Race & History
advertisement

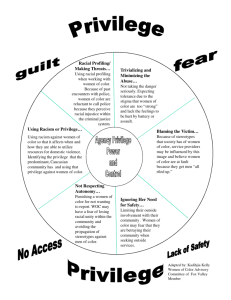
Race is a symbolic category based on phenotype. It is constructed according to specific social and historical contexts that is misrecognized as a “natural” category. Phenotype refers to a person’s physical appearances. Race does not exist on the genetic level, but rather on the social and political levels. Race is a symbolic category also based on a person’s ancestry (lineage, regional, or national affiliations). Ethnicity refers to a shared lifestyle informed by cultural, historical, religious and/or national affiliations. ▪ Race and ethnicity tend to be decoupled for white Americans but tightly bound for nonwhite Americans. Nationality is equated with citizenship – membership in a specific delineated territory controlled by a formal power. ▪ Citizenship is accompanied by many social privileges. All three categories can be neither separated nor collapsed into one. Racial social inequality can be functional for some groups, and create strong social bonds Racial and ethnic inequality also aggravates social problems and is dysfunctional for society as a whole Economic competition creates and maintains racial and ethnic group tensions (Minorities have far less power and resources). Minorities who are disproportionately underprivileged and unemployed serve the interests of those in power (usually by keeping wages low). Meanings and definitions contribute to the subordinate status of racial and ethnic groups. Negative terms associated with "black" (black knight is evil, white knight is good). Negative stereotypes of racial and ethnic groups lead to self fulfilling prophecy. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MqSFqn UFOns Stereotypes: Exaggerations or generalizations about the characteristics and behavior of a particular group. Negative stereotyping of minorities leads to a self-fulfilling prophecy—a process in which a false definition of a situation leads to behavior that, in turn, makes the originally falsely defined situation come true. Some people argue that race is something that no longer matters. Notion of a “color-blind society” The consistency (and perhaps rise) of many forms of racial injustices are undeniable: Hate crimes Employment inequalities Poverty Incarceration disparities Media representation Stereotypes are often believed to be facts. Social differences between people become naturalized; social inequalities become natural inequalities biological determinism and naturalization. ▪ This allows us to leave institutional and cultural processes unexamined as issues and problems are rooted in the race itself. Racism: the belief that one category of people is superior to another in some way Racism continually shape-shifts. Contemporary racism is not always obvious; it is so familiar than it is often unnoticeable. History always structures the present. Native American / Alaska Native Asian and Pacific Islander African Americans Hispanic / Latino Caucasian Why should we have only five main racial groups – why not 50? Why not base divisions based on foot size, or height, or whether we live in the northern or southern hemisphere? Genocide- the annihilation of an entire group of people (including, but not limited to racial groups) Colonialism- A racial or ethnic group from one society dominates the racial or ethnic group(s) of another society. Acculturation- Refers to adopting the culture of a group different from the one in which a person was originally raised (can include language, behaviors, and names) Assimilation- The process by which formerly separate groups merge and become integrated as one. (primary vs. secondary) Pluralism-Refers to a state in which racial and ethnic groups maintain their distinctness but respect each other and have equal access to social resources. While nonwhites have certainly achieved greater equality than in the past, overt racism is still common. Racism cannot and should not be defined only by those actions and values of extreme groups and their extreme acts. ▪ “To define racism only through extreme groups and their extreme acts is akin to defining weather only through hurricanes.” Racism can also be covert, existing in common, unnoticeable and everyday forms. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Zqh6Ap9ldTs Institutional racism is systemic white domination of people of color that is embedded and operating with our culture and its social institutions People do not often see institutional racism as racism since it operates outside the scope of individual intent. Prejudice An attitude or judgment, usually negative, about an entire category of people. Discrimination Actions or practices that result in differential treatment of categories of individuals. Institutional discrimination Occurs when normal operations and procedures of social institutions result in unequal treatment of minorities. There is no such thing as reverse (institutional) racism – or nonwhite institutional racism – because there is no centuries-old socially ingrained and normalized system of domination designed by people of color to deny whites full participation in the rights, privileges, and access to power in our society. While racism can flow from dominated groups to the dominant group, it does not pack the same punch. Symbolic violence refers to the process of nonwhites unknowingly accepting and supporting the terms of their own racial domination (internalized oppression). The normalized racial “order of things” seems to feel natural and legitimate. Everything we see, think, and do are done within the modes of domination and are therefore products of domination. Racial domination does not exist inside a vacuum. Sociologists use the term intersectionality to explain the overlapping systems of advantages and disadvantages that affect people differently positioned in society. Different identity characteristics lead to different experiences The matrix of domination There is no monolithic experience; we must look people’s lives in their full complexity. Moving away from racial essentialism Whiteness often goes unnamed or unnoticed; white = raceless White people have a hard time coming to terms with their whiteness and become uncomfortable when having to analyze it. Whiteness: the dominant category of race with which all other categories are compared or contrasted. White privilege is the collection of unearned cultural, political, economic, and social advantages and privileges possessed by people of Anglo-European descent or by those who pass as such. Some white people are fully aware of how the current system of racial domination benefits them and work to uphold the system. Some white people do not recognize their privilege and unknowingly support a system of racial domination. Color-blindness refers to (typically well-intentioned) behaviors and thought processes that aims to ignore all racial markers: “I don’t see color at all.” Requires simultaneous recognition and non-recognition Denying race also denies any related privileges or domination that exists. We can use our sociological imagination, which is one’s ability to understand everyday life not through personal circumstances but through the broader historical forces that structure and direct it. Reflexivity: looking within ourselves to uncover taken-forgranted ways of thinking that influence of we understand the social world. Relationality: exploring the networks of relationships within which individuals or groups are embedded to better understand them Reconstruction: taking our new-found knowledge and using it to change the world in which we live Affirmative Action: A broad range of policies and practices in the workplace and educational institutions to promote equal opportunity as well as diversity. Federal Affirmative Action Affirmative Action in Higher Education Affirmative Action Pros: Produces benefits for women, minorities, and the economy. Employers adopting affirmative action increase number of women and minorities by 10 to 15%. Has increased percentage of blacks attending college by a factor of three and percentage of blacks in medical school by a factor of four. Affirmative Action Cons: Some minorities argue that it perpetuates feelings of inferiority. Fails to help the most impoverished of minorities. Not needed because laws “should” prohibit discrimination.