and Lugenia Burns Hope and what they supported. 19th Amendment (no notes) • Women were being denied the right to vote. • The 19th Amendment gave women that right when it was passed by the majority of states in 1920. • Georgia was one of only 5 states not to pass the amendment.