Chemical Reaction
advertisement

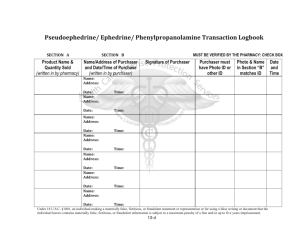
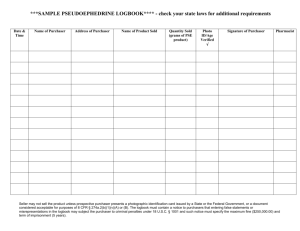
7F Simple chemical reactions 7F Simple chemical reactions Chemical change Reactions with acid Reactions with oxygen © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college 7F Simple chemical reactions Chemical change © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Next Generation Science Standard(s): • MS-PS1-2. Analyze and interpret data on the properties of substances before and after the substances interact to determine if a chemical reaction has occurred. • MS-PS1-5. Develop and use a model to describe how the total number of atoms does not change in a chemical reaction and thus mass is conserved. © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Objectives: Content Objective(s) • Differentiate between chemical change and physical change. • Identify evidences of a chemical change. © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Language Objective(s) • • Define the types of chemical reactions and substances that affect chemical reaction. Differentiate between chemical and physical change and give one example using the following sentence frame: “The difference between physical and chemical change is ________________. One example of a physical change is _______________. I know this is a physical change because_____________. One example of a chemical change is ________________. I know this is a chemical change because ___________. Vocabulary: • Synthesis: is a reaction in which two or more substances combine to form one new compound. (synonyms: mixture, fuse, blend) • Decomposition: is a reaction in which a single compound breaks down to form two or more simpler substances. (synonyms: corrode, decay, breakdown) • Single Displacement: Sometimes, an element replaces another element that is a part of a compound. This type of reaction is called a single-displacement reaction. (synonyms: move, shift, rearrange) • Double Displacement: A double-displacement reaction is a reaction in which ions from two compounds exchange places. (synonyms: move, shift, rearrange) • Chemical Reaction: when two or more molecules interact and the molecules change or forms a new substance. © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Vocabulary: • Catalyst: a substance that increases the rate of chemical reaction. • Inhibitor: a substance that decreases the rate of chemical reaction. • Law of Conservation of mass: states that during a chemical reaction or a physical change, mass is not created or destroyed but transformed into a new substance. • Endothermic reaction: a reaction where energy in the form of heat is absorbed. • Exothermic reaction: a reaction where energy in the form of heat is released. © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college 7F Chemical change – Changing materials Materials can be changed in different ways. A physical change means a material changes size, shape or state of matter. e.g. Ice melts at room temperature. A physical change can be easy to reverse. What is the reverse of ice melting? © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college 7F Chemical change – Changing materials A chemical change to a material results in a completely new material being made. e.g. A bicycle left outside has become rusty. A chemical change is very difficult to reverse. Could you change the rusty bicycle back into a non-rusty one? © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Physical and Chemical Changes © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Physical Change and Chemical Change Behind physical change: • Changing the form of a substance or the appearance of a substance. • The physical change does not change the material into a new substance. • Examples: cutting or tearing © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Behind chemical change • When two or more substances combine to form a new substance with new properties. • Examples: wood burning, rusting, baking a cake Physical Change vs. Chemical Change © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Insert these cards into the correct pockets. Physical Chemical Physical Chemical Physical Chemical © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Continuation Chemical Physical Chemical © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Physical Chemical Chemical 7F Chemical change – Physical or chemical? © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Types of Chemical Reaction © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Copy behind proper Chemical Reaction • Synthesis: Two or more simple substances combine to form a more complex substance. • Decomposition: A complex substance breaks down into simpler substances. • Single Displacement: One element trades places with another element in a compound. • Double Displacement: Two elements trade places with each other in two different compounds. © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Endothermic vs. Exothermic Reaction © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Exothermic vs. Endothermic Reaction Copy this behind Endothermic • • • • • • • System gains energy Surroundings lose energy Surroundings feel cooler Ex. Melting, evaporation Endo ”into” Ex. Breaking chemical bonds If you place a thermometer in a beaker filled with a solution undergoing an endothermic reaction, the temp will go down. • Ex. Baking soda and vinegar © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Copy this behind Exothermic • System loses energy • Surroundings gain energy • Surroundings feel warmer • Ex. Freezing, condensation • Exo “exit/out of” • Ex. Sweating 7F Chemical change – What is a chemical reaction? A chemical change is also called a chemical reaction. A chemical reaction can be shown by a word equation: reactants The starting materials that react with each other are called the reactants. products The new materials produced by the reaction are called the products. What does the arrow in the word equation mean? © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Chemical Reaction Formula © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Chemical Reaction Formula MUST COPY! © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Reactant The starting materials before a chemical reaction occurs. Arrow The arrow represents the chemical reaction or chemical change © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Product The product are the elements or compounds that exist after the chemical reaction. 