Ch. 1 - SchoolRack

Ch. 1
CLASSIFYING
ORGANISMS
Vocabulary
Classify- to put things into groups
Kingdom- the highest or most general group of organisms
Phylum- the second level of classification below the level of kingdom
Class- the level of classification below phylum
Vocabulary
Species- the lowest level of classification
Vertebrate- an organism with a backbone
Invertebrate- animals without backbones
Lesson 1
Why do we classify?
Biologists classify a living thing by comparing and contrasting the living thing’s physical characteristics with the physical characteristics or known organisms
A classification systems helps organize information and makes communication more exact.
What dog are you thinking of?
This is what I was thinking of.
Classification Systems
Today’s classification system was developed by many people and is still changing
The seven levels of classification are:
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Classification Systems
The six KINGDOMS of living things are:
Archaebacteria
Eubacteria
Protists
Fungi
Plants
Animals
Classification Systems
Archaebacteria- live as single cells.
Many do not need oxygen or sunlight to live
Eubacteria- single cells that have materials not found in archaebacteria
Protists- most protists are single cells, but some have many cells. Algae are protists
Classification Systems
Fungi- Mushrooms and molds are fungi. Fungi can be made of one or many cells
Plants- plants have many cells and make their own sugar for food
Animals- Animals have many cells and get their food by eating other organisms
Lesson 2
How do we classify vertebrates?
Every animal has characteristics that distinguish it from all other animals
Vertebrates:
They are multi-cellular. They are made of more than one cell
They do not create their own food.
They can move on their own during part of or all their lives.
Vertebrates
Almost all animals do not have backbones.
Those that do are classified as vertebrates.
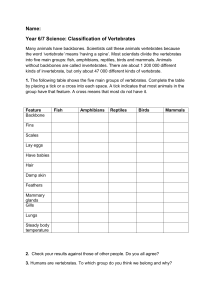
Vertebrates:
Fish
Amphibians
Reptiles
Birds
Mammals
Characteristics of Mammals
Breathe air with lungs
Make milk for their young
Most mammals have fur
Warm blooded
Babies are born looking like their parents
Life Cycle of Mammals
Birth
Growth
Reproduction
Death
Characteristics of Reptiles
Hatch from eggs
Scaly skin
Young feed themselves
Cold blooded
Lay eggs
Vertebrates
Life Cycle of Reptiles
Hatched (soft shelled eggs)
Growth independently
Reproduction
Death
Characteristics of Birds
Feathers
Young are fed
Warm blooded
Lay eggs
Vertebrates
Life Cycle of Birds
Hatched (hard-shelled eggs)
Growth
Reproduction
Death
Characteristics of Amphibians
Soft skin
Cold blooded
Does not feed young
Life Cycle of Amphibians
Metamorphosis- many changes occur during their life
Frog’s Life Cycle
Egg
Tadpole
Grow legs and tail gets shorter
Develop lungs
Start living on land
Characteristics of Fish
Scales
Cold blooded
Do not feed their young
Oxygen through gills
Live in water
Life Cycle of Fish
Hatched (soft shelled eggs)
Growth independently
Reproduction
Death
Discovery of Dinosaur Fossils
Scientist study fossils to classify animals that lived in the past
Fossil evidence indicates that dinosaurs were similar to present day lizards in many ways including:
Skeleton with backbone
Scales
4 legs
Dinosaurs and lizards have different structures for their legs.
Review
What are the five types of vertebrates?
How many cells does a multicellular organism such as a bear have?
Humans are classified as mammals. What can you predict about the life cycle of humans?
How are birds and mammals alike?
Why is the ability to fly not a defining characteristic of birds?
Review
Why are young birds hatched with parents present, while most young reptiles hatch long after parents have left the nest?
How are amphibians and reptiles similar?
What class of vertebrates did you find if you discovered an animal that hatched from an egg, spent the next stage of its life entirely in water, and then began to get oxygen through lungs rather than gills?
Review
Tadpoles may be found in water and get their oxygen using gills. Why are tadpoles not classified as fish?
What do scientists compare dinosaur fossils with to classify them?
Why do scientists think dinosaurs are more closely related to reptiles than mammals
Lesson 3
How do we classify invertebrates?
Invertebrates are by far the most numerous animals on Earth
Invertebrate are animals that do NOT have backbones.
Invertebrate animals can range in length from microscopic to the width of a basketball court
Invertebrates Classification
Invertebrates
Mollusks
Worms
Arthropods
Cnidarians
Mollusks
Mollusks have soft bodies without backbones.
Phylum includes:
Snails, Slugs, Clams, Squids (largest invertebrate)
Some mollusks get oxygen through their skin and other get oxygen through gills
Worms
Flatworms- flat and very thin, they live in wet and damp places
Roundworms- can live on water or land
Segmented worms- include earthworm
Arthropods
Largest phylum of animals
Have bodies that are divided into separate parts
All arthropods are invertebrates
Dichotomous key- an organized series of questions designed to lead to the identification of an unknown organism
Arthropods
Examples of Arthropods:
Insects
Lobsters
Spiders
Arthropods receive oxygen in different ways:
Gills
Tubes in the body
Book lungs
Dichotomous Key
Review
What animals is the largest invertebrate?
How are mollusks, worms, and coral different from fish, birds, and reptiles?
How do mollusks obtain oxygen?
What are the identifying characteristics of arthropods?
Lesson 4
How are other organisms classified?
Plants produce their own food
Phyla (phylum) includes:
Mosses
Ferns
Conifers
Flowering plants
Plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make their own sugar for food
Plants
Vascular plants- have special tubes that carry food and water to parts of the plant
Parts of a plant:
Roots
Leaves
Organisms in the plant kingdom are multicellular
Mosses
Characteristics of moss:
Not vascular
No seeds
No flowers
Grows on trees
Small plant with tiny leaf-like structures
Ferns
Characteristics of Ferns:
Vascular
No seeds
No flowers
Have feather-like leaves
Will grow larger than moss because it is vascular
Conifers
Characteristics of conifers:
Vascular
Has seeds
No flowers
Phylum includes:
Pine, Firs, Spruce
Needle-like leaves
Flowering Plants
Characteristics of Flowering Plants:
Vascular
Has seeds
Has flowers