File - Social Sciences @ Groby
advertisement

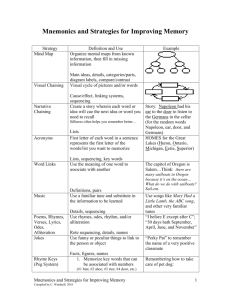
Memory Improving Memory Starter • Think of as many reasons as possible as to why psychologists might be interested in techniques that improve memory… …there’s a prize for whoever gets the most! Learning Objective • To understand a range of memory improvement strategies. Success Criteria 1. Make notes on verbal mnemonics, visual imagery mnemonics and method of loci on page 27 of your booklet. Challenge Criteria Think about the strengths and weaknesses of these strategies. 2. Have a go at using the memory improvement strategies. 3. Evaluate memory improvement strategies on page 28 of your booklet. Remember this… TVCIAOMNILTMSTMNASA Recall the letters Is this easier? TV CIA OMNI LTM STM NASA • Which method does this use? Mnemonics • Verbal Mnemonics – Acronyms • How do you remember the colours of the rainbow? • ROYGBIV or Roy G. Biv • Give me another example of an acronym – Acrostics • How do you remember the order of the planets? • My Very Easy Method Just Speeds Up Naming Planets • Give me another example of an acrostic Mnemonics • Verbal Mnemonics – Rhymes • How do you remember the letters of the alphabet? • A little song… • “Twinkle, twinkle little star…” – Chunking • How do you remember your phone number? • 0116 287 _ _ _ _ • What else do you chunk? 30 seconds to memorise as many objects as you can! Write down as many objects as you can in one minute.... 30 seconds to memorise as many objects as you can! Write down as many objects as you can in one minute.... There’s an object missing from the previous slide...what is it??? What method did that experiment use? Organisation of material into categories Tulving and Pearlstone (1966) Mnemonics • Visual Imagery Mnemonics – The Method of Loci – This method helps you remember things by travelling through a familiar location. – Remember this??? Mnemonics • Visual Imagery Mnemonics – The Method of Loci – This method helps you remember things by travelling through a familiar location. – In each room there is an item and this item is linked to a piece of information – The more memorable (smelly, funny, weird) the link, the more likely you are to remember, and recall the information. Activity • Use the method of loci technique to remember the multi-store model… – Where are you travelling (your house, on your way to school etc.) – What items do you have to retrieve? • This will really help with your revision. Peg Words • I am going shopping and need to buy the following items: 1. Fish 2. Carrots 3. Rice 4. Sausages 5. Oranges 6. Rice Krispies 7. Bread 8. Milk 9. Yogurt 10. Dog food Peg Word One Two Three Four Five Six Seven Eight Nine Ten Bun Shoe Tree Door Hive Sticks Heaven Gate Line Hen Fish Carrots Rice Sausages Oranges Rice Krispies Bread Milk Yogurt Dog Food Can you remember your shopping? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Fish Carrots Rice Sausages Oranges Rice Krispies Bread Milk Yogurt Dog food The Narrative Chain • This links words in a list together into a sentence or a story. This disorganised information is put into a meaningful context to be coded semantically. • By using the words and associating them with each other you create a firmer connection between the new words and those already stored in your memory. • This song is an example of a narrative chain: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e54m6X OpRgU The use of narrative chaining • Bower and Clark (1969) asked participants in their study to learn 12 lists of disconnected words each containing 12 words. The narrative group recalled 94% (135.4 on average) of the words and the control group recalled just 14% (20.2 words on average) of the words. Therefore the method was better than any other memorizing method used. • Create your own narrative chain on page 27. Evaluation Tasks 1. Fill in the blanks on page 28 2. Make notes on the role of organisation and elaborative rehearsal on page 28 Evaluation • Gruneberg (1973) found 30% of psychology students use mnemonics to revise for final exams. • Glidden et al (1983) found verbal mnemonics were effective with children with learning disabilities. • Most research has been conducted in labs. Studies in real-life settings (e.g. classrooms) show mixed results, for example, mnemonics are useful for teaching foreign language vocabulary, but may not be so effective at actually speaking in a foreign language. • Mnemonics work through rehearsal and organisation. • Organisation is also important, this helps the brain find the information more quickly. • Elaborative rehearsal is the process of giving something a meaning, and strategies such as mind maps work well for this. Assessment for Learning Alice is visiting the doctor. She needs to remember all of the information that the doctor tells her. Outline TWO methods of memory improvement that might help Alice, and explain why they should improve recall. [4 Marks] Practice Exam Question • Psychology students sometimes revise for an exam by reading their notes over and over again. However, psychologists suggest that other memory improvement strategies may be more effective. Explain how a student could use their knowledge of strategies for memory improvement (other than repetition) to help revise for a psychology exam. (4 marks) Mark Scheme