Linear Equations Vocabulary: Key Terms & Definitions
advertisement

Linear Equations Vocabulary
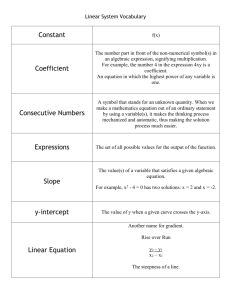
Constant
f(x)
Coefficient
The number part in front of the non-numerical symbol(s) in
an algebraic expression, signifying multiplication.
For example, the number 4 in the expression 4xy is a
coefficient.
An equation in which the highest power of any variable is
one.
Consecutive Numbers
A symbol that stands for an unknown quantity. When we
make a mathematics equation out of an ordinary statement
by using a variable(s), it makes the thinking process
mechanized and automatic, thus making the solution
process much easier.
Expressions
The set of all possible values for the output of the function.
Slope
y-intercept
The value(s) of a variable that satisfies a given algebraic
equation.
For example, x2 - 4 = 0 has two solutions: x = 2 and x = -2.
The value of y when a given curve crosses the y-axis.
Another name for gradient.
Rise over Run
Linear Equation
y2 – y1
x2 – x1
The steepness of a line.
Following on from each other in order.
Variable
For example, 1, 2, 3, and 4 are consecutive numbers. 5, 7, 9,
and 11 are consecutive odd numbers.
The measure of the steepness of a line that shows the slants
upward from left to right.
Solutions
For example, y = x + 2 has a slope of 1.
Increasing Intervals
Coordinate Plane
A plane formed by two intersecting and perpendicular
number lines used to help locate the position of any point
on a map or graph.
Domain
An algebraic expression is made up of three things:
numbers, variables, and operation signs such as + and -.
Following is a list of some examples:
2a
a+b
a2
ab
Range
The set of all possible input values for a function or
relation.
Function
A quantity that does not change its value. In the equation y
= 4x+1, the numbers 4 and 1 are constants.
Function Notation
The general form of a linear equation is y = mx + b, which
is a straight line on a Cartesian coordinate graph. The
parameter m is the slope of the line, and b is the y-intercept.
Positive Slope
A function of the type y = f(x) = ax + b because its graph is
a straight line.
Negative Slope
A relationship between two variables that shows one
variable decreases as the other one increases.
x-axis
A relationship between two variables that shows both
variables increase or decrease together.
y-axis
Origin
x-intercept
The value of x when a given curve crosses the x-axis.
A relation between two variables that vary together. If one
variable always increases as the other increases, the
relationship is said to be positive or direct. Otherwise, the
relationship is negative or inverse.
Data that is plotted as points on a graph to show a possible
relationship between two sets of data.
An arithmetic sequence is a sequence in which the
difference between each term and the one after it is
constant. For example, {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, ... }. This constant
difference between successive terms is called the common
difference.
Arithmetic Sequence
Each term after the first can be found by adding (or
subtracting) the common difference. The general formula
for the nth term in an arithmetic sequence is:
an = a1 + (n-1)d
in which an is the nth term, a1 is the first term, and d is the
common difference.
Geometric Sequence
Parallel Lines
Two or more straight coplanar lines that do not intersect.
Same Slopes and different y – intercepts.
The point where the reference axes in a coordinate system
meet. The values of coordinates are normally defined as
zero.
Perpendicular
Two lines that intersect at right angles.
Opposite Slopes.
A sequence in which each term (after the first one) bears a
fixed ratio to its previous term.
For example, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16...
Scatter Plot
Correlation
Line of Best Fit
Positive Correlation
Negative Correlation
The general formula for the nth term of a geometric
sequence an is a1rn-1 in which a1 is the first term and r is the
fixed ratio.
Usually the vertical axis in a Cartesian coordinate system.
Intuitively, a straight line drawn through as near as possible
to the various points on a scatter diagram so as to best
represent the trend.
Usually the horizontal axis in a Cartesian coordinate
system.
Denoting the situation in which no apparent pattern can be
formed when plotting data points for two variables in a
scatter diagram. It shows that there is no relationship
between the two variables.
The measure of the steepness of a line that shows the line
slants downward from left to right.
No Correlation
For example, y = -x + 2 has a slope of -1.
Decreasing Intervals
http://www.mathematicsdictionary.com/math-vocabulary.htm