7F Chemical change – Formation of water The word equation for the formation of water is: hydrogen + oxygen water Name the reactants and the product of this reaction. © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Signs of chemical change © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Evidence of Chemical Reaction © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college 7F Chemical change – Test your reactions! 1. In a chemical reaction, the properties of the reactants and products are… a) exactly the same. b) very different. c) very colourful. 2. When a chemical reaction takes place, the products can be turned back into the reactants… a) very easily. b) with difficulty. c) with a magic wand. © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college 7F Chemical change – Test your reactions! 3. The speed of a chemical reaction… a) is always very slow. b) is always very fast. c) can range from very slow to very fast. 4. The products of a chemical reaction are shown on the left-hand side of a word equation. a) Always. b) Sometimes. c) On Thursdays. © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college 7F Chemical change – Test your reactions! 5. The arrow in the middle of a word equation means… a) “turn right”. b) “react to make”. c) “equals”. 6. The starting materials involved in a chemical reaction are said to… a) act like each other. b) react with each other. c) read to each other. © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college 7F Chemical change – Test your reactions! 7. Which of these processes is an example of an everyday chemical reaction? a) Freezing water. b) Melting butter. c) Baking bread. 8. Which of these is not a sign that a chemical reaction has taken place? a) Boiling. b) Bubbling. c) Blowing. © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college 7F Chemical change – Test your reactions! 9. When sodium metal is heated it can react with chlorine gas. The word equation for the reaction is: sodium + chlorine sodium chloride What is the product of this reaction? a) sodium. b) chlorine. c) sodium chloride. 10. Rust forms when iron reacts with oxygen in the air. The word equation for this chemical reaction is: a) iron + rust oxygen b) iron + oxygen rust c) iron rust + oxygen © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college Exit Card: You must write in a piece of paper and submit before you leave. • “The difference between physical and chemical change is ________________. One example of a physical change is _______________. I know this is a physical change because_____________. One example of a chemical change is ________________. I know this is a chemical change because ___________.” © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college STOP! © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college 7F Simple chemical reactions Reactions with acid © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college 7F Reactions with acid - Acids in chemical reactions What do you know about acids? Weak acids, like lemon juice and vinegar, are harmless. Strong acids must be handled with care. They are dangerous because they can react easily with materials such as skin, wood and cloth. You need to know about the chemical reactions of acids with metals and carbonates. © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college 7F Reactions with acid - Metals in chemical reactions What do you know about metals? Metals are usually solid, shiny and strong. They are also good conductors of heat and electricity. Metals can be changed into new substances when they are involved in a chemical reaction. Some metals can react with acids. This type of chemical reaction is called corrosion. © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college 7F Reactions with acid - Reaction of metals with acid Do all metals react with acids in the same way? sodium magnesium iron lead copper iron magnesium lead copper - -the the metal no metal -bubbles, the reacts reacts metal no slowly, very reacts reaction slowly, producing quickly with producing with acid a few thestrong very bubbles acid, reaction sodium -- the metal bursts into flames, a very few bubbles producing lots of bubbles © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college 7F Reactions with acid - Reaction of metals with acid When a metal does react with acid, the metal gets smaller and seems to disappear. But has the metal really disappeared? The metal has reacted with some of the acid. The products of this chemical reaction are a salt and the gas hydrogen. Complete the word equation for the reaction of a metal with an acid: metal + acid © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college ? + ? 7F Reactions with acid - Reaction of carbonates with acid Carbonates are chemicals that contain carbon and oxygen. Carbonates can react with acids. © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college 7F Reactions with acid - Reaction of carbonates with acid Calcium carbonate reacts with acid to produce a gas which turns the limewater cloudy. What is the name of this gas? The other products of this reaction are a salt and water. Complete the word equation for the reaction of a carbonate with acid: carbonate + acid © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college ? + ? + ? 7F Simple chemical reactions Reactions with oxygen © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college 7F Reactions with oxygen – What is burning? Burning is a chemical reaction. When things burn they react with oxygen in the air and energy is released as heat and light. This chemical reaction is also called combustion. Can you name the three things needed for combustion? © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college 7F Reactions with oxygen – Fire triangle A fire only burns with all three parts of the fire triangle. oxygen heat This colourless gas is needed for all substances to burn. Some energy is needed to start the burning reaction – this is usually heat energy from a spark or a flame. fuel fuel Any substance that can burn (or combust) is called a fuel. How can firefighters use the fire triangle to control fires? © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college 7F Reactions with oxygen – Products of burning Complete the word equation for this reaction: carbon + oxygen © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college ? 7F Reactions with oxygen – Candle in bell jar Oxygen is a gas found in the air around us. Is oxygen the only gas found in the air? © OUP: To be used solely in purchaser’s school or college