Asset Management and Revolving Loan Changes
advertisement

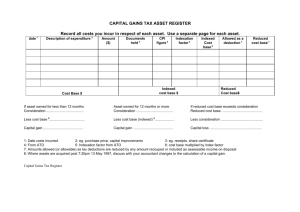
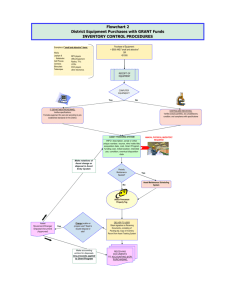
Bob Schneider & Kelly Green Michigan Department of Environmental Quality Revolving Loan Section Asset Management Plan (AMP) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Asset Inventory Critical Assets Level of Service O&M Strategies Capital Improvement Planning Asset Management Community Water Supplies Serving Publicly Owned CWS >1,000 <=1,000 Privately Owned CWS >1,000 <=1,000 n/a n/a Rule 1606 Capital Improvements Plan CIP developed by 1/1/2016 Propose CIP developed by 1/1/2018 Rule 1606 Asset Management Program Propose AMP developed by 1/1/2018 Propose AMP developed by 1/1/2018 n/a AM Provision in Permits Proposed AM Permit Language has been drafted to be included in NPDES permits for some municipal systems – “Operation, Maintenance & Replacement/Asset Management” First up: Detroit Water and Sewerage Department (DWSD) – Current Draft Permit Includes AM Provision Then: All Major Municipals reissued in FY13 and the remainder over the next cycle (5 years) After that: “Significant” Municipal Minors DEQ - Asset Management 4 Proposed AM Permit Language Permit Language Requires an Approvable AM Program to address: Staffing Mapping Collection System Inventory and Assessment of Fixed Assets Budget and Rate Sufficiency Annual Report DEQ - Asset Management 5 SAW Expectations • • • • Funds can be used to address any or all of the 5 AMP components; however after the 3 year grant period the final product is a complete and approvable AMP covering all 5 components. The applicant will need to certify that all grant activities have been completed at the end of three years. For wastewater systems the applicant must demonstrate significant progress towards funding the AMP. A stormwater funding structure is not required however an analysis of the costs to maintain the system and support the AMP is required. If the wastewater AMP identifies a gap in the current revenue needs to meet expenses, then significant progress must be made toward achieving the funding structure necessary to operate the system. Significant progress is defined as a 5-year plan to eliminate the gap with a minimum initial rate increase to close at least 10 percent of the funding gap. The first rate increase must be implemented within three years of the executed grant. SAW/NPDES Interface Under the SAW grant the asset analysis can involve grouping of asset types, i.e. 50 manholes. Under the NPDES asset management requirements DEQ will require a detailed asset analysis, i.e. manhole 1, manhole 2…. This will have to be done in 1 year for WWTP assets and 3 years for collection system assets. For Majors, those with discharges greater than 1 MGD, when the NPDES comes up for renewal the NPDES asset management requirements take effect. NPDES requirements will supersede the SAW asset management requirements. So for example if you get a grant in 2013 and your NPDES permit comes up for renewal in 2015, you can begin with a broad asset analysis in 2014 but in 2015 the NPDES permit requirement for a detailed analysis will come into effect. For Minors, it is understood that when their NPDES permit comes up for renewal, asset management will be a part of that permit, however the implementation schedule in the permit will follow that of SAW. If the applicant does not have a detailed asset analysis, the timeframe for completing that requirement will be negotiated with the Permits Section. Asset Inventory Table 1 Directions A. List assets B. Enter asset information C. To add more assets use insert function and add rows then copy first asset row to new rows to transfer formulas D. Enter information in highlighed cells E. Remaining cells will calculate automatically. A Source Assets B C D E F Material Location Manufacturer Original Cost Replacement Cost G H I J K L Remaining Useful Likeliness of Consequence Life in Years Condition Redundancy Failure of Failure Criticality Factor well #1 pump 0 Enter asset 0 0 5 5 25 0 Enter asset 0 0 Enter asset 0 0 Enter asset 0 0 Enter asset 0 0 Enter asset 0 0 If Criticality Factor is greater than 16 cell will turn RED If Criticality Factor is greater than 16 A Treatment Assets B C D E F Material Location Manufacturer Original Cost Replacement Cost G H I J add to CIP table K L Remaining Useful Likeliness of Consequence Life in Years Condition Redundancy Failure of Failure Criticality Factor chlorinator 0 Enter asset 0 4 5 20 Enter asset 0 Enter asset 0 2 3 6 Enter asset 0 4 4 16 Enter asset 0 5 5 25 Enter asset 0 0 0 0 If Criticality Factor is greater than 16 cell will turn RED If Criticality Factor is greater than 16 add to CIP table American Iron & Steel requirement For DWRF and SRF funded projects Beginning January 2014 State will have ongoing compliance reviews Onsite visit Review of compliance documentation Photographs Follow-up letter State Revolving Fund Changes State Revolving Fund - SRF Low interest loan funds to municipalities to plan, design, and build water pollution control projects Interest rates for loans are set below market rates each year Projects on publicly owned sites $4,372,430,000 in loans since 1988 in Michigan Architectural/Engineering Procurement - QBS Applicant issues a RFQ based on scope of work RFQ must be publicly advertised May choose to send RFQ to specific firms Statement of qualifications are evaluated Firms are ranked Discussions must be conducted with no fewer than three firms Cost can not be a factor when ranking firms Architectural/Engineering Procurement Applies to all A/E services for SRF projects executed after 10/1/2014 Project Planning Design Surveying Mapping Engineering Construction Management Project Management Feasibility Studies Must be used by all applicants regardless of longstanding relationships with specific A/E firms Not required if work is done in-house or not included in SRF loan QBS Certification Must attach the RFQ advertisement Must list all firms that responded If less than 3 firms must describe efforts taken to solicit Certification Form will be submitted with the Part III application. Form is still required if QBS does not apply Fiscal Sustainability Plans Applies to all projects that include repair, replacement, or expansion Does NOT apply to NPS or construction of new treatment works projects SRF projects with project plans submitted after Oct. 1, 2014 must comply Applicants must self-certify they are complying or are exempt Not required to be a stand-alone document, info can be located in various documents and/or databases. FSP Minimum Requirements Can be project based Inventory of critical assets Evaluation of the condition and performance of inventoried assets Financial plan for maintaining, repairing/replacing assets Certification that the recipient has evaluated and will be implementing water and energy conservation efforts as part of the plan Loan Terms and Rates 20 and 30 year loans Interest rates for loans may differ Dependent on Useful Life of project assets Only disadvantaged communities eligible for 30 year loan (similar to DWRF) Useful Life Determination is completed by the engineer and included in the project plan May use weighted average For projects involving a variety of components Equipment with varying useful life estimates Average must not be less than 20 yrs for typical loan, not less than 30 yrs for disadvantaged loan Stay in the Know Updated Guidance and Documents GovDelivery www.Michigan.gov/drinkingwaterrevolvingfund www.Michigan.gov/cleanwaterrevolvingfund Michigan Department of Environmental Quality Revolving Loan Section 517-284-5433 Bob Schneider 517-388-6466 schneiderR@michigan.gov Kelly Green 517-284-5409 greenk1@michigan.gov