Carsten Denker NJIT - Center for Solar
advertisement

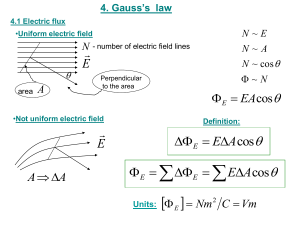
Physics 121: Electricity & Magnetism – Lecture 3 Carsten Denker NJIT Physics Department Center for Solar–Terrestrial Research Coulomb’s Law and Flux Gauss’ law uses symmetry and is fully equivalent to Coulomb’s law. Which one you have to use depends on the application! Gauss’ law relates the electric fields at a point on a (closed) Gaussian surface and the net charge enclosed by that surface. v cos A January 31, 2007 vA cos v A Center for Solar-Terrestrial Research Flux of an Electrical Field Electric flux through a Gaussian surface E A E dA discrete form integral form The electric flux through a Gaussian surface is proportional to the number of field lines passing through that surface. January 31, 2007 Center for Solar-Terrestrial Research Gauss’ Law Gauss’ law 0 qenc Gauss’ law 0 E dA qenc Gauss’ law and Coulomb’s law 0 E dA 0 E dA qenc 0 E dA 0 E 4 r 2 q E= 1 q 4 0 r 2 January 31, 2007 Center for Solar-Terrestrial Research A Charged Isolated Conductor If an excess charge is placed on an isolated conductor, the amount of charge will move entirely to the surface of the conductor. None of the excess charge will be found within the body of the conductor. E 0 January 31, 2007 Conducting surface Center for Solar-Terrestrial Research Cylindrical and Planar Symmetry Cylindrical symmetry E 2 0 r January 31, 2007 Planar symmetry E 2 0 Center for Solar-Terrestrial Research Spherical Symmetry Spherical shell 1 q E 4 0 r 2 E0 r R r R A shell of uniform charge attracts or repels a charged particle that is outside the shell as if the shell’s charge were concentrated at the center of the shell. Uniform charge (field at r R) A shell of uniform charge exerts no electrostatic force on a charged particle that is located inside the shell. 1 E r 3 4 0 R January 31, 2007 Center for Solar-Terrestrial Research