Barcodes - Binghamton

Barcodes
Professor Koon ISE 370
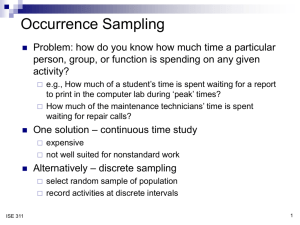
Code Reading Technology
Original Barcode Readers
Contact Wand
Professor Koon ISE 370
Code Reading Technology
Non-Contact Scanner
How a checkout scanner works
Optoelectronics:
Optical Image to electrical
Signals
Professor Koon ISE 370
Code Reading Technology
Non-Contact Scanner
Professor Koon ISE 370
Code Reading Technology
Professor Koon ISE 370
BarCode History
Grocery stores need for a system to automatically read items at checkout
Increase Productivity
Reduce Human Error
Silver, Woodland and Johanson
1948 Drexel Institute of Technology
Students
1949 First patent for “Classifying
Apparatus and Method”
Linear
“Bulls-eye”
Image: http://www.ournewhaven.org.uk/images/uploaded/scaled/Shop_s.jpg
Professor Koon ISE 370
Standardization
“Without the advancements involving lasers and microchips, the development of the Universal Product Code and the dream of an automated checkout would not have been possible.” – Marvin L.
Mann
Professor Koon ISE 370
UCC >> First BarCode (1974)
Professor Koon ISE 370
UPC – Universal Product Code
12 Digits (6 ID, 5 item, 1 check)
Symbology is a standard that defines the printed symbol.
How scanners should read and decode the symbol.
Professor Koon ISE 370
Decode Barcode
Black Bars with White Bars
Between
Thinnest Bar = 1 unit wide
All Bars 1 to 4 units wide
Start (L) is 1-1-1 (B-W-B)
Final ( R) is 1-1-1 (B-W-B)
All Digits add to 7 widths
Professor Koon ISE 370
UPC Barcode
How to read a standard 12 decimal digit code
Digit Pattern Digit Pattern
0 0001101 5 0110001
1 0011001 6 0101111
2 0010011 7 0111011
3 0111101 8 0110111
4 0100011 9 0001011
Professor Koon ISE 370
How To Read a Barcode
Professor Koon ISE 370
Check Digit (UPC Code)
Add all digits in Odd positions
Multiply sum results by 3
Add all digits in Even positions
Add 3x Odd sum to Even sum
This sum plus check digit must be a multiple of 10. (e.g. 110)
Try 63938200039
Professor Koon ISE 370
Different Types of Barcodes
Other most commonly used codes:
UPC-A, UPC-E, and UPC Supplemental
EAN-13 (13 Digits: One for Flag)
Code 39 (US Military 1981)
Interleaved 2 of 5
Code 128 (Alphanumeric)
Two-Dimensional (Stacked, Multi-row)
Professor Koon ISE 370
Interleaved 2 of 5
Numbers Only
Long as Necessary
Check Digit is optional
Digit is encoded in the bars
Next digit is encoded in the spaces
Start >> NB-NS-NB-NS
Data = five bars each
Stop >> WB-NS-NB
Professor Koon ISE 370
Number Pattern 2 of 5
0 >> NNWWN
1 >> WNNNW
2 >> NWNNW
3 >> WWNNN
4 >> NNWNW
5 >> WNWNN
6 >> NWWNN
7 >> NNNWW
8 >> WNNWN
9 >> NWNWN
Professor Koon ISE 370
Different Types of Barcodes
American Standard Code for
Information Interchange ( ASCII )
Coding Standard
Professor Koon ISE 370
Different Types of Barcodes
>> Linear or Matrix (2D)
Code 39
A symbology that can encode uppercase letters (A through Z), digits (0 through 9) and a handful of special characters like the
$ sign.
Military Usage
Drawbacks
Low Data Density
Requires More Space
Professor Koon ISE 370
Different Types of Barcodes
Code 128
A very high-density barcode symbology
Used extensively world wide in shipping and packaging industries
Can encode all 128 characters of ASCII
Professor Koon ISE 370
CODE 49
Professor Koon ISE 370
Code 49
2 to 8 rows stacked
Cross between UPC & Code 39
Developed in 1987 Intermec
Corp.
Modified Scanner Needed
Professor Koon ISE 370
Different Types of Barcodes
Data Matrix
A 2D matrix barcode consisting of black and white “cells” or “modules” arranged in either a square or rectangular pattern.
Most common in marking small items (as small as 2-3mm 2 )
Pack a lot of information in a very small space. Stores between 1 to 500 characters. Can scale down to 1 mil square. (500 million characters per inch).
Professor Koon ISE 370
Aztec Code
Design for ease of printing & ease of decoding
Square central bullseye finder.
Smallest 15 x 15 modules.
Largest 151 x 151 modules.
1995 by Welch Allyn Inc.
Professor Koon ISE 370
3D Barcode
(Bumpy)
Small circular symbols
Shiny, curved metal surfaces
Professor Koon ISE 370
SuperCode
In public domain.
Invented in 1994.
Packet structure (multi-row).
Greater freedom in placing packets.
32 error correction levels.
Professor Koon ISE 370
Radio Frequency Identification
(RFID)
No contact of line of sight
Active or Passive Tags (See note sheet)
Electromagnetic Waves
Active tags contain a battery and can transmit signals autonomously.
Passive have no battery and require an external source to provoke signal
Transmission.
Cost under ¢10
Implementation into cell phones
Professor Koon ISE 370
Standardization
4/10/2020
Problems with standardizing new technology
Will Barcodes Prove to be Economic?
IBM proposed designed by George J. Laurer
12 Decimal Digit code S LLLLLL M RRRRRR E
(S) Start – Bit pattern of 101
(L) Left – 7 Bit pattern
(M) Middle – Bit pattern of 01010 known as guard bars
(R) Right – 7 Bit pattern
(E) End – Bit pattern of 101
Professor Koon ISE 312 27
What is a Barcode?
1
A bar code (also barcode ) is an optical machine readable representation of data.
Originally, bar codes represented data in the widths (lines) and the spacings of parallel lines and may be referred to as linear or 1D barcodes or symbologies.
Now they also come in patterns of squares, dots, hexagons and other geometric patterns within images termed 2D matrix codes or symbologies.
1 Image and Definition: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barcode
4/10/2020 Professor Koon ISE 312 28
Questions?
Professor Koon ISE 370