Freud and
Psychoanalytical
Theory
Sigmund Freud (1856-1939)
• Austrian Psychologist
• Founded the clinical practice of psychoanalysis
to treat psychopathology in patients through
dialogue
• Investigated the interaction of conscious and
unconscious elements in the mind
– Repressed fears and conflicts are brought into the
conscious and faced openly, instead of remaining
buried in the unconscious
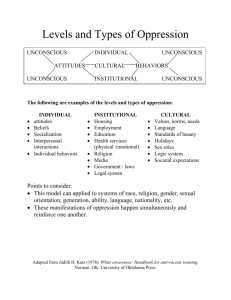
• The
Unconscious is
a dimension of
the human
mind that is
only partially
accessible to
consciousness
• Repository of
repressed
desires,
memories, and
instinctual
drives
– Many have to
do with
sexuality and
violence
Dreams
• The unconscious often
expresses itself in dreams
• Express wishes or desires that
cannot be expressed
consciously because they go
against society
• Dreams distort the
unconscious material and
makes it more acceptable
towards the conscious
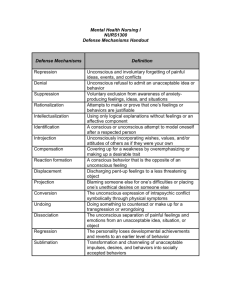
Defense
Mechanisms
• psychic procedures for
avoiding painful
admissions or
recognitions
• Screen Memory –
inconsequential memory
whose function is to
obliterate a more
significant one
• Freudian Slip – repressed
material in the
unconscious finds an
outlet through slips of
the tongue, slips of the
pen, or unintended
actions
Repression and Sublimation
• Repression
– Forgetting or ignoring of unresolved
conflicts, unadmitted desires, or
traumatic past events
– Forced out of the conscious into the
unconscious
• Sublimation
– Repressed material is promoted into
something grander or is disguised as
something noble (religious
experiences, art, etc…)
Displacement and
Condensation
• Displacement
– One person or event is
represented by another, which
is in some way linked to or
associated with it
– Because of similar sounding
word or symbolic substitution
• Condensation
– A number of people, events,
or meanings are combined
and represented by a single
image in the dream
Displacement and
Condensation II
• They disguise the repressed fears and wishes
contained in the dream
• Gets past the censor that prevents wishes and fears
from surfacing into the conscious mind
• They fashion fears and dreams into images,
symbols, and metaphors
Transference and
Projection
• Transference
– The patient under
psychoanalysis redirects
the emotions recalled
towards the
psychoanalyst
• Projection
– When aspects of
ourselves are not
recognized as part of
ourselves
– Rather they or perceived
in or attributed to
another
3 Part Model
of the Psyche
• Ego – has to manage
the demands of the
superego, while
resisting the desires
of the id
• Id – inappropriate
desires and impulses
• Superego – the
conscience or what
society deems
acceptable
Sexuality
Begins at infancy, not puberty
3 stages
Oral
Anal
Phallic
Libido – energy drive associated with sexual desire
Eros – life instinct
Thanatos – death instinct
Oedipus Complex
• Male infant desires to
eliminate the father and
become the sexual partner of
the mother
• Only the father’s intervention
prevents incest
• Male infant gives up sexual
attraction to mother and
identifies with father
• Learns to desire other women
other than the mother
Homosexuality
and Women
• Freudian theory based
upon heterosexual
men
• Negative views of
women
– Sexuality based on
feelings of narcissism,
masochism, and
passivity
– Penis envy: women
suffer from an innate
form of inferiority
complex
Psychoanalytic Criticism
• The unconscious (like a poem, novel, or play)
cannot speak directly and explicitly
• Speaks through images, symbols, and
metaphors
• Literature expresses experience through
imagery, symbolism, and metaphor
Psychoanalytic Critics
Give central importance to the distinction
between the conscious and unconscious mind
Pay close attention to unconscious motives and
feelings
Those of the author
Those of the characters
Demonstrate the presence of psychoanalytic
symptoms, conditions, or phrases
Oral, anal, phallic stages
Oedipus Complex
Defense Mechanisms