Death & Dying
advertisement

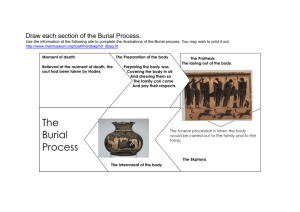
Death & Dying Presented By: Lisa Anderson Patricia Carberry Amanda Edwards Joseph Mendler Joe Salonga Jennie Sones Sandra Truman Lilia Vandermeijden What Is To Follow? • The physical aspects of death • Private mourning • Various cultural perspectives – – – – – Catholic Jewish Buddhist Hindu Navajo Indians – – – – Slavic Aztec Egyptian American When The Heart Stops Beating... • • • • Oxygen deprivation occurs Followed by brain death within three minutes Blood drains from capillaries Build up of lactic acid and rigor mortis with three hours after death • Decomposition Decomposition The long and natural process of the body being broken down into simple compounds. • Bacteria begins the internal process • Maggots begin the external process • Putrefaction • Various insects – Beetles, mites, wasps, moths Photo R. Major Death Is Declared • Certified by a medical officer with a death certificate • Time and cause of death • Coroner • Autopsy Preparation Of The Body • Depending upon religion, any of the following may occur – – – – – – – Body is washed Body is bandaged Cavities are filled Embalming Makeup Body bag or casket Refrigeration Disposal Of The Body • Depending upon religion, any of the following may occur – – – – Exposure Cremation Burial Eco-friendly Private Mourning • • • • • • An unstable process A lonely journey Self doubt Intense emotion Detached from life Unable to concentrate • • • • • Disorganized A lot of crying Exhausted Unable to sleep Vivid dreams or nightmares Coping With The Grief • Support groups • Online sites on how to cope • Therapists who specialize in grief counseling • Family and friends Various Cultural Perspectives • • • • • Catholic Jewish Buddhist Hindu Navajo Indians • • • • Slavic Aztec Egyptian American Catholic Beliefs • • • • Eternal life Resurrection of the body Burial takes place in a grave Cremation is accepted in some circumstances Catholic Burial Customs • • • • • Meeting with the family to prepare the funeral Prayer held for the family at the funeral home A prayer service held for the community The main funeral is celebrated at the church Prayers of committal take place at the cemetery Jewish Traditions • • • • • A Rabbi delivers a eulogy A Cantor sings Family and friends deliver memorials Open caskets are not acceptable Cremation is not acceptable, except for Reform Jews Buddhist Beliefs • Individuals pass through many reincarnations until they are liberated. • Liberation is nirvana • Funeral ceremonies consist of three components: – Sharing – The practice of good conduct – Developing a calm mind (Meditation) Buddhist Burial Customs • Often there will be three ceremonies: – Service at the home of the bereaved – Service at a funeral home – After burial a service is performed either at the home of the bereaved or at a temple • Always an open casket • Quotes are given from the Sutra (collected sayings of the Buddha Hindu Beliefs • The individual soul has no beginning and no end • The reincarnation depends on the karma of the person • Once the true nature of reality is realized, through many reincarnations, the individual soul is lost upon death and becomes one with Brahman, the one. Hindu Burial Customs • White clothing is customary at the funeral • Hindu priests or senior male members of the family are the major officials • Cremation is practiced • A last food offering is symbolically made to the deceased before cremation • The cremation is held at home Navajo Indian Beliefs • Life is a constant cycle of growth, death and new life • This cycle flows in a circular motion - all things must begin and end at the same point • There is no afterlife • All but the very young and old generate evil spirits • Hooting of an owl forebodes death • Coyote signifies the imminence of evil or death Navajo Indian Burial Preparation • Items to be buried with the body are gathered • The dying person is taken to a special dwelling to await death • Four mourners are hired to prepare the body – The body is bathed and dressed in fine clothing – A Navajo blanket is placed with the deceased. – Purification rituals are performed Navajo Burial Customs • Burial takes place on or after the fourth day • After grave is dug, no footprints can be left behind • Once body is buried, all tools used are destroyed • After the burial, mourners return to the village by a different path, so the dead could not follow • Today’s practices are similar to mainstream American funerals, although the spiritual beliefs remain intact Slavic Beliefs • Death is a separation of the soul from the body • After death, the soul is judged based on its behavior, character, and communication with God • This judgement determines whether the soul travels to heaven or hell Slavic Death Signs and Omens • Dogs howling or owls screeching at night means someone nearby will die • If a bird flies into a house, someone in that house will die • A seriously ill person who suddenly undergoes a state of euphoria will soon die • Death will come soon to a dying person who asks for special food or drink Slavic Burial Preparation • One prepares for their own funeral • When a person dies, all mirrors are covered with towels • After death, eyes and mouth of the deceased are closed • Neighbors are relatives that were not close to the deceased wash and dress the body • Various wakes are held over the body to protect against evil spirits • Young children are asked to touch the feet of the deceased Slavic Burial Customs • • • • The coffin remains open during the ceremony Relatives pay their respects The pallbearers are male relatives The coffin is placed in the grave so that the feet point toward the cross • All guests throw three handfuls of earth on the coffin • The grave is decorated with flowers and wreaths Aztec Death Rituals “To the Aztecs death was not an altogether abhorrent idea, being little more than an incident in the continuity between this life and the next” Aztec Beliefs • It is the manner of death, not the persons’ behavior in life that decides the individual’s final destination in the afterlife • Three destinations exist for the afterlife: – Paradise of the sun – Terrestrial paradise – The underworld Paradise of the Sun • Warriors who died in battle or were sacrificed assemble to greet the sun as it rises by beating upon their shields • Women who died during childbirth escort the sun to the horizon • Therefore, the sun is eternally kept in motion through the help of the warriors at the rise and the women at the set Terrestrial Paradise • Those who die of the following are sent to this paradise – Dropsy, gout, scabies, leprosy, drowning, or struck by lightning • This is the home of the rain god • No cremation takes place in this case • In loser classes, the burial takes place under the floor of the house, to maintain connection with the living The Underworld • Those that die of natural death or old age are sent to this destination • The underworld consists of a long road full of perils and menaces • This means of dying is not perceived as desirable and honorable Death of a Lord • The deceased is shrouded in a squatting position, then cremated • The photo portrays fire on top of the funerary bundle • A slave is sacrificed by extracting his heart to accompany the lord in the afterlife • Wives were buried alive to serve their husbands in the afterlife Death of a Merchant • He is cremated and buried with his wealth • Feline skins are placed around him, with his possessions, to enable him to continue his occupation in his final resting place Egyptian Beliefs • They were sons of the sun god Ra (or Re) • The pyramids were built to honor the gods • The body’s life force or spirit, called the ka, lived on after death • To keep the life force happy, bodies are mummified after death • Only those free from sin can enjoy the afterlife Embalming • The brain is removed through the nose • The innards are removed through an incision on the left side • The body and major organs are placed in occurring salt, called natron for a month • This blackens the skin, so workers would dye the body red for men and yellow for women • Families would provide linen that had been soaked in herbs to be placed in the empty body cavity Embalming, cont... • The organs would be wrapped and either placed back in the body or in special containers in the tomb chamber • The body and limbs were wrapped in cloth strips and then wrapped in a shroud • Another layer of cloth wrapped the entire body, giving the appearance of a mummy • Included in the wrappings were good luck charms and trinkets Egyptian Burial Customs • The body was placed in a sarcophagus, or a stone coffin • Accompanying the body in the tomb was a portrait statue in case the body dissipated • Paintings on the inner walls and ceiling were done to ensure happiness of the ka • The chamber is then closed off after the burial The American Definition of Death • The irreversible cessation of life and the imminent approach of death as we know it • When the vital functions cease breathing and circulation • A modern view of death is the death of the brain American Outlook of Death • • • • Death sells newspapers and insurance policies Creates plots for television programs Acts as a crime deterrent It can also measure the adequacy of social life, such as national homicide rates • Death moves from a cultural order, to an institutional order, and finally to an individual order Facing Mortality in America • In general, it is a taboo subject • Medical professionals demonstrate that dying can be a rich experience for both, the terminally ill and their loved ones • Living wills and advance directives are becoming more common everyday • They prevent disputes among families if treatment ever becomes an issue The Fear of Death and Dying • The fear seems to be based on two things: – The presence and certainty of death – And the uncertainty of what follows • Material welfare is used as a distracting ploy to see death as an objective event • Such approaches keep death outside of ourselves, so we know death only as observers, not participants American Burial Preparation • The most popular burials are those of cremation or embalming, then either buried, stored in mausoleum, scattered or destroyed • Cremation allows a less personal representation of the deceased • The body can also be buried in a casket and laid to rest in a cemetery, with a tombstone placed over the grave Immortality American Style • The Alcor Life Extension Foundation – http://www.alcor.org – Cryonic preservation – Freezing people for possible awakening later on or possible future cloning • Cards From Beyond – Offer the ability to send cards to loved ones after their death Immortality, cont... • Loving Pup, Inc. – http://timelessmail.com/ – Leave family and friends an e-mail to be delivered after you pass on • AT&T Labs’ Natural Voices – http://www.naturalvoices.att.com/ – Type your message and the voice cloning allows the dead to utter your words Resources • The Physical Aspects of Death – – – – – – – – – – – www.deathonline.net/decomposition/decomposition/index.htm www.deathonline.net/what_happens/autopsy/autopsy_steps.cfm http://web.utk.edu/~anthrop/index.htm http://www.cnn.com/2000/HEALTH/10/31/body.farm/ www.deathonline.net/disposal/cremation/process.cfm www.funerals.org/personal/eco.htm www.deadonline.net/what_happens/options/index.cfm www.deathonline.net/index.cfm http://web.utk.edu/~anthrop/index.htm www.bbc.co.uk/health/ask_doctor/death_body.shtml www.funerals.org/personal/eco.htm Resources • The Physical Aspects of Death, cont… – – – – – www.le.ac.uk/pathology/teach/va/welcome.html www.hbo.com/autopsy/ http://www.cnn.com/2000/HEALTH/10/31/body.farm/ Books: Modern Mummies, Christine Quigley, Mc Farland and Company, 1998 – What is Death: A Scientist Looks at the Cycle of Life, Tyler Volk, John Wiley and Sons, 2002 – Stiff: The Curious Lives of Human Cadavers, Mary Roach, W.W. Norton And Company, 2003 – One Foot in the Grave: Secrets of a Cemetery Sexton, Chad Daybell, Cedar Fort, 2001 Resources • Private Mourning, Catholic, Jewish, Buddhist, and Hindu Perspectives – – – – – – http://www.buddhanet.net http://www.webhealing.com http://www.icctampa.org http://www.americancatholic.org http://www.biomed.lib.umn.edu http://www.thefuneraldirectory.com • Navajo Indian Perspective – http://www.biomed.lib.umn.edu/hw/releasing.html – http://www.espacoacademico.com.br/030/30ekeyes.htm Resources • Navajo Perspective, cont… – http://www.jammed.com/~mlb/hogan.html – http://www.sfu.ca/archaeology/museum/papers/contents/leml.ht ml – http://www.uua.org/clf/betweensundays/earlychildhood/Lessons Loss.html – Books: – Native American Worldviews, Jerry Gill, 2002 – The Elements of Native American Traditions, Arthur Versluis, 1995 – A Native American Encyclopedia, Barry M. Pritzker, 2000 Resources • Slavic Perspective – http://web2.iastate.edu/!stdt_couns_info/cultureandcrisis/ukraine .html – http://hometown.aol.com/hpsofsnerf/ – http://death.monstrous.com/death_rituals_across_cultures_.htm – http://www.showcase.ca/sixfeetunder/features/flashtour.asp – Books: – Chelovek pered likom smerti, Aries Philippe, Moscow, 1992 – Reinterpreting Russia, Geoffrey Hosking, 1999 – Death and Bereavement Across Cultures, Colin Murray Parkes, 1996 – In Search of the Immortals: Mummies, Death and the Afterlife, Howard Reid, 2001 Resources • Aztec Perspective – Soon to be added Resources • Egyptian Perspective – soon to be added Resources • American Perspective – – – – – – http://encarta.msn.com http://www.mountsinai.org http://www.mskcc.org http://www.mercynorthiowa.com/new/archived/hospice/shtml http://death.monstrous.com/common_rituals.htm Encyclopedia of Death and Dying, Howarth, Glennys, and Oliver Leaman, eds., 2001 – Understanding Dying, Death, and Bereavement, Michael R. Leming and George E. Dickinson – Death and the Afterlife: A Cultural Encyclopedia, Richard Taylor, 2000