Knee (Tibiofemoral) Joint
advertisement

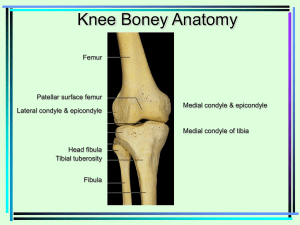
Knee (Tibiofemoral) Joint Bones of the Knee Joint •Femur -Longest and strongest bone in the body • Lateral and medial epicondyles -The widest points of the femur at the knee -Round prominences above lateral and medial condyles -Will be attachments for thigh and leg muscles and knee ligaments • Medial and Lateral Condyles -distal end of the femur -smooth round surfaces inferior to medial and lateral epicondyles • Intercondylar Fossa -Groove separating the medial and lateral condyles Bones of the Knee Joint Bones of the Knee Joint •Tibia -Larger bone of the lower leg -Only weight bearing bone of crural region -If tibial fracture occurs, what may a patient not be able to do? • Medial and Lateral Condyles -Articulate with medial and lateral condyles of the femur -Insertion points for leg muscles • Intercondylar Eminence -ridge separating medial and lateral condyles of tibia Bones of the Knee Joint • Tibial Tuberosity -can be palpated just below the patella -An attachment for the powerful leg muscles that extend the knee *****Important for muscle insertions (Quads) Bones of the Knee Joint •Fibula -Slender lateral bone of lower leg -Stabilizes the ankle, but does not bear any of the bodies weight • Head -Proximal end of fibula -This Portion is thicker and broader than the distal end • Patella -roughly triangular sesamoid bone embedded in the tendon of the knee Knee Ligaments • Fibular or lateral collateral ligament • Extends from the lateral epicondyle of femur to the lateral surface of the head of fibula • Tibial or medial collateral ligament • Extends from medial epicondyle of femur to medial condyle and superior, medial part of tibia • Oblique popliteal ligament • Expansion of tendon of semimembranosus • Strengthens joint capsule posteriorly • Arcuate popliteal ligament • Arises from posterior aspect of the fibular head • Passes over the popliteus tendon and covers posterior surface of knee joint Knee Ligaments and cartilage • Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) • Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) • ACL is the weaker of the two • Cross like an X • Medial Meniscus • Adheres to tibial collateral ligament • Lateral Meniscus • Popliteus tendon separates it from the Lateral collateral ligament • Transverse Ligament • Attaches the lateral portion of the menisci Patellar Ligament and Quadriceps Femoris Tendon • Patellar ligament is an extension of the quadriceps femoris tendon Knee Bursae • Prepatellar bursa • Suprapatellar bursa • Deep infrapatellar bursa • Subcutaneous infrapatellar bursa Clinical Concerns • Torn ACL • Can be partial or complete • Common sports injury for soccer, basketball and football players • Can result from changing direction rapidly, stopping quickly, direct contact, and landing a jump incorrectly • Disrupts stability of knee, requires surgery ACL Reconstruction The muscles of the patellar joint: • Rectus Femoris: • • • • • Origin: Anterior inferior iliac spine Insertion: Tibial tuberosity Action: Hip flexion, knee extension Nerve: Femoral nerve Roots: L2-L4 Vascular supply for the Rectus femoris: • Lateral circumflex femoral artery Nerve innervation Rectus femoris: • Femoral nerve • L2-L4 Vastus intermedialis, lateralis, and medialis: • Origin: anterior femur( VI) and Linea aspera (VL And VM) • Insertion: Tibial tuberosity via patellar tendon • Action: Knee extension • Nerve: Femoral nerve • Roots: L2-L4 • Vascular supply: Lateral circumflex Biceps femoris • Origin: • Long head: Ischial tuberosity • Short head: Lateral lip of linea aspera • Insertion: Fibular head • Action: • Long head: Extends hip and flex knee • Short head: Flex knee Vascular Supply: • Inferior gluteal artery Nerve Innervation • Long head: Tibial division of sciatic nerve • Short head: Common peroneal nerve • Roots: L5, S1, and S2 Semimembranosus: • Origin: Ischial tuberosity • Insertion: Posterior surface of medial condyle of tibia • Action: Extend hip and flex knee • Nerve: Sciatic nerve • Roots: L5, S1, and S2 • Vascular supply: Inferior gluteal artery Popliteus: • Origin: Lateral condyle of femur • Insertion: Posteriorly on medial condyle of tibia • Action: Initiates knee flexion • Nerve: tibial nerve • Roots: L4-5, S1 Vascular supply to popliteus: • Popliteal artery • Popliteal vein Semitendinosus: • Origin: Ischial tuberosity • Insertion: Anteromedial surface of proximal tibia • Action: Extend hip and flex knee • Nerve: Sciatic nerve • Roots: L5, S1, and S2 Vascular supply to semitendinosus: • Deep femoral artery Gastrocnemius: • Origin: Medial and lateral condyles of femur • Insertion: Posterior calcaneus • Action: Knee flexion, ankle plantar flexion • Nerve: Tibial nerve • Roots: S1-2 • Vascular supple: popliteal artery Other nerves to know: • Deep fibular • Superficial fibular Other arteries we need to know: Other veins to know: Surface Anatomy: Posterior • Popliteal fossa • Medial and lateral head of gastrocnemius • Semitendinous tendon • Semimembranosus Tendon • Soleus • Biceps fermoris tendon Surface Anatomy: Anterior • Patella • Vastus medialis • Vastus lateralis