File
advertisement

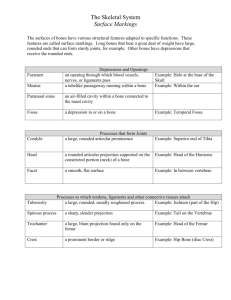
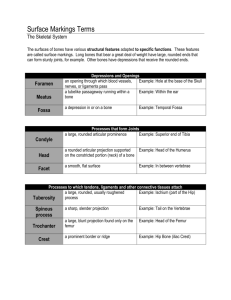
The Skeletal System – Chapter 5 Parts of the skeletal system Divided into two divisions – Axial skeleton – Appendicular skeleton Functions of Bones Hematopoiesis Bones of the Human Body Osseous tissue Two types of bone tissue: Figure 5.2b Classification of Bones 1. Long bones Examples: Classification of Bones 2. Short bones Examples: Classification of Bones 3. Flat bones Examples: Classification of Bones 4. Irregular bones Example: Classification of Bones on the Basis of Shape Figure 5.1 Gross Anatomy of a Long Bone Diaphysis Epiphysis Figure 5.2a Structures of a Long Bone Periosteum – Sharpey’s fibers Arteries Figure 5.2c Structures of a Long Bone Articular cartilage (Articular – relates to the joints) Figure 5.2a Epiphyseal Plate Structures of a Long Bone Medullary cavity – Infants – – Adults – Figure 5.2a Quick Write Draw and label bone: – Diaphysis – Epiphysis – Periosteum (what do I do??) – Sharpey’s fibers (what do I do??) – Articular Cartilage (what do I do??) LET’S DO THE CHICKEN DANCE!!!!!! Microscopic Anatomy of Bone Osteon (Haversian System) Central (Haversian) canal Volkmann’s (perforating) canal Microscopic Anatomy of Bone Lacuna – Canaliculi – Lamella – Detail of Figure 5.3 Quick Write How do osteocytes receive nutrients? Changes in the Human Skeleton Ossification Cartilage remains in isolated areas (hyaline, fibro, elastic, articular) Types of Bone Cells Osteocytes Osteoblasts Osteoclasts remake entire skeleton about every 10 years – 10%/year Bone Growth Epiphyseal plates allow for growth of long bone during childhood Stages of Bone Growth 1. 2. Bone Remodeling Dependent on: Bone Fractures –Closed (simple) fracture – –Open (compound) fracture – Treatment: Common Types of Fractures – (p. 137) Table 5.2 surgery Broken bone kickboxing medical wr Repair of Bone Fractures (diagram) STOP Bone Markings • Bulges, depressions, and holes that serve as: –Sites of attachment for muscles, ligaments, and tendons –Joint surfaces –Conduits for blood vessels and nerves Bone Markings (see table pg 134) Categories of bone markings –A. Projections and processes – grow out from the bone surface “T” –B. Depressions or cavities – indentations “F” Bone Markings: Projections – Sites of Muscle and Ligament Attachment • Tuberosity – rounded projection • Crest – narrow, prominent ridge of bone • Trochanter – large, blunt, irregular surface • Tubercle – small rounded projection • Epicondyle – raised area above a condyle • Spine – sharp, slender projection • Process – any bony prominence Bone Markings: Projections – Projections That Help to Form Joints • Head – bony expansion carried on a narrow neck • Facet – smooth, nearly flat articular surface • Condyle – rounded articular projection • Ramus – armlike bar of bone Bone Markings: Depressions and Openings • Meatus – canal-like passageway • Sinus – cavity within a bone • Fossa – shallow, basin-like depression • Foramen – round or oval opening through a bone