How does HR Planning occur?
advertisement

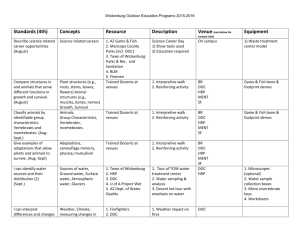
TATAP MUKA MINGGU KE VI Presented By Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO HR Planning • What is HR Planning? Why is it rarely done? What is the connection between a firm’s strategic orientation and HR planning? Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO Organizational Life-Cycle Stages and HR Activities LIFECYCLE STAGE STAFFING COMPENSATION TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT LABOR / EMPLOYEE RELATIONS Introduction Attract best technical and professional talent. Meet or exceed labor market rates to attract needed talent. Define future skill requirements and begin establishing career ladders. Set basic employeerelations philosophy of organization. Growth Recruit adequate numbers and mix of qualifies workers. Plan management succession. Mange rapid internal labor market movements Meet external market but consider internal equity effects. Establish formal compensation structures. Mold effective management team through management development and organizational development. Maintain labor peace, employee motivation, and morale. Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO Organizational Life-Cycle Stages and HR Activities (cont’d) LIFE-CYCLE STAGE STAFFING COMPENSATION TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT LABOR / EMPLOYEE RELATIONS Maturity Encourage sufficient Control turnover to minimize compensation layoffs and provide costs. new openings. Encourage mobility as reorganizations shift jobs around. Maintain flexibility and skills of an aging workforce. Control labor costs and maintain labor peace. Improve productivity. Decline Plan and implement workforce reductions and reallocations, downsizing and outplacement may occur during this stage. Implement retraining and career consulting services. Improve productivity and achieve flexibility in work rules. Negotiate job security and employmentadjustment policies Implement tighter cost control. Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO How does HR Planning occur? 1. What does the environment look like? 2. What are our future personnel needs? (forecast demand) a. Judgmental Estimates Rule of Thumb Delphi Technique NGT Brainstorming Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO The Nominal Group Technique A small group of 4-5 people gathers around a table. Leader identifies judgment issue and gives participants procedural instructions. Participants write down all ideas that occur to them, keeping their lists private at this point. Creativity is encouraged during this phase. Leader asks each participant to present ideas and writes them on a blackboard or flipchart, continuing until all ideas have been recorded. Participants discuss each other’s ideas, clarifying, expanding, and evaluating them as a group. Participants rank ideas privately in their own personal order and preference. The idea that ranks highest among the participants is adopted as the group’s judgment. The Delphi Technique Leader identifies judgment issues and develops questionnaire. Prospective participants are identified and asked to cooperate. Leaders send questionnaire to willing participants, who record their judgments and recommendations and return the questionnaire. Leaders compiles summaries and reproduces participants’ responses. Leader sends the compiled list of judgment to all participants. Participants comment on each other’s ideas and propose a final judgment. Leader looks for Consensus Leader accepts consensus judgment as group’s choice. How does HR Planning occur? 1. What 2. does the environment look like? What are our future personnel needs? a. forecast demand b. Statistical (regresion) Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO Statistical Techniques Used to Project Staffing Demand Needs Name Description Regression analysis Past levels of various work load indicators, such as sales, production levels, and value added, are examined for statistical relationships with staffing levels. Where sufficiently strong relationships are found, a regression (or multiple regression) model is derived. Forecasted levels of the retained indicator(s) are entered into the resulting model and used to calculate the associated level of human resource requirements. Productivity ratios Historical data are used to examine past levels of a productivity index (P): P = Work load / Number of People Where constant, or systematic, relationships are found, human resource requirements can be computed by diving predicted work loads by P. Statistical Techniques Used to Project Staffing Demand Needs (cont’d) Name Description Personnel ratios Past personnel data are examined to determine historical relationships among the employees in various jobs or job categories. Regression analysis or productivity ratios are then used to project either total or key-group human resource requirements, and personnel ratios are used to allocated total requirements to various job categories or to estimate for non-key groups. Time series analysis Past staffing levels (instead of work load indicators) are used to project future human resource requirements. Past staffing levels are examined to isolate and cyclical variation, long-tem terms, and random movement. Longterm trends are then extrapolated or projected using a moving average, exponential smoothing, or regression technique. Regression Analysis 1. Statically identify historical predictor of workforce size Example: FTEs = a + b1 sales + b2 new customers 2. Only use equations with predictors found to be statistically significant 3. Predict future HR requirements, using equation Example: (a) FTEs = 7 + .0004 sales + .02 new customers (b) Projected sales = $1,000,000 Projected new customers = 300 (c) HR requirements = 7 + 400 + 6 = 413 Determining the Relationship Between Hospital Size and Number of Nurses How does HR Planning occur? 2. What are our future personnel needs? (demand forecast cont.) b. Statistical (cont.) Ratio analysis Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO TATAP MUKA MINGGU KE VIII Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO How does HR Planning occur? 3. Are resources available – internally or externally – to fill those needs? a. Internal Replacement charts Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO Employee Replacement Chart for Succession Planning How does HR Planning occur? 3. Are resources available – internally or externally – to fill those needs? a. Internal Replacement charts Promotability Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO Presented By Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO How does HR Planning occur? 3. Are resources available – internally or externally – to fill those needs? a. Internal Replacement charts Promotability Succession planning Skills inventory Transition (Markov) matrix Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO A Sample Transition Matrix Part A: Personnel Supply Estimated Personnel Classification in Year T + 1 (%) Classifications in Year T P Partner Manager Supervisor Senior Accountant .70 .10 M .80 .12 S .60 .20 Sr .55 .15 A Exit .65 .30 .10 .28 .25 .20 Part B. Staffing Levels Estimated Personnel Availabilities in Year T + 1 (%) Classifications in Year T Partner Manager Supervisor Senior Accountant Beginning Levels P 10 7 30 3 50 100 200 10 M 24 6 30 S 30 20 50 Sr A 55 30 85 130 130 Exit 3 3 14 25 40 How does HR Planning occur? 3. Are resources available – internally or externally – to fill those needs? b. External – what do you look at? - Try to determine availability of qualified labor; Surplus? Shortage? Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO How does HR Planning occur? 4. What should we do? Create plan of action to reconcile supply and demand a. Set objectives b. Generate alternatives Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO Staffing Alternatives to Deal with Employee Surpluses Source: Compliments of Dan Ward, GTE Corporation Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO Staffing Alternatives to Deal with Employee Shortages Source: Compliments of Dan Ward, GTE Corporation Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO How does HR Planning occur? 4. What should we do? create plan of action to reconcile supply and demand a. Set objectives b. Generate alternatives c. Assess alternatives Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO Alternative Scheduling Options Alternative Percent Using (N = 427 companies) The following definitions were used in this survey for alternative scheduling strategies: • Part-time: A regular employee who works fewer than 35 hours per week. 84% • Flextime: A system than enables employees to vary their schedules: Usually, the flexibility applies to starting and finishing times. 40% • Compressed workweek: A full-week schedule (usually 40 hours) than occurs in fewer than five days, such as four 10-hour days. 23% • Job sharing: Two or more employees split a full-time position, diving the responsibilities, and, to some degree, the compensation. 18% • Work-at-home: A program that enables employees to complete work at home (or at a remote office closer to home) on a regular basis. It is often referred to as “flexplace” or “telecommuting.” 13% How does HR Planning occur? 4. What should we do? create plan of action to reconcile supply and demand a. Set objectives b. Generate alternatives c. Assess alternatives d. Choose alternative – KEEP PHILOSOPHY IN MIND Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO How does HR Planning occur? 5. How did we do? a. Did company avoid surplus/shortage? b. Evaluate usefulness of methods used c. Goals v. Production Levels, etc. Presented By HRP/HERMIEN.DOC Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO