Pictorials
advertisement

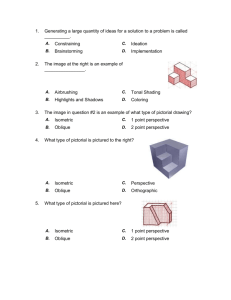
Thursday, October 21st 2004 Pictorials with AutoCAD Class 8.2 : Using AutoCAD to Create Pictorial Drawings Learning Objectives Use AutoCAD to draw an oblique of an object given orthographic views of the object Select the best orientation of an object in pictorial Define what makes a drawing a: cavalier oblique, cabinet oblique, general oblique, isometric, axonometric, perspective, or orthographic views Use AutoCAD to generate Isometric Drawings of objects given the orthographic views of the object. Types Obliques – – – OBLIQUE Axonometrics – – Cavalier Cabinet General Isometrics Dimetric, Trimetric AXONOMETRIC Perspectives 1,2,or 3 points PERSPECTIVE Cavalier Oblique Front view true size Receding Axis Angle (Normally 30°, 45° or 60°) is Variable Depth dimension (receding axis) true size 45° CAVALIER OBLIQUE Cabinet Oblique Front view true size Receding Axis Angle (Normally 30°, 45° or 60°) is Variable Depth dimension (receding axis) half size General Oblique Front view true size Receding Axis Angle (Normally 30°, 45° or 60°) is Variable Depth dimension (receding axis) between half (D/2) and full size (D) Angles in Oblique Angles in front view are drawn true size Other angles must be located using coordinates Appearance of angles may be distorted D1 D1 D2 D2 ORTHOGRAPHIC VIEWS PLOTTED ANGLES Obliques Obliques are theoretical drawings. In reality, you can not actually view an object as an Oblique Thin parts look very good as Obliques Parts with angular features on multiple planes are difficult to draw as Obliques Circles in Oblique Drawn true size in front view Drawn as ellipses on receding planes Layout using a Rhombus Today’s AutoCAD commands Drawing setup – MOVE – COPY – TRIM Review polar coordinates used with copy and move: Example: @1.2<45 ZOOM General Concepts – Editing and inquiry – Drawing Aids Display control – Keyboard Coordinates Object Snap – – – ENDPoint TANgent NEArest Display Control ZOOM -- scales the screen view to an area of the drawing surface – – – “Window” will zoom down to a window “All” will zoom out to show the larger of the drawn entities or limits Realtime allows you to shrink or enlarge the display in real time. PAN -- moves around on the drawing surface Formats of Keyboard Coordinates Either absolute or relative – – Absolute is the default Precede relative coordinates with an @ sign – Absolute -- references origin of drawing (0,0) Relative -- references previously selected point @10,20 or @ 10<45 Direct Distance – Enter a distance in the direction of the cursor and return Grips Grips serve two purposes: – – Basic editing of properties Modification of size/location Grips are the small hollow squares which appear when you select an object If you click on a hollow square grip, it will become active and you can drag the grip to a new location. The actual effect of this will vary depending on what object and which grip you select. Modifying Properties via Grips Once an object is selected and the grips are visible, you can change the Layer, Linetype, Color, and LineWeight by using the properties toolbar at the top of the screen. Anytime you have an object activated with grips, the properties toolbar modify the object properties, not the drawing settings. Drawing Obliques in AutoCAD Always make a rough pencil sketch of the object first to get an idea of what your drawing should look like. Draw the front view as a flat orthographic view Use the COPY command along with keyboard coordinates to place the front view along the receding axis to represent all frontal surfaces in the object Connect the copies with lines representing the depth of the object. Remember to use OSNAP to assist in this process Use ERASE and TRIM as appropriate to remove unwanted lines/arcs Example Example Construction of an oblique Draw the front view using normal AutoCAD commands and techniques Construction of an oblique Use the COPY command to replicate the front view to depict the depth Command: COPYE Select objects: [Other corner:[ 11 found Select objects:E <Base point or displacement>/Multiple: E Base point: [ m Second point of displacement: @.8<40 E Second point of displacement: E @1.8<40 Second point of displacement: E Construction of an oblique ERASE the portions of the depth profiles which will not be seen. Command: eraseE Select objects:[ Select objects:[ … Select objects: [ Select objects: E Construction of an oblique Add receding lines using OSNAP and the LINE command. Command: lineE From Point: endpE of[ To Point: endpE of[ To Point:E … Construction of an oblique TRIM and ERASE the remaining lines which would not be visible. E Command: TRIM Select cutting edges: (Projmode = UCS, Edgemode = No extend) [1 found Select objects:E Select objects: <Select object to Trim>/Project/Edge/Undo: <Select object to trim>/Project/Edge/Undo: E [ Exercise 8.2.1: Cavalier Oblique. Use Template English1.dwt with a receding axis of 30º Isometrics Axes equally separated (120°) H, W, and D measurements are true size along iso. axes Angles must be located by coordinates Circles appear as ellipses on all surfaces Drawing Isometrics in AutoCAD Initially you should do a rough sketch of the object by hand to get an idea of what your drawing should look like Switch the crosshairs to isometric mode (snap, style, iso) Draw the object using the LINE and ELLIPSE commands Use F5 to toggle the current isometric plane Use OTRHO and OSNAP to assist you in the drawing Copy face planes along isometric axes and connect corners similar to oblique method shown earlier TRIM or ERASE any portions which are not visible Using isometric snap If the crosshairs are not set in isometric mode, use the Drafting Settings dialog box. – Right click on snap button and choose settings Drawing Ellipses In isometrics, circular features which lie on the principal planes are shown as ellipses These MUST be drawn using the ELLIPSE command with the Isocircle Command: ellipse [ENTER] Arc/Center/Isocircle/<Axis endpoint 1>: I [ENTER] option Center of circle: [ENTER] <Circle radius>/Diameter: [ENTER] Individual Exercise; Draw an Isometric pictorial of the object shown on the next slide using AutoCAD. The grid is a .2” grid Use template English1.dwt Isometric Example Individual Assignment 41 B&C: Cabinet oblique 43 B&C: Cavalier oblique 48 C&D: isometric 49 C&D: isometric Due: Thursday 28 October 2004