Presentation1 - internationalmanagement
advertisement
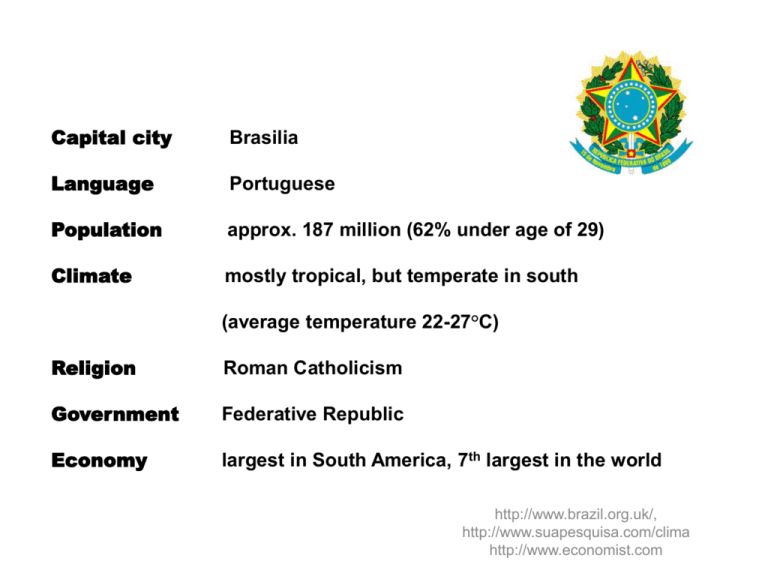
Capital city Brasilia Language Portuguese Population approx. 187 million (62% under age of 29) Climate mostly tropical, but temperate in south (average temperature 22-27°C) Religion Roman Catholicism Government Federative Republic Economy largest in South America, 7th largest in the world http://www.brazil.org.uk/, http://www.suapesquisa.com/clima http://www.economist.com Cultural differences GERMANY BRAZIL • Polychromic culture • Relaxed and flexible approach to time • When invited for dinner arrive on time • Arrival to dinner should be at least 30 • Written communication is favored • Honest, rational, say what they think • Face to face communication preferred (literal and direct culture) • Small lies told to avoid confrontation, • min later not to hurt anyone`s feelings (coded Doing culture and diplomatic culture) • Being culture http://www.worldbusinessculture.com, http://www.kwintessential.co.uk Hofstede`s Dimensions 80 76 69 65 68 67 38 38 60 38 40 20 0 UAI PDI Brazil Germany IND MAS Adapted from Hofstede & Hofstede (2005) from Luthans & Don (2009) Uncertainty (UAI) • GERMANY (65%) • BRAZIL (76%) • Belief in experts and their • Highly structured • “Custo Brazil” – real cost of business knowledge • Technical skills and strong and clear (legal & bureaucratic complications, leadership required • etc) Methodical approach with clear • indentified goals • Law, rules, regulations and religion used to avoid uncertainty Considerable amount of preparation and in depth planning (meetings, schedule, etc to avoid ambiguity) • Lots of rules and regulations http://www.worldbusinessculture.com, Hofstede, G, (2002) "Difference and danger: cultural profiles of nations and limits to tolerance" from Albrecht, M, Power distance (PDI) • GERMANY (38%) • BRAZIL (69%) • Decentralized and flatter • Very hierarchical, decisions made at most senior levels organizational structure (functional structure) • Clear instructions are necessary if task to be performed fully • Equal qualifications • Exercise of power is more flexible • Lot of internal politics • Strong respect for authority (formal • Understanding of the corporate power structure is important relationships, even in public) • Relationships and personality come before business http://www.worldbusinessculture.com Individualism/Collectivism (IND) • GERMANY (67%) • BRAZIL (38%) • Competence over seniority • Seniority over competence • Free market economy encourages • Publicly own companies encourage individualistic tendencies • Status and position is based on collective culture • individual achievements • Business and family life is separate Loyalty and trust over individual needs (relationships orientated) • Importance of family (also evident in business culture) Adapted from Malinak (2007) from http://www.communicaid.acom, http://www.worlbusinessculture.com Masculinity (MAS) • GERMANY (68%) • BRAZIL 38%) • Professional goals are more important • More caring for others, less self than personal • Assertive, tough, competitive and centered • focused on material success More emphasis on work balance (quality of life) • Work balance is of low importance • • Gender quality in workplace, although business • Emotion is seen as weakness women are treated fairly) • Traditional values (dominance of men Very tactile and emotive culture http://www.kwintessential.co.uk Brazil • DO`S • DON`TS • time spent on building relationships is never wasted Pay attention to your appearance Do your homework (“custo brazil) Use local legal expertise Manage Learn language Make sure you deal with decision maker Be yourself, be honest • Show feeling of frustration or impatience Publicly criticize your Brazilian counterparts Worry if agendas at meetings are not followed Change your negotiating team Rely on emails to give information Be detached Avoid the use of humor in business situations Speak Spanish • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Adapted from Malinak (2007) from http://www.communicaid.acom, http://www.worlbusinessculture.com • • Hofstede, G, (2002) "Difference and danger: cultural profiles of nations and limits to tolerance" from Albrecht, M, International HRM : managing diversity in the workplace pp.9-23, 658.3008/ALB: Blackwell Publishers • Adapted from: CIA World Factbook 2007, Author: Cora Malinak, M.A. Intercultural Communication from http://www.communicaid.com • http://www.kwintessential.co.uk • http://www.worldbusinessculture.com • http://www.brazil.org.uk/, • http://www.suapesquisa.com/clima • http://www.economist.com • http://everyculture.com