Potentially Inappropriate Medications
advertisement

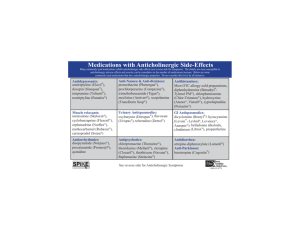
Nursing Facility Inservice Reducing the Use of Inappropriate Medications Propoxyphene (Darvocet, etc.) & Medications with Anticholinergic Effects Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) Reducing the Use of Inappropriate Medications • [INSERT PHARMACY NAME] is implementing new procedures to address the use of medications potentially inappropriate for use in the elderly • Initial focus is on propoxyphene (e.g., Darvon, Darvocet, Wygesic) and medications with anticholinergic effects • Goal is to reduce new orders for potentially inappropriate medications and increase monitoring for adverse effects where suitable alternatives are not available • This should result in improved patient care and documentation required for survey process Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) Propoxyphene Product Alert (Darvon, Darvocet N, Darvocet A 500, Wygesic) • Propoxyphene is inappropriate for use in elderly patients due to its adverse effects and questionable efficacy • Studies have demonstrated that propoxyphene is no more effective than acetaminophen (Tylenol) or aspirin in reducing pain, and in most studies was less effective Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) Number of Double-blind Studies Propoxyphene (Darvon, etc.) vs Aspirin or Acetaminophen 7 6 5 4 Propoxyphene Questionable Efficacy 3 2 1 0 ASA or acetaminophen more effective than propoxyphene 7 studies ASA or acetaminophen equal to propoxyphene 1 study ASA or acetaminophen less effective than propoxyphene No studies Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) Estimated Cost of a Single Week of q4h Therapy $7.00 $6.00 $5.00 Propoxyphene More Costly $4.44 $6.59 $4.62 $4.00 $3.06 $3.00 $2.00 $1.00 $1.00 $0.42 $0.00 Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) $5.07 What makes propoxyphene inappropriate for elderly patients? • CNS Side Effects – Dizziness, Sedation, Drowsiness, Confusion – May increase risk for falls • Research has identified propoxyphene use as a risk factor for hip fractures • Other Adverse Effects – – – – Poor appetite Nausea, vomiting Trouble urinating or emptying bladder Constipation Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) What makes propoxyphene inappropriate for elderly patients? • Active metabolite has cardiotoxic, arrhythmic effects, and CNS toxicities • Active metabolite has long elimination half-life of 30-36 hours, which poses high risk of accumulation if given repeatedly • Older adults are especially prone to increased serum concentrations or reduced elimination of propoxyphene • Note: There is a 50% decline in renal (kidney) clearance of medications in people age 75 and older Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) Propoxyphene and RAPs • Propoxyphene may cause, aggravate, or contribute to the following RAP problems due to its adverse effects: 1. Delirium 2. Cognitive Loss/Dementia 3. Visual Function 4. Communication 5. ADLs 6. Urinary Incontinence 8. Mood State 9. Behavioral Symptoms 11. Falls 15. Dental Care Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) Alternatives to Propoxyphene for Episodic (non-continuous) Pain • Mild to Moderate Pain – Acetaminophen is drug of choice – Pain not controlled by acetaminophen is unlikely to be controlled by propoxyphene – Traditional NSAIDs should be avoided in patients who require long-term daily analgesic therapy • Moderate to Severe Pain – Hydrocodone (Vicodin) prn Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) Propoxyphene Alert [Pharmacy] Procedures • Propoxyphene Alert Letter – Sent to prescribers for all new propoxyphene orders with recommendation for alternative therapy • Propoxyphene Alert Card (see example) – Sent by pharmacy for all propoxyphene refills – Punch hole in card and place in front of patient’s MAR • Contact your Consultant Pharmacist for any questions Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) What You Can Do • Mild or moderate pain – Do not encourage or recommend propoxyphene – Episodic pain: Acetaminophen 650mg po q4h prn pain. – Continuous pain: Acetaminophen 650mg po q4h. Do not exceed 4000mg per day. • Moderate to severe pain not controlled by acetaminophen – Episodic pain: Hydrocodone prn – Continuous pain: Hydrocodone • A prophylactic bowel regimen should be initiated with the commencement of persistent opioid therapy • For patients receiving propoxyphene – Monitor for adverse effects and document if observed – Report adverse effects to prescriber Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) Pain Management • For chronic, severe, or uncontrolled pain, contact your Consultant Pharmacist for therapy recommendations Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) Anticholinergic Alert • Many medications