Overview of exam and material covered
advertisement

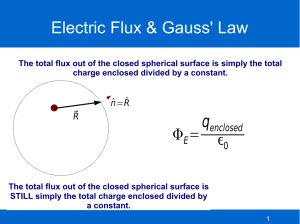
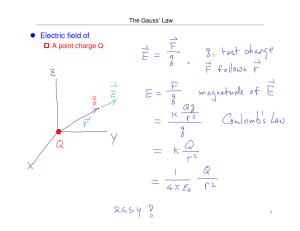
Agenda Phys 121 Common Exam 1 Review • • • • Exam overview & mechanics Sample Exam # 1 or # 4 Other Sample Problem Sets Open Agenda Exam Mechanics and Scope • • • • • • • • • • The exam covers Lectures 1 – 4, comprising material in Chapter 21, Chapter 22.1 – 5. and some selected material from the introductory lecture (see the course syllabus). There are 18 multiple choice questions. 100% on the exam means 16 questions answered correctly. It is possible to score greater than 100%. Students are expected to show work on the question paper in order to get credit for answering questions correctly. There is otherwise no penalty for wrong answers. Circle your chosen answers on the test paper as well as on the Scantron sheet. Use the back of the test paper if you need more room to do scratch work. For long questions, tell the grader to look there. Bring calculator & #2 soft pencils for marking the SCANTRON forms. A formula sheet will be provided. It is at the end of the exam package and is identical to the one posted on Janow’s web site. Turn off cell phones, pagers, laptop computers, any other communication devices or noise makers. A suggestion: first work the problems you know how to do, then come back and finish the ones that are doubtful. Be sure to comply with the Honor Code Pledge. Electricity and Magnetism Introduction to Physics 121 • • • • Syllabus, rules, assignments, exams, etc. iClickers Quest Course content overview First Lecture: Intro • Review of vector operations • Dot product, cross product • • • • Scalar and vector fields in math and physics Gravitation as an example of a vector field Gravitational flux, shell theorems, flow fields Methods for calculating fields 3 Electricity and Magnetism Lecture 2 - Electric Charge Physics 121 • • • • • • • • • • • - SJ Chapter 23, Sec. 1 - 3 History Electromagnetism Electric Charge Quantization of Charge Structure of Matter Conservation of Charge Conductors and Insulators Coulomb’s Law – Force Shell Theorem Examples Summary 4 Summary: Chapter 21: Electric Charge Charge: Matter: Coulombs Law: Vector Form: Superposition Shell Theorem Lecture 2 Electricity and Magnetism Lecture 3 - Electric Field Physics 121 - Chapter 23 Sec. 4 – 7 (See also 26.6) • • • • • • • • Recap & Definition of Electric Field Electric Field Lines Charges in External Electric Fields Field due to a Point Charge Field Lines for Superpositions of Charges Field of an Electric Dipole Electric Dipole in an External Field: Torque and Potential Energy Method for Finding Field due to Charge Distributions – – – – • • Infinite Line of Charge Arc of Charge Ring of Charge Disc of Charge and Infinite Sheet Crossed Electric Fields: CRT example Summary 6 Summary: Electric Field Lecture 3 E dq k dist e r 2 r̂ Physics 121 Lecture 04 - Gauss’ Law SJ Chapter 24 Sec. 1 - 4 • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Gaussian Surfaces Flux Example: Flowing Water Flux of an Electric Field Gauss’ Law Gauss’ Law Near a Dipole A Charged, Isolated Conductor Gauss’ Law: Charged Conducting Infinite Sheet Spherical Symmetry: Conducting Shell with Charge Inside Cylindrical Symmetry: Infinite Line of Charge Field of Non-Conducting Sheet Conducting and Non-conducting Plate Examples Proof of Shell Theorem using Gauss Law Examples Summary 8 Summary: Gauss’s Law Lecture 4