neutron stars new window to understand nuclear interactions
advertisement

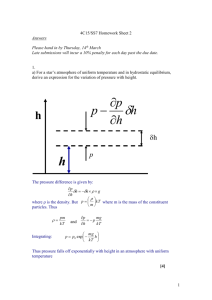
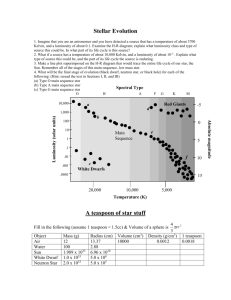
M. Bhuyan Institute of Theoretical Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences Beijing-100190, China P.R CUSTIPEN-2015 Introduction Theoretical Formalisms Relativistic mean field theory Effective field theory motivated RMFT Results and Discussions Normal Nuclear Matter Neutron Star Matter Static Neutron Star (SNS) Rotating Neutron Star (RNS) Gravitational wave strain amplitude Summary According to Einstein's theory of gravity, an accelerating mass causes the fabric of space-time to ripple like a pond disturbed by a rock. These ripples are Gravity Waves. http://focus.aps.org/story/v8 This picture represents Gravity Waves produced by a pair of rotating neutron stars. Neutron stars radiate gravitationally in a number of ways. The most promising scenarios involve: Inspiralling Binaries: Post Newtonian approximation Supernova core collapse: Violent dynamics Rotating compact stars: Shape asymmetry Oscilation and Instability: Superfluid core There are also many other sources for the gravitational wave radiations. …. The oscillation in the X and Y directions and the wave moves in the Z direction. Gravity waves have two polarizations like electromagnetic Waves. The only difference is that Gravity Wave polarization lies in a horizontal-vertical “+” shape and 45 degrees to that in a “x” shape. a. The three US detectors, LIGO, have ofcially reached their initial design sensitivity. b. The Anglo-German detector GEO600 is at design sensitivity at frequencies above 200 Hz. c. The 6th science run, taking coincident data, began in November, and will last about 18 months. d. The Italian-French VIRGO is carrying out engineering runs, but is getting close to science mode. People are beginning to get jumpy... To estimate the gravitational wave strain amplitude , it is necessary to deal the neutron star fundamental correctly. a. The structure and dynamics of a neutron star is governed by the equation of state EoS of the dense nuclear matter. b. It is necessary to include other fundamental particles as a function of density in prediction of nuclear EoS of the neutron star or compact star. c. The fundamental properties such as Mass, Radius, rotational frequency and elipticity etc. of the rotating neutron star (RNS). How to deal all these above properties??? To deal all above these properties, we need a standard theoretical approach, which can explain the nuclear EoS correctly. Mass: 1.97 ± 0.4 M0 MAX υ: 716 Hz Radius: 10-15 Km The structure and dynamics of a neutron star is governed by the equation of state EoS of the dense nuclear matter TYPICAL DENSITY: (3 – 10) TIMES NORMAL NUCLEAR DENSITY. >> CONSTRAINTS !!! J. Antoniadis et al., Science 340, 6131 (2013). Here we have introduced the effective field theory relativistic mean field model (E-RMF) for the present analysis. The form of the Lagrangian density expressed as: Forces NL3 Linear σ, ω, ρ σ, ω, ρ NonLinear Cross coupling σ G2+Λ σ, ω σ-ω, σ-ρ, ω-ρ NL3 S. K. Singh, M. Bhuyan, P. Panda & S. K. Patra, J. Phys. G, 40, 085104 (2013) M. Bhuyan, R. N. Panda, T. R. Routray & S. K. Patra, Phys. Rev. C 82, 064602 (2010) The obtained results for the energy density as a function of baryon for symmetric nuclear matter. S. K. Singh, M. Bhuyan, P. Panda & S. K. Patra, J. Phys. G, 40, 085104 (2013) M. Bhuyan, R. N. Panda, T. R. Routray & S. K. Patra, Phys. Rev. C 82, 064602 (2010) The obtained results for the pressure density as a function of baryon for symmetric nuclear matter. S. K. Singh, M. Bhuyan, P. Panda & S. K. Patra, J. Phys. G, 40, 085104 (2013) To see the variation of pressure and energy density with respect to density with different constituents. Nucleaonic Matter Feed to TOV & RNS EQUATIONS NUCLEONS/ HYPERONS/ QUARKS ε/P ρ Schematic diagram for EoS M. Bhuyan & Shan-Gui Zhou, to be appeared in PRC Here, we have shown the particle fraction or the Yield product as a function of baryon density. Here, we have considered all baryon octet family (n, p, Λ, Σ-, Σ0, Σ+, Ξ- & Ξ0). M. Bhuyan, S. K. Patra & Shan-Gui Zhou, to be appeared in PRC To estimate the gravitational wave strain amplitude , it is necessary to deal the neutron star fundamental correctly. Is attained when the OUTWARD neutron degeneracy pressure equal to the INWARD gravitational potential The rotation stabilizes the system as GRAVITATIONAL PULL is counteracted by the PRESSURE + CENTRIFUGAL FORCE G P The neutron star mass and radius from E-RMFT for various force parameters M. Bhuyan et al., arxiv: 1312.5840, to be appeared in PRC The realistic approximation that when neutron star is rotating with static, axial symmetric, space-time, the time translational invariant and axial-rotational invariant metric in spherical polar coordinate, For a perfect fluid, the energy momentum tensor can be given by with the four-velocity The final expression for the maximum rotation i.e. the Kepler frequency in the relativistic approximation is as, N. K. Glendenning et al., Phys. Rev. D 50, 3836 (1994); M. Bhuyan et al., arxiv: 1312.5840 The comparison of static and rotating neutron star properties from E-RMF Model for various forces. M. Bhuyan et al., arxiv: 1312.5840, to be appear in PRC The quadrupole moment of a rotating neutron star depends on the maximum mass M and radius R with a simple relation, here σmax is called breaking strain of the crust. The ellipticity of the rotating neutron star is connected to the quadrupole moment by a simple relation The moment of inertia along the z-axis and for conventional rotating neutron star is given as M. Bhuyan et al., arxiv: 1312.5840, to be appear in PRC The maximum rotational frequency of the stable rotationary neutron star can be given by the simple relation Finally, using these above calculated quantities, we can estimate the gravitational wave strain amplitude, a. Neutron stars are the natural laboratories to understand cold dense matter interaction and their compositions. b. Hyperons constitutes a sizable population in dense matter, where the –ve charged particles are more favored over natural & +ve charged particles. c. The estimation of gravitational wave strain amplitude from rotating neutron / compact star is one step ahead in the nuclear matter study. d. Neutron stars are a promising candidate for gravitational wave generation We are involved in a variety of efforts to detect them and can give insight into other fields of physics. Shan-Gui Zhou, ITP-CAS, Beijing, China S. K. Patra, Institute of Physics, India S. K. Singh, Institute of Physics, India X. Vi˜nas, University of Barcelona, Spain Raj K. Gupta, Punjab University, India P. Arumugam, Indian Institute of Technology, India Thanks for your kind attentions and welcome for discussions CUSTIPEN-2015