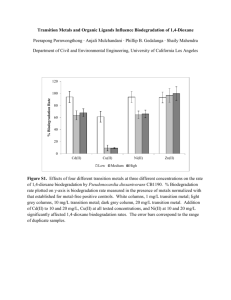
Analysis of Isopropyl para-Toluenesulfonate in palm
advertisement

Gas Chromatography-flame ionization detection of 1,4-dioxane in palm oil-based fatty alcohol ethoxylates Bonnie Tay-Jones Yen Ping Principal Research Officer Quality and Environment Assessment Unit Malaysian Palm Oil Board 6th International Conference and Exhibition on Analytical & Bioanalytical Techniques MALAYSIAN PALM OIL BOARD Malaysian Palm Oil Board Vision To become the premier, research and development institution providing leadership and impetus for the development of a highly diversified, value-added, globally competitive and sustainable oil palm industry. Mission To enhance the well-being of the Malaysian oil palm industry through research, development and excellent services. ABBREVIATIONS GC-FID – Gas Chromatography-flame ionization detector FAEO – fatty alcohol ethoxylate I & I – industrial and institutional EO – ethylene oxide S/N – signal-to-noise ratio LOD- limit of detection LOQ – limit of quantification RSD – relative standard deviation AOAC – Association of Official Analytical Chemists FDA – Food & Drug Administration (USA) NIST – National Institute of Standards and Technology OVERVIEW Introduction Methodology Validation of method Confirmation of 1,4Dioxane • 1,4-dioxane the issue • 1,4-dioxane origin • Fatty alcohol ethoxylate and its applications • 1,4-dioxane toxicity • Regulatory Limit • Sample preparation • Instrumentation • Validation Parameters • LOD, LOQ, Precision, Accuracy, Specificity • Identification of 1,4-dioxane in fatty alcohol ethoxylate by GC-MSD INTRODUCTION 1,4-DIOXANE : THE ISSUE Production of oleochemical derivatives :current developing industry in Malaysia Local oleochemical companies: setting up of new commercial plant to produce palm-based fatty alcohol ethoxylates (FAEO). Research group in AOTD,MPOB currently setting a pilot plant producing ethoxylates. 1,4-dioxane presence : levels up to 279 ppm*** in personal care products formulated with ethoxylated products e.g alcohol ethoxylate, alcohol ethoxy sulfates, polyethylene glycol and polysorbates (Black, 2001***). FDA,USA (2001) : detected up to 1410 ppm in cosmetic raw materials ***Black RE, Hurley FJ, Havery DC. 2001. Occurrence of 1,4-dioxane in cosmetic raw materials and finished cosmetic products. Journal of AOAC International 84(3): 666-670. 1,4-DIOXANE : THE ISSUE 1,4-dioxane : recognized as a toxic substance, need to be controlled. (realised by local manufacturer) A request for method to be developed by Quality and Environment Unit, Advanced Oleochemical Technology Division Method for detection of 1,4-dioxane in palmbased FAEO not available. Local industry and MPOB research unit need to perform quality control of products for customer requirements. 1,4-DIOXANE ORIGIN A by-product that can be produced during the manufacturing of fatty alcohol ethoxylates. Ethoxylation Process: Addition of ethylene oxide to a linear alkyl fatty alcohol (carbon chains ,C12-C14) normally derived from palm kernel oil/coconut oil. 1,4-dioxane may be formed due to dimerization of ethylene oxide (under certain reaction conditions). Continue… CHEMICAL STRUCTURES 1,4-dioxane Fatty alcohol ethoxylate n = number of moles EO COMMERCIAL PALM-BASED ALCOHOL ETHOXLYATES WITH DIFFERENT EO COMPOSITIONS FAEO 20 FAEO 12 FAEO 2 FAEO 1 FAEO 3 FAEO 4 FATTY ALCOHOL ETHOXYLATE APPLICATIONS Home Care 1 2 3 4 5 6 Source: Thai Ethoxylate Co. Ltd, Thailand Textile Degreasing agent Wetting agent fertilizer inseciticide Agrochemicals Scouring agent Paint and rubber Herbicide/fungicide Emulsion polymerization I & I cleaners Household cleaner Dishwash detergent Hard surface cleaners Laundry detergent (liquid) Personal care