Classification of Matter: Chemistry Flowchart & Notes
advertisement
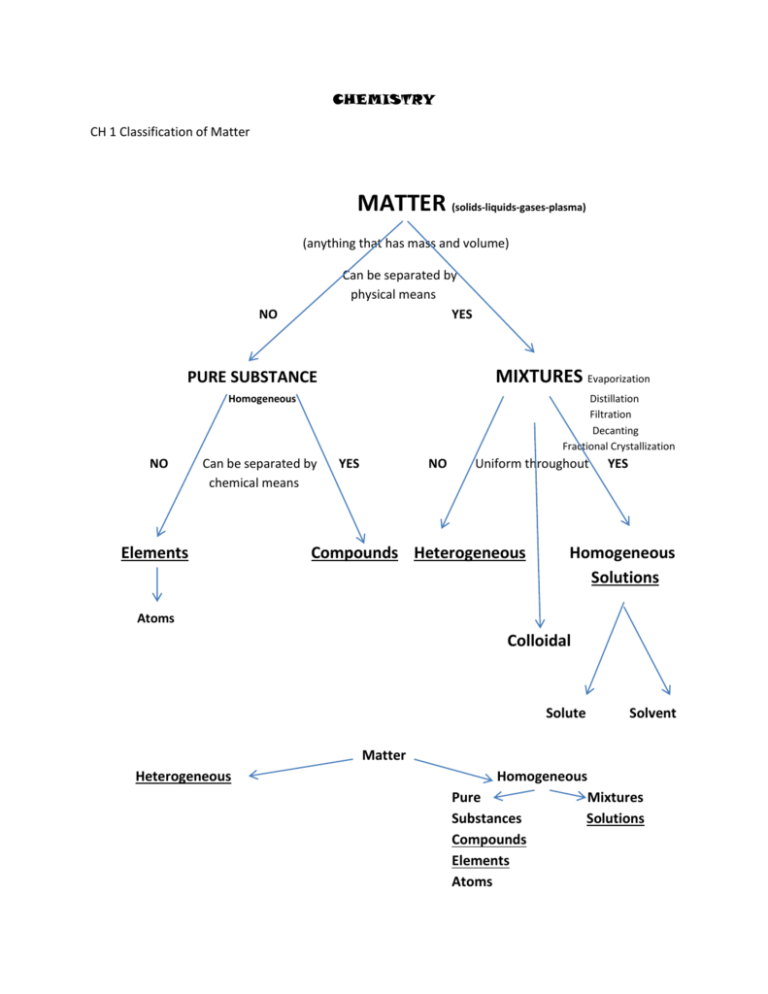
CHEMISTRY CH 1 Classification of Matter MATTER (solids-liquids-gases-plasma) (anything that has mass and volume) Can be separated by physical means YES NO MIXTURES Evaporization PURE SUBSTANCE Homogeneous NO Distillation Filtration Decanting Fractional Crystallization Can be separated by chemical means Elements YES NO Uniform throughout Compounds Heterogeneous YES Homogeneous Solutions Atoms Colloidal Solute Solvent Matter Heterogeneous Homogeneous Pure Mixtures Substances Solutions Compounds Elements Atoms Examples of Matter Matter (anything that has mass and volume) Examples: Almost anything…. Pure Substances (not a mixture, looks uniform throughout, will not settle out over a period of time, homogeneous, are either compounds or elements) Examples: All elements and compounds, (water, carbon dioxide, oxygen, iron) Compounds (two or more elements that have chemically bonded. Can only be separated by a chemical process, water, through electrolysis, can be separated into hydrogen and oxygen, and has properties that are different from its elements) Examples: water H2O, carbon dioxide CO2, iron oxide Fe2O3, sulfur dioxide SO2, sugar, etc. Elements (made up of the same kind of atoms and cannot be separated through a chemical process) Examples: Refer to the periodic table of elements Mixtures (two or more materials mixed together that has not chemically bonded, they retain their own properties and identities and can be separated into their individual parts by physical process, like boiling point differences, size of particles, if magnetic, solubility differences) Examples: Salt water (evaporization), sand and water (filtering), oil and water (decanting), alcohol and water (distillation) Heterogeneous (mixtures that are not uniform throughout, you can see differences within it, its particles will settle over a period of time (paint), it can have more than one phase (carbonated soft drink) (gas and liquid) Examples: Granite, wood, paint, salad dressing, pizza, paper, rocks. Homogeneous (can either be pure substances or mixtures, if mixtures we call them solutions. Matter that looks uniform throughout, if mixtures, the materials that make it up are evenly distributed, you cannot distinguish one part from another, their particles will not settle over a period of time. Made of only one phase.) Examples: all elements and compounds (substances), mixtures (solutions) air, alloys (brass, stainless steel), glass, saltwater, gasoline, vinegar Solutions (A homogeneous mixture in which its particles and extremely small and evenly distributed throughout, particles will not settle out and contains only one phase. Solutions are made up of a solute (being dissolved) and solvent (doing the dissolving)) Examples: air, alloys (brass, stainless steel), glass, saltwater, gasoline, vinegar Solute (what is being dissolved in a solution and the one in lesser amount) Example: Saltwater, the salt is the solute. Brass (copper and zinc), zinc is the solute because it’s in lesser amount. Solvent (what is doing the dissolving in a solution and the one in greater amount) Example: Saltwater, the water is the solvent, Brass, the copper is the solvent because it’s in greater amount. Colloids (A mixture that can be either heterogeneous or homogeneous that its particles are larger than solutions but smaller than suspensions. The particles will not settle out over a period of time, but they can show separation within the mixture) Examples: paint, milk, mayonnaise, smoke gelatin, fog







