Selling expenses
advertisement
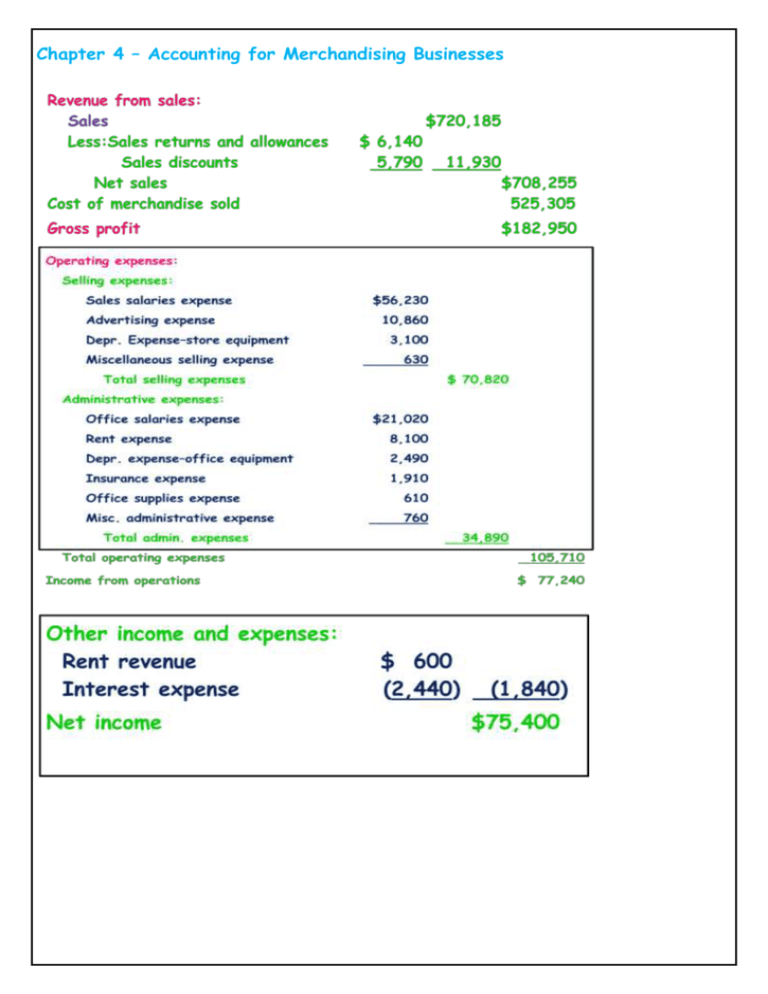
Chapter 4 – Accounting for Merchandising Businesses Chapter 4 – Accounting for Merchandising Businesses Exercises 1 : Sales Transaction Cash Sales On January 3, Alsaud sold 1000 RS of merchandise for cash. The cost of merchandise sold was 200 RS Date Jan. 3 Description Debit Credit Jan. 3 Sales on Account On January 12, Alsaud sold merchandise on account for 5000 RS . The cost of merchandise sold was 2000 RS . Date Jan. 12 Description Debit Credit Jan. 12 Receipts on Account On January 17, Alsaud deducted (………… ) Date Jan. 22 Description Credit Memo receives the amount due within ten days, so the buyer (15000 x 3 %) from the invoice amount. Debit Credit Chapter 4 – Accounting for Merchandising Businesses A credit memorandum, often called a creditmemo, authorizes a credit to (decreases) the buyer’s account receivable. On January 13, issued Credit Memo No. 32 to Krier Company for merchandise returned to Alsaud . Selling price, 5000 RS ; cost to Alsaud , 1500 RS . Date Jan. 13 Description Debit Credit Jan. 13 Purchase Transactions On January 3, Alsaud s purchased merchandise for cash. 2500 Rs On January 4, Alsaud purchased merchandise on account from Thomas Corporation 5000 RS Date Jan. 3 Description Debit Credit Jan. 4 2-Purchases Discounts ALsaad issues an invoice for 3000 RS 5/10, n/30. Alsaud to Alsaud dated March 12, with terms is trying to determine if it should pay the invoice within the discount period. Based on the calculation in the previous slide, Alsaud pays the amount due, less the discount, on March 22. Date Mar. 12 Description Debit Credit Chapter 4 – Accounting for Merchandising Businesses Mar. 22 Purchases Returns and Allowances A debit memorandum, often called a debit memo, informs the seller of the amount the buyer proposes to debit to the account payable due the seller. Debit Memo NetSolutions receives a delivery from Maxim Systems and determines that $900 of the items are not the merchandise ordered. Debit memorandum #18 is issued to Maxim Systems. NetSolutions records the return of the merchandise as follows: Date Mar. 7 Description Debit Credit Merchandise Purchased On May 2, Alsaud purchased 5000 RS of merchandise on account from Delta Data Link, terms 2/10, n/30. On May 4 ,Alsaud returned 3000 Rs of the merchandise purchased from Delta Data Link. Date May. 2 Description Debit May. 4 Exercises 2 : Complete the following table : Gross profit - Total operating expenses = Income from operations 50000 15000 Credit Chapter 4 – Accounting for Merchandising Businesses - Other expenses and losses 5000 = Net income Exercises 3 : 1. On March 18, Diamond Store sold $25,000 of merchandise on account. The merchandise was carried in inventory at a cost of $18,000. 2. On June 8, Diamond. sold merchandise costing $3,500 for $6,000 on account. Credit terms were 2/10, n/30. Let’s prepare the journal entries. 3. On June 17, Diamond Store . received a check for $5,880 in full payment of the June 8 sale 4. On June 14, merchandise with a sales price of $800 and a cost of $470 was returned to Diamond Store . The return is related to the June 12 sale Date Description Debit Credit Chapter 4 – Accounting for Merchandising Businesses Exercise 4: Barton Company Income Statement For Year Ended December 31, 2009 Sales Less: Sales discounts Sales returns Net sales Cost of Goods Sold Gross profit from sales Operating expenses: Selling expenses: Salaries expense $ 29,600 Advertising expense 13,300 General and administrative expenses: Adm. salaries expense $ 18,200 Insurance expense 1,200 Rent expense 8,100 Supplies expense 1,000 Total operating expenses Net income $ 323,800 $ 4,300 2,000 6,300 233,200