Laundry dtergent (powder) Hand cleaner Mole Shower cream/gel shampoo FATTY ALCOHOL (C12-C14) ETHOXYLATES WITH 1 – 6 MOLES ETHYLENE OXIDE APPLICATIONS Metal working 7 8 9 10 11 12 15 Home Care Textile Degreasing agent Wetting agent fertilizer inseciticide Agrochemicals Scouring agent Paint and rubber Herbicide/fungicide Emulsion polymerization I & I cleaners Household cleaner Dishwash detergent Hard surface (cleaners) Laundry detergent (liquid) Personal care Laundry detergent (powder) Hand cleaner Moles Shower cream/gel shampoo Fatty alcohol (C12-C14) ethoxylates with 1 – 6 moles ethylene oxide applications Metal working TOXICITY OF 1,4-DIOXANE International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) Section 5, pg.595, Vol.71, 1999 5.1 Exposure data Exposure to 1,4-dioxane may occur during its manufacture and its use as a solvent in a wide range of organic products. It has been detected in ambient air. 5.2 Human carcinogenicity data Deaths from cancer were not elevated in a single, small prospective study of workers exposed to low concentrations of dioxane. 5.3 Animal carcinogenicity data Oral administration and inhalation exposure study in mice, rats and guinea-pigs: increased incidence of tumour occurrence in the tested animals. Continue….. Continue… 5.5 Evaluation There is inadequate evidence in humans for the carcinogenicity of 1,4-dioxane. There is sufficient evidence in experimental animals for the carcinogenicity of 1,4-dioxane. Overall evaluation 1,4-Dioxane is possibly carcinogenic to humans (Group 2B). REGULATORY LIMIT No regulatory limit for 1,4-dioxane in palm-based fatty alcohol ethoxylate produced in Malaysia International cooperation on cosmetics regulation (ICCR) , an international group of regulatory authorities for cosmetics (Japan, United States, Canada and European Union) : proposal to set exposure level limits in cosmetic and personal care products. •8th ICCR meeting held on the July, 2014: the reports on 1,4-dioxane in cosmetic products are undergoing final review METHOD DEVELOPMENT METHOD AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION Method Name: Determination of 1,4-Dioxane in fatty alcohol ethoxylates by using GC-FID Method performance: assessed by doing a method validation based on International Committee on Harmonization (ICH) /AOAC guidelines Matrices for spiking/recovery: palm-based fatty alcohol ethoxylates with different EO composition SAMPLE PREPARATION FOR ANALYSES (DIRECT INJECTION ) 0.5 g of FAEO sample weigh into volumetric flask (5 ml) reconstitute with acetonitrile Inject into GC-FID Note: Fast sample preparation and no clean up of matrices required (cost saving method) AGILENT TECHNOLOGIES GC-FLAME IONISATION DETECTOR 7890 GC-FID CONDITIONS FOR DETECTION OF 1,4-DIOXANE GC oven temperature program : initial temperature was (50oC) held for 4 min, then increased at 10oC/ min to 110oC (held 20 min). Post Run , 300oC held for 10 min. Total run time was 34 minutes. Carrier gas: helium (set at constant flow of 0.8 mL/ min) Inlet temp, Pressure: 200oC; 4.47 psi Detector temp : 310oC Split ratio: 10:1 Column: HP-5 column (30 m length x 0.32 mm internal diameter (i.d.); Agilent Technologies) GC-FID SAMPLING CONDITIONS OPTIMIZATION FOR DIRECT INJECTION A split focus liner with deactivated glass wool was used at the inlet port, and replaced if contaminated over time. The glass wool in the liner is able to trap the heavier ethoxylates and only allow the volatiles through (prevent matrix interference). Additional post run for 10 mins at 300oC was included after every analysis to remove other volatile residues (arising from solvent and matrixs) from the column. INSTRUMENTATION – STRUCTURE CONFIRMATION GC conditions from GC-FID method