RIAS - Psychological Assessment Resources, Inc.
advertisement

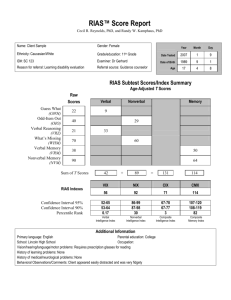
Reynolds Intellectual Assessment Scales (RIAS ) TM TM Cecil Reynolds, PhD Randy Kamphaus, PhD Acknowledgments Coauthor Cecil Reynolds PAR president Bob Smith and staff Travis White, Christine Maguire, Paul Jurica, Mario Rodriguez, Jim Gyurke, and Judy Zimmerman Students Nancy Hatcher, Cheryl Hendry, and Ellen Rowe Mentors John Nolan, Alan Kaufman, Pete Prunkl, George Ratajak, and Dennis Campbell Researchers Carl Huberty, Roy Martin, George Hynd, and Paul Frick Summary of Eight Primary Goals for Development of the RIAS Verbal, Nonverbal, and Memory Components Structure and Components of the RIAS Indexes 1. Guess What (GWH) Requires verbal reasoning, vocabulary, language development, and verbal knowledge base Directions: “Listen carefully while I read you a question. When I finish, tell me your answer.” 1. Guess What (GWH) What is made of wood, filled with lead, and used for writing? Pencil What has drawings of places on it, is color coded, and is used to study geography? Map What makes use of a cathode ray tube, has an antenna, and outputs both audio and video? Television set 2. Odd-Item Out (OIO) Measures nonverbal reasoning skills, requiring the examinee to use spatial ability and visualization Directions: “Look at this picture. Point to the one that doesn’t belong, the one that doesn’t go with the others.” Odd-Item Out (OIO) Odd-Item Out (OIO) Odd-Item Out (OIO) 3. Verbal Reasoning (VRZ) Measures verbal-analytical reasoning ability with fewer vocabulary and general knowledge demands than GWH Directions: “Listen carefully while I read something to you. When I finish, tell me your answer.” Verbal Reasoning (VRZ) Grass is to green, as sky is to ____? Blue Fire hydrant is to short, as skyscraper is to ____? Tall Waiter is to restaurant, as masseuse is to ___ ? Spa 4. What’s Missing (WHM) Measures nonverbal reasoning where the individual must conceptualize the picture, analyze its gestalt, and deduce the essential missing element Directions: “Look carefully. What’s missing in this picture?” What’s Missing (WHM) What’s Missing (WHM) 5. Verbal Memory (VRM) Assesses the ability to encode, briefly store, and recall verbal material in a meaningful context where associations are clear and evident Directions: “Listen carefully while a read you a sentence/story. When I stop reading, tell it back to me. Do the very best you can. Try to tell it back to me using the same words.” Verbal Memory (VRM) Stories Scoring examples for the RIAS Verbal Memory subtest: Sentences Scoring examples for the RIAS Verbal Memory subtest: Stories Verbal Memory Subtest Items by Age 6. Nonverbal Memory (NVM) Assesses the ability to encode, store, and recognize