Persuasion and Propaganda
advertisement

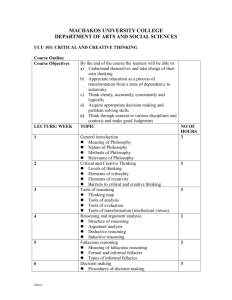
Fallacious Reasoning vs. Logical Reasoning (Persuasive vs. Argumentative Writing) Essential Question: Compare and contrast Fallacious Reasoning and Logical Reasoning. I. Fallacious Reasoning (persuasion) One kind of faulty reasoning is a fallacy, a breakdown of logic. A fallacious argument is one that tries to argue from A to B, but because it contains hidden assumptions or factual irrelevancies, reaches an invalid conclusion. a. Does not provide sufficiently good grounds for its conclusion b. Employs unwarranted, unaccepted, unproven or incorrect assertions c. Ignores or overlooks important information *Example of Fallacious Reasoning: – Persuasion: to convince the readers that the writer is right, often using the emotional appeal instead of intelligence! A. Propaganda (a.k.a. emotional appeals) When a writer or speaker wants to persuade you, he or she may use emotional appeals which are statements directed at your feelings instead of facts. 2. Propaganda is any form of communication aimed at persuading an audience, often containing false or misleading information to present a point of view to persuade the reader (or audience). 1. A. 5 Common Types of Propaganda Used to Persuade 1. Loaded Language- Language that stirs up either very positive or negative feelings in people. EX: Positive Language: The state legislature should pass the Bear Protection Act because bears are noble, brave animals. EX: Negative Language: The state legislature should not pass the Bear Protection Act because bears are savage, vicious animals. 2. Name-calling- Attacks a person’s personality instead of focusing on his or her ideas. EX: Don’t fall for my fast-talking opponent’s plan. He wouldn’t recognize a good idea if he fell over one! 3. Bandwagon- Statements appeal to a person’s desires to be like everyone else. EX: Everyone wants to ride the Corkscrew Coaster of Doom! 4. Snob Appeal- Targets people who want to stand out from the crowd. EX: This jacket will make your friends drool with envy! 5. Testimonial- tells you to do something because other people are doing it. EX: Using a celebrity to sell a product (proactive with Jessica Simpson) II. Logical Reasoning (Argumentative) a. Provide a conclusion based on facts Example 1: When it rains, the grass gets wet. Example 2: It rains. Thus, the grass is wet. b. Must contain ALL of the relevant information and not just a portion of the relevant information c. Must include the counterargument d. Is not bias e. uses “logos”-facts and evidence to support claim (opinion) f. uses “ethos”- appeals to writer’s or speaker’s credibility Fallacious vs. Logical Fallacious Reasoning Logical Reasoning Advertisement/Media TV or magazine ads, movies, bulletin boards, military, ads/commercials Academic Writing *Propaganda *emotional appeal *unsupported inferences *misleading!! *Supported claims with evidence!! *Credibility/trustworthy of source and writer What is the difference between argument and persuasion? Persuasive Essay Argumentative Essay *May make claims based on opinion *May not take opposing ideas into account. *Persuades by appealing to the audience’s emotion or by relying on the character or credentials of the writerless on the qualities of his or her reasons and evidence. *Emotion-based. *Makes claims based on factual evidence. *Makes counter-claims *The author takes opposing views into account *Neutralizes or defeats serious opposing ideas. *Convinces audience through the qualities and reasonableness of the claims and proofs offered. *Often compares texts or ideas to establish a position *Logic based. Although emotional appeals work well in ads, try to avoid using propaganda when trying to convince readers to agree with your viewpoint. The more facts the better. Are you ready to practice Argumentative Writing? Let’s pick a stance on various topics Work with opponent to ensure we include the counterargument. Write Present!