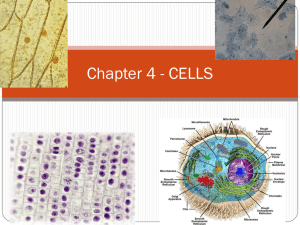
Parts of the Cell
advertisement

Control center of the cell Contains the genes (genetic materials) DNA – molecule in the cell that is used to construct proteins Interesting facts about the nucleus The shape of the nucleus will conform to the shape of the cell Absolutely necessary for cell reproduction. A cell that has lost or ejected its nucleus is only programmed to die Nuclear Envelope – double membrane barrier around the nucleus Nucleoli (plural of nucleolus)– small, darkstaining round bodies where ribosomes are assembled Chromatin – DNA that is combined with protein to form a loose network of bumpy threads and is scattered throughout the nucleus. During replication, this will coil and condense to form chromosomes Fragile, transparent barrier Consists of two lipid layers arrange “tail to tail” Protein molecules float around in the membrane. Example include: Enzymes Receptors for hormones Protein channels (tiny pores) Carriers (carry wanted materials into the cell) Microvilli – tiny finerlike projections that greatly increase the surface area for faster absorption Membrane Junctions Tight Junctions – impermeable junctions that bind cells together into “leak proof sheets” Desmosomes – anchoring junctions that prevent cells from being pulled apart Gap Junctions – allow communication in between cells. The two cells are connected by connexons (hollow cylinders that span width of the membranes) The cellular material outside the nucleus and inside the plasma membrane Three major elements Cytosol – semitransparent fluid that suspends the other parts Organelles – means little organs, these are the specialized compartments that are designed for specific tasks inside the cell Inclusions – extra chemical substances in the cell Mitochondria – bean shaped cellular power plants Ribosomes – tiny, bilobed, dark bodies that are the protein making factories of the cell Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)– serves as a minicirculatory system and provides a network of channel to carry substances Rough ER – covered with ribosomes (makes it rough). So it takes the newly made proteins, allows them to finish folding into their normal shape, and then ships them to other parts of the cell Smooth ER – lipid metabolism and detoxification takes place here. • Golgi Apparatus – post office, it receives proteins from the rough ER, modifies them, and then packages them in secretory vesicles. – These vessels travel to the plasma membrane, fuse with it, and then eject its contents out of the cell • Lysosomes – “breakdown bodies,” sacs filled with digestive enzymes capable of digesting old cells or foreign materials • Peroxisomes –detoxify the cell of poisonous materials and deactivate free radicals using oxidase enzymes • Cytoskeleton – network of proteins that for the “bones and muscles” of the cell. It consists of: – Intermediate filaments – “wires” that help to resist pulling forces on the cell – Microfilaments – involved in cell movement and in producing changes in cell shape – Microtubules – determines the overall shape of the cell and distribution of organelles • Centrioles – rod shape bodies near the nucleus that help direct cell division Don’t forget, the next memory check is going to be… Homework • Complete the Cell Diversity Worksheet