are potentially inappropriate for use in elderly patients due to their anticholinergic effects – For some of these medications, there are no suitable alternatives • Anticholinergic side effects are among the most common drug-related effects experienced by elderly nursing facility residents • It is important to know commonly used medications with anticholinergic effects • Anticholinergic adverse effects may be more likely or severe if the patient is receiving several medications with anticholinergic effects • Observe patient for adverse effects so problems can be avoided, managed, or reversed Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) Symptoms of Anticholinergic Effects • Dry or sticky lips; difficulty beginning to speak (need to lick lips first) • Urinary disorders, necessitating use of catheter • Dry, pale, cool skin • Insecure movement; falls without obvious reason • Blurred vision • Increased anxiety, with rapid shallow breathing, tachycardia (rapid heart rate), cardiac arrhythmias • Drowsiness, sedation • Fatigue, weakness • Constipation • Memory impairment, confusion, disorientation • Hallucinations, delirium Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) Spectrum of Anticholinergic Side Effects Mild Moderate Severe Dryness of mouth Thirst Speech problems Reduced appetite Difficulty chewing, swallowing, speaking Impaired perception of taste/ texture of food Mucosal damage; Dental decay, denture misfit Malnutrition Dilation of pupils Vision disturbances Dizziness Increased risk of falls Exacerbate acute angle glaucoma Constipation Fecal impaction Paralytic ileus, pseudo-obstruction Reduced gastric secretions/emptying Altered absorption of medications Urinary hesitancy Urinary retention, UTI Increased heart rate Decreased sweating Conduction disturbances, supraventricular tachycardia Exacerbation of angina Congestive heart failure Hyperthermia Drowsiness Fatigue Excitement Restlessness Profound restlessness, disorientation, agitation Mild amnesia Inability to concentrate Confusion Memory impairment Hallucination, delirium Exacerbation of cognitive impairment Ataxia, muscle twitching, seizures Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) Anticholinergics and RAPs • Medications with anticholinergic effects may cause, aggravate, or contribute to the following RAP problems due to adverse effects: 1. Delirium 2. Cognitive loss/Dementia 3. Visual Function 4. Communication 5. ADLs 6. Urinary Incontinence 8. Mood State 9. Behavioral Symptoms 11.Falls 15.Dental Care Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) Medications with Anticholinergic Effects Anti-nausea/dizziness promethazine (Phenergan) prochlorperazine (Compazine) trimethobenzamide (Tigan) meclizine (Antivert) cyclizine (Marezine) Antihistamines diphenhydramine (Benadryl) chlorpheniramine (ChlorTrimeton) hydroxyzine (Atarax/Vistaril) cyproheptadine (Periactin) Urinary and GI Antispasmodics Oxybutynin (Ditropan) flavoxate (Urispas) dicyclomine (Bentyl) hyoscyamine; belladonna alkaloids; clindinium; propantheline Antiparkinson benztropine; biperiden; procyclidine; trihexyphenidyl; ethoproprazine Muscle Relaxants metaxalone (Skelaxin) cyclobenzaprine (flexeril) orphenadrine (Norflex) Antiarrhythmics disopyramide (Norpace) procainamide (Pronestyl) quinidine Antidepressants amitriptyline (Elavil) doxepin (Sinequan) imipramine (Tofranil) trimipramine (Surmontil) nortriptyline (Pamelor) protriptyline (Vivactil) amoxapine (Asendin) maprotiline (Ludiomil) clomipramine (Anafranil) Anti-migraine belladonna alkaloids Antipsychotics: chlorpromazine (Thorazine) thioridazine (Mellaril) clozapine (Clozaril) fluphenazine (Stelazine) thiothixene (Navane) Antidiarrhea Lomotil Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) Anticholinergic Alert [Pharmacy] Procedures • Direct communication with prescriber; recommendation for safer alternative • Anticholinergic Alert Form (see example) – Completed by Consultant Pharmacist as part of drug regimen review for new orders – Indicates all medications with anticholinergic effects that patient is receiving • Anticholinergic Alert Card (see example) – Sent by pharmacy with all refills for medications with anticholinergic effects – Punch hole in card and place in front of patient’s MAR • Contact your Consultant Pharmacist for any questions Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05) What You Can Do • Become familiar with symptoms of anticholinergic effects and the medications that cause them • Note when patient is receiving more than one medication with anticholinergic effects • Monitor for adverse effects and document if observed • Resist temptation to request additional medication to treat symptoms of anticholinergic effects – Contact Consultant Pharmacist to resolve medication-related problems Fleetwood Toolkit v 1.0 (11/05)