111070_Phylogeny
advertisement
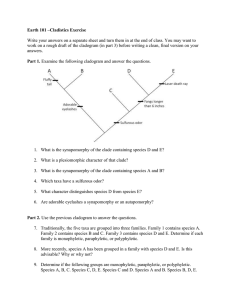
Phylogeny and Systematics 2.10.15 Phylogeny • Evolutionary history of a species of a group of related species • Information used to construct phylogenies includes: – Fossil record – Molecular comparison (DNA, RNA, proteins) – Breeding behavior/embryological development – Biogeography – Morphology Systematics • The study of biological diversity in an evolutionary context • Encompasses taxonomy, goal is to trace phylogeny • Modern phylogenetic systematics = classification based on evolutionary history Cladogram • Phylogenetic diagram based on cladistics – Cladistics = form of taxonomy based on shared characteristics not found in ancestral group – Clade = evolutionary branch in cladogram; consists of ancestral species and all descendants Clade • A clade consists of ancestral species & all descendants – Grouping of species is known as monophyletic if it meets this standard – Circle the monophyletic group that includes organisms E and H: Clade • A clade consists of ancestral species & all descendants – Grouping of species is known as monophyletic if it meets this standard – Circle the monophyletic group that includes organisms E and H: Non-monophyletic groups: Constructing a cladogram: #1: Sort homology from analogy • Homology: – Similar structure and shared ancestry – The greater # of homologous parts the more closely related • Analogy: – Different structure; similar function (wings of birds vs. butterflies vs. bats) – Come to resemble each other because experience similar environmental pressures #2: Identify shared derived characters Shared primitive characters • Not limited to group being studied • Example: backbone & mammals (backbones not limited to mammals) Shared derived characters • Evolutionary novelty unique to clade • Example: hair is unique to mammals #3: Outgroup comparison • Outgroup = species closely related to species being studied • Ingroup = species being studies – Identify characteristics to be studied – Create data matrix comparing characteristics – Construct cladogram Example Example Example Example from molecular data Example from molecular data Example from molecular data