Ch 1 PPT

Sc 9: Ch 1 Matter
Some Vocabulary Review to
Start…
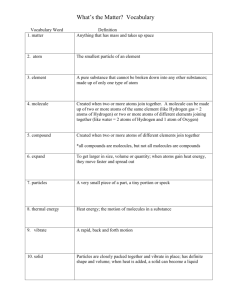
Matter
: Anything that has mass and volume
Mass
: the amount of matter in a substance
Volume
: The amount of space that matter occupies.
Property
: A characteristic used to describe matter.
Qualitative: can be described but not measured
Quantitative: can be measured numerically.
Atom
: the smallest part of an element that still has the same properties of that element.
Molecule
: two or more atoms chemically combined.
(either the same or different atoms)
Element
: A substance that contains only one type of atom
Compound
: A substance that contains two or more different types of atoms, chemically combined.
Pure Substance
: A substance that has the same properties in any sample you choose. Can be an element or a compound .
Models for Matter
Each geometric shape represents a type of atom . When the shapes are drawn together, they represent atoms that are chemically combined .
Ex. 1: Mixture or Pure Substance?
Element Compound Both?
Total # of atoms:
# of molecules:
# of different types of atoms:
# of different types of compds
Ex. 2: Mixture or Pure Substance?
Element Compound Both?
Total # of atoms:
# of molecules:
# of different types of atoms:
# of different types of compds
Ex. 3: Mixture or Pure Substance?
Element Compound Both?
Total # of atoms:
# of molecules:
# of different types of atoms:
# of different types of compds
Ex. 4: Mixture or Pure Substance?
Element Compound Both?
Total # of atoms:
# of molecules:
# of different types of atoms:
# of different types of compds
Ex. 5: Mixture or Pure Substance?
Element Compound Both?
Total # of atoms:
# of molecules:
# of different types of atoms:
# of different types of compds
Ex. 6: Mixture or Pure Substance?
Element Compound Both?
Total # of atoms:
# of molecules:
# of different types of atoms:
# of different types of compds
Changes to Matter
Physical Changes
: Changes in which no new substance is formed.
Ex.
Chemical Change
: Changes in which new substances are formed.
Ex.
Clues that suggest a CHEMICAL change has occurred:
1. a new colour may appear
2.
3.
Gas
Light or or bubbles may be given off
Sound may be formed.
4. A solid material (a precipitate may form in a liquid
5. The change may be difficult to reverse
Activity 1-2A – Bag of Change
Activity 2B: Observing Changes in Matter. Science Probe 9, page
24,25
Purpose : To observe and classify physical changes, chemical changes, or situations where nothing appears to change.
Materials:
Safety goggles, Lab Coat
Gloves Small piece of steel wool
Two pieces of copper wire (2cm)
Tongs
Bunsen burner
Dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl)
Four test tubes in a rack
Magnesium ribbon (2 cm strip)
Sodium carbonate solution (NaCO
3
)
Calcium chloride solution (CaCl
2
)
Copper sulphate crystals (CuSO
4
)
Heat proof test tube
KMT!
solid, liquid, gas animation
All matter is made up of
The particles are always
There is _____ between the particles
In a gas:
In a liquid:
IN a solid: shows what happens when temp is increased
To make the molecules
Move faster, you…
3. The particles are contstan
Changes of State and KMT liquid solid
Solidification
(freezing) condensation gas melting evaporation
Eureka - molecules in solids
Summary
State Shape Volume Space between molecules small
Solid
Liquid
Fixed
Takes shape
Of Container
Gas
Fixed fixed Medium
Takes shape
Of container
Takes as much
Volume as allowed
V. Large
Atomic Theory
Our understanding of the atom didn ’ t happen overnight!!
Contributions: John Dalton1766-1844
Some of Dalton's symbols for the elements with his estimates of molecular weight
What did Dalton ’ s
Theory state: (4 things)
Matter is made of atoms
Atoms are indivisible, and
Cannot be created or destroyed
Different elements have different
Sized and shaped atoms
Compounds =different atoms chemically combined
“ The solid sphere model ”
Atoms are seen as solid, indestructible spheres (like billiard balls)
J.J Thomson
“ raisin Bun ” model
Discovered electrons
(atoms ≠indivisible?!)
-thought atoms were like a ball
Of (+) charged particles with
(-) charged particles dispersed
Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937)
Some bounced back?!
Like shooting a cannon at a piece of paper and having it bounce back!
Discovered
The
NUCLEUS.
Later, he
Figured out
That the
Nucleus
Is made of
PROTONS
Rutherford had discovered the
NUCLEUS.
Later, he named the
PROTONS and
NEUTRONS that make up the nucleus.
Rutherford ’ s
Model of an
ATOM
Niels Bohr (1885-1962)
Electrons are restricted to
“ energy levels ”
= “ shells or orbitals ”
the Atomic Theory Song
Today ’ s Model of Atoms
Mass in AMU!
Electrons don ’ t “ orbit!
”