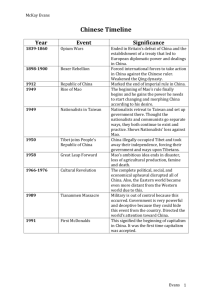
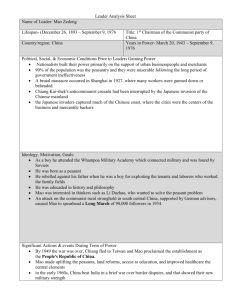
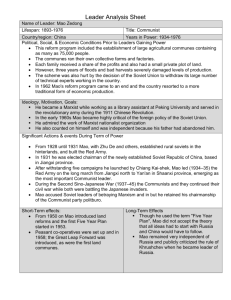
Communist China
advertisement

• Please sit in your assigned seat. • Get out your notes, charts, and your major themes sheet Good morning! • First Four Chart Four Minutes • Round 2 Activity 3 • Label & date your paper • Write a thesis statement for 2.2 guiding question • List supporting evidence • Keep this with all of your other First Four work. End • First Four • Quiz • Videos • 2.2 Vocab Review • Communist China Today’s Agenda Communist China • 1927-1949 • Nationalists v Communists • Nationalist leader: Jaing Jieshi (Chaing Kai-shek) • Communist leader: Mao Zedong Civil War • At first the nationalists were winning • Chased the communists on their “Long Walk” north to Yanan region. • Pause in civil war 19371945 to fight Japanese • Fighting starts again in 1945 Civil War • America supported the ______________ side in the war. • However, high taxes and government corruption meant that many ordinary Chinese did not. • Most Chinese lived in the countryside and were poor. • Mao promised them more land and prosperity Civil War Civil War • Communists fought a guerilla style war against the nationalists and began accruing victories. • By 1949 Mao declared the birth of the new communist state : The People’s Republic of China • Only hold out: Taiwan; Chaing Kai-Shek went there. • What OTHER major Communist victory occurred in 1949? 1949 Woes The Red Menace • World wide spread of communism • A global conspiracy • Must commit to containment • Berlin, Korea, etc. How does the US see this? • China: world’s greatest population • Wanted the be regarded on par with USA and USSR • 1964- nuclear capabilities A New Superpower? • Surprisingly tense relations between USSR & China • Mao felt that Stalin did not support him enough during the revolution. • USSR did not see China as an equal partner in their quest for world wide domination, and did not want to share global leadership. Sino-Soviet Split • After Stalin: Khrushchev • The Chinese considered him too friendly toward the west. • USSR brought home many Soviet scientists and engineers • 1968-1970 China and the USSR cam e close to war over arguments about territory. • Poor terms until the 1980s. Sino-Soviet Split • 1958 • Once Mao was in power, he wanted to make changes to the Chinese economy. • Collective farms: communes • New factories • This attempt to increase output: The Great Leap Forward • Unsuccessful… The Great Leap Forward • Mao’s plan to consolidate power and rid China of the communist haters. • Ensure that communist thought was THE ideology of China • Red Guard: Youthful supporters of Mao • Terrorized people throughout the countryside and cities of China The Cultural Revolution • Wide distribution of Mao’s Quotations of Chairman Mao Tse-Tung • “Little Red Book” • Bound in pocket sized editions • Anyone know who traditional Chinese society quoted/turned to for advice or wisdom? Cultural Revolution • The west was not too keen on the Cultural Revolution • Remained strained through 1950s and 1960s • US President Nixon wanted to build a stronger relationship with China • USA “recognized” the government of China for the first time, and Nixon visited in 1972. • All thanks to…. USA and China USA and China • RIP Mao: 1976 • Power struggle between radical and moderate commies • Radicals: Gang of Four • Included Mao’s widow Jaing Qing • And the winner was….. After Mao • The Moderates! • Led by Deng Xiaoping • Gang of Four blamed for chaos of Cultural Revolution and put in prison • In the 1980s, Deng Xiaoping abandoned many ideas of communist economics and encouraged…. After Mao • Competition and free enterprise!!! • We call this _____________________ GASP! • Capitalist style economics are not the same as a free society. • There was no increase in personal freedoms in China simply because the economy changed… DO NOT BE CONFUSED • Many students believed that the increase in economic freedom should equate to an increase in personal freedom… • A “pro-democracy” movement sprung up especially among students in early 1989. • Demonstrators camped out in Tiananmen Square, a park in Beijing. • Demanded free speech and free elections. BUT MANY WERE CONFUSED • Eventually the students were joined by ordinary citizens • June 3, 1989, the army was sent in to clear the square. • Thousands of people were killed • Leaders of pro-democracy movement arrested • Shocked the world, and created tension with western trading partners • China’s government continues to operate with a capitalist style economy and no political/personal freedom. Tiananmen Square Tiananmen Square What ever happened to Tank Man?