Marketing Strategies
advertisement

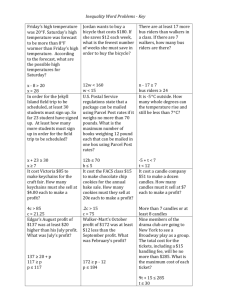
Marketing Strategies What is a strategy? The method selected to carry out a carefully devised plan of action TO ACHIEVE A SPECIFIC GOAL Marketing Plan Consists of the company’s marketing goals and the marketing mix formula for achieving them Examples of goals To introduce a new product or service To gain interest in a cause To promote an idea Specific ways that they will meet these goals are called TACTICS Marketing Strategy Outlines how the company will carry out the marketing plan 2 main kinds: 1. Brand Strategy 2. Distribution Strategy Brand Strategies Primary goal is to communicate the value of a product or service (P/S) to the consumer VALUE: the difference between the perceived cost of the product and the perceived satisfaction gained from the product Value Equation TOTAL BENEFITS – TOTAL COSTS If the cost outweighs the benefits, the consumer won’t buy it. Brand strategies develop and communicate the benefits of the brand, minimize the costs, and encourage the consumer to set up a positive value equation EXAMPLE: TRIP TO BARBADOS Brand Strategy cont.. Marketers strive to either: 1. add benefits to the product (new flavours, green-friendly) or 2.reduce the costs (lower prices, more convenient distribution) Activity – G/S BMW X5 Toys ‘R Us Cell Phone Costco MacLean’s Magazine Theatre ticket GQ Magazine iPod Distribution Strategy Focuses on the best way to deliver a P/S to the target market. 3 ways: Push Pull Combination Push Consumers buy P/S every day that haven’t been on their minds. Generic products, non-branded products or unknown brands Bought because a bargain, a gift or on impulse Push Push Strategy: sells the product to retailers, importers or wholesales, and not to end use consumers Push Reasoning If the product is out there where consumers can see it, they will buy it Companies rely on the retailer to display the product and sell it to the customers who come into the store. Push strategy requires the marketer to focus all of the promotional activities on the distributor Need buying incentives: promotional discounts, prizes, display fixtures, product-knowledge seminars Example How many of you have candles in your home? What brand? Candle-lite Candles Glade Candles Concord Candles Scentsations Candles Yankee Candles Canadian Candles Waxman Candles Upper Canada Candles Colonial Candles Doozy Candles Party-lite Candles Pull Strategy What people usually think of when they think of marketing Attempts to increase consumer demand directly, rather than rely on retailers to sell the product Pull Manufacturers try to convince consumers that they need their product, and that they should look for it by name when they go shopping. Pull Requires major advertising and promotional effort. Many believe this strategy is the most important or most useful marketing strategy. Combination The pull strategy is difficult to use alone Requires distribution partners (usually retailers) to fulfill the demand created by the manufacturer. The push strategy needs no partnership with the consumer Combination The pull strategy needs to combine with the push strategy to optimize effectiveness Homework Prepare an inventory of several different items in one room of your home. Which of these items was purchased because of a marketer’s pull strategy? Which items are in the room because of a push strategy?