File - World History with Mr. Pierce

At a time of European Expansion
And the End of the Great Ming Naval Expeditions
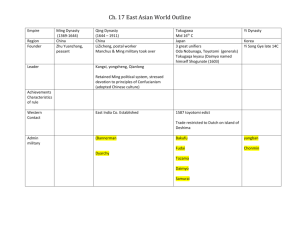
What is a dynasty?
• In sports?
Dynasty:
• A line of people from the same family who rule a country
China’s history is a history of dynasties
Begins with the Qin dynasty – 221 BC
• United various kingdoms
Last two: Ming & Qing
1368 – 1644
Begins when Ming Hong Wu overthrows Mongols
Accomplishments
•
• Expanded territory
Strengthened Great Wall
•
•
•
• Naitonwide School system
Bureaucratic government
Improved Infrastructure
Expanded Navy
Then Disbanded Navy…
Emperor Yong Le 1402 –
1424
• “Perpetual happiness”
Led many of the great
Ming accomplishments
•
•
•
• Moved capital from
Nanjing to Beijing
Construction of the
Imperial City
Grand Canal
Sponsored naval voyages to Africa
Yong Le sponsored 7 naval voyages to Africa
Led by Zheng He
Sailed in LARGE ships called junks
Established trade in
Africa & India
Brought back riches & exotic animals from Inda
& Africa
BEFORE Europeans found sea passage around
Africa
Voyage stop after Yong Le’s death
More traditional Chinese bureaucrats in charge of gov’t
Main reasons:
Voyages were costly – money and lives
Diverted attention away from immediate domestic/security concerns – Mongols
• Rather strengthen Great Wall
Trade seen as an inferior occupation
Portuguese arrive in 1541
•
• Establish trade
First contact w/ Europe in long time
• Christianity introduced
Chinese not bothered at first
Portuguese later expelled
Further trade greatly restricted
Ming dynasty falls in 1644
•
•
Incompetent, young rulers
Corruption & high taxes
• Famine & sickness
1644 peasant revolts force
Ming out of China
• Emperor commits suicide
Peasants now control China
• Opportunity??
Manchus from the North soon march on Beijing
• Easily defeat unorganized peasants
• Announce new Dynasty: Qing or
“pure”
Force Manchu culture on
Chinese
• Queues
Eventually restore peace and end economic/social problems
And Japan’s Isolation
For centuries Japan operated according to a strict feudal system
Emperor/Shogun at top
• Shogun = Supreme millitary commander
Daimyo next
• Ruled the different territories like governors
Samurai
Warrior class •
Farmers, Artisans,
Merchants at bottom
• In that order!
Japan was divided into
250 “hans” or territories
Each was controlled by a different Daimyo
But Daimyo were not all loyal to the Emperor
Samurai were loyal to respective Daimyo
Led to much Civil War
Land disputes & power struggles for centuries
3 Great Unifiers
•
•
Oda Nobunaga
Toyotomi Hideyoshi
• Tokugawa Ieyasu
Unite Japan through military measures and economic improvements
Tokugawa Ieyasu completes unification
•
•
•
Family rules Japan from 1603
– 1868
“Tokugawa Shogunate”
“Edo Period” or “Great
Peace”
How to keep Daimyo loyal?
Hostage System
• Daimyo had to maintain two homes
External threats
Christianity
• Rulers fearful that citizens’ allegiances would be with the West
(Christianity)
Technology
• Rulers fearful that western tech would fall into the wrong hands
Edicts issued in 1635 that essentially ban all foreign trade
(coming in and going out)