was transferred to an Agilent Technologies 7890A GC fitted with 5975 C Mass spectrometric detector Data handling and system operations controlled by GC-MS NISTO5 software . Mass spectra obtained were obtained for 1,4dioxane spiked in FAEO. METHOD VALIDATION Limit of detection Limit of quantification Precision Linearity and working range Accuracy Selectivity GC-FID chromatograms of 1,4-dioxane, blank FAEO & spiked FAEO 1 ug/ml 1,4-dioxane RT : 8.589 mins FAEO (blank) FAEO ( spiked at 1 ug/ml) RT 1,4-dioxane : 8.583 mins LOD /LOQ LOD & LOQ : based on S/N ratio approach Acceptable S/N ratio for LOD was 3:1 and 10:1 for LOQ (ICH guideline) For this method: LOD : 10 µg/g of FAEO LOQ : 30 µg/g of FAEO PRECISION (INTRA DAY) Concentration of 1,4-dioxane (μg/g)* n= 4 Percentage Recovery (%) RSD (%) 15.5 (low) 99.4 0.4 77.5 (medium) 100.6 0.4 505.0(high) 101.4 0.2 * Same analyst, same instrument Evaluation Criterion: AOAC Guidelines at ppm level, acceptable RSD for ppm : < 6% INTERMEDIATE PRECISION 2 conditions: same analyst on different days; different analyst on different days n= 6 replicates Inter-day and intermediate precision RSD (%) for 1,4-dioxane at 100 µg/g n=6 Day 1 0.5 Day 2 0.4 Analyst 1 0.5 Analyst 2 0.4 Evaluation Criterion: AOAC Guidelines at ppm level, acceptable RSD for ppm : < 6% LINEARITY AND WORKING RANGE A series of 6 calibration solution were prepared at the LOD up to the highest expected working concentration. These standards were run for 6 different batches. Linear Regression 1,4-dioxane working Data range (5.0 – 700 µg/g) n=6 Slope 0.6524 Intercept 0rigin Standard error 0.05 R2 value 0.9999 ACCURACY o Accuracy estimated by using recovery studies (spiking 1,4-dioxane in FAEO) o Evaluation criterion for accuracy : 80 – 115% (AOAC Guidelines) 1,4-dioxane (μg/g) FAEO FAEO FAEO (3 moles EO) (7 moles EO) (9 moles EO) Recovery RSD Recovery RSD Recovery RSD (%) (%) (%) (%) (%) (%) N= 6 N=6 N =6 30 103.5 1.5 99.9 2.4 96.8 2.3 60 101.4 2.5 100.0 2.4 98.4 2.9 100 99.9 1.3 98.0 1.5 96.9 3.3 200 101.8 2.2 97.3 2.9 96.2 1.9 500 104.3 3.0 96.5 3.8 97.2 2.1 MONITORING OF COMMERCIAL FAEO WITH DIFFERENT ETHYLENE OXIDE COMPOSITIONS • 22 types of commercial FAEO samples from local and overseas manufacturing companies with various ethylene oxide compositions (1,2, 3, 5,7, 9,12 and 20) were found to be free from 1,4-dioxane. MASS SPECTRUM OF SPIKED FATTY ALCOHOL ETHOXYLATE OBTAINED FROM 7890 AGILENT TECHNOLOGIES GC-5975C TRIPLE AXIS MSD Mw: 88.1 (for 1,4-dioxane) Spectrum matching from experiment (spiked at 500 µg/g ) and NIST library GC-MSD: 94% CONCLUSIONS Method is fit for the detection of 1,4-dioxane in palmbased fatty alcohol ethoxylate with different moles ethylene oxide at LOD of 10 µg/g of FAEO within the range of 5 µg/g to 700 µg/g with precision < 6%, and accuracy within 80 - 115% Method will be useful for routine monitoring of 1,4Dioxane ,due to its simple preparation ,and the use of a commonly available instrument (GC-FID) at the Quality control laboratory of local FAEOs producers. Local and overseas commercial FAEOs were found to be free from 1,4-dioxane. FURTHER INFORMATION Gas Chromatography with flame ionization detection of 1,4-dioxane in palm-based fatty alcohol ethoyxlates Bonnie Tay Yen Ping ; Zulina A Maurad and Halimah Muhammad JAOCS, 2014, 91, 1103 – 1110. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT Committee Members of 6th Bioanalytical conference –for their kind invitation to present at this conference Director General of Malaysian Palm Oil Board for permission to present this work Malaysian Palm Oil Board – for funding this research Thai Ethoxylate Ltd, Bangkok, Thailand – providing fatty alcohol ethoxylates samples for spiking/recovery work Thank you