BY 124 SI worksheet 6: Fungi Fungi: Are heterotrophic organisms
advertisement

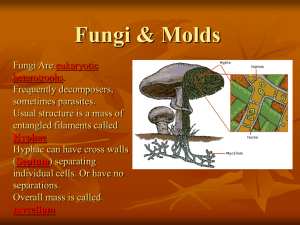
BY 124 SI worksheet 6: Fungi 1. Fungi: a. b. c. d. Are heterotrophic organisms that get their nutrition directly from photosynthesis Secrete hydrolytic exoenxymes that absorb nutrients from living hosts Are often saprobes that absorb nutrients None of the above 2. Parasitic fungi have modified hyphae called _________, which penetrate and absorb nutrients from host tissues. a. Haustoria b. Mycelia c. Asci d. Basidia e. None of the above 3. In contrast to plans, the cells walls of fungi are composed of _______. a. Lignin b. Peptidoglycan c. Cellulose d. Chitin e. Pectin 4. The fact that karyogamy and meiosis do not immediately follow Plasmogamy a. Is necessary to create Coenocytic hyphae b. Is characteristic of all fungi c. Allows fungi to produce asexually most of the time d. Results in heterokaryotic cells that may benefit from the variation present in two genomes e. Is characteristic of yeasts 5. The traditional group deuteromycetes a. Represents the most ancient lineage of fungi b. Includes the fungal components of lichens c. Has abnormal forms of sexual reproduction d. Consists of fungi that are predatory e. Consists of fungi whose sexual stage is absent or unknown 6. Which of the following statements accurately describes ascomycetes? a. Sexual reproduction occurs by conjugation b. Spores often line up in a sac in the order in which they were formed by meiosis c. Asexual spores form in sporangia on erect hyphae d. Most hyphae are dikaryotic e. Reproduction is always sexual 7. Lichens are symbiotic associations that a. Usually involve an ascomycete and a green algae or cyanobacterium b. Can reproduce sexually by forming soredia c. Require moist environments to grow d. Fix nitrogen for absorption by plant roots e. Are unusually resistant to air pollution What is the difference between dikaryon and heterokaryon? - - - Plasmogamy – the union of the cytoplasms of two parent mycelia. o Usually the two haploid nuclei don’t fuse right away, creating heterokaryon fungi. (“Different nuclei”) Sometimes the two nuclei can exchange genetic information. o If the nuclei pair off two to a cell its called dikaryotic (“two nuclei”) As the cells the divide the two nuclei divide in tandem. (two separate haploid nuclei different than a diploid cell) During karyogamy the haploid nuclei fuse, producing diploid cells. Zygotes and other transient structures form during this phase. Meiosis then restores the haploid status quo, leading to the formation of spores that can be dispersed. Heterokaryoin just refers to more than one nuclei. dikaryon refers to just two. Fill out the following table. Fungal Phylum Distinguishing Features Chytridiomycota Flagellated spores (no other fungi have this), mostly aquatic, very similar to protists, cell walls made of chitin, absorptive nutrition, coencytic hypha Zygomycota Coenocytic, zygote fungi, rhizopus, asexual spores, sexual (+ and -) Glomeromycetes Broken up from asomycota, associated with mycorrhizae, residence in plant cells Ascomycota Varied, lichens, control parasitist (fungi holds algae captive), asexual reproduction takes place in conidiophore, sexual reproduction (karyogamy)dikaryotic hyphae, harmful to humans Basidiomycota Most common of the fungi (mushrooms, etc.), mostly sexual reproduction and mushroom is the only reproductive part *Coenocytic: no septum, continuous *Rhizopus: black break mold that’s everywhere, can’t rid of these spores because they’re everywhere Briefly describe the following terms: Septa – Cross walls between spores, with pores Coenocytic – multinucleated hyphae, no septa Karyogamy – Fusion of nuclei from the two parents to form the diploid state In what ways to mycorrhizal fungi benefit plants? In what ways do plants benefit the fungi? The mycorrhizae provide the plants with an increased surface area and absorptive capabilities for its roots. The plants, in turn, provide carbohydrates for the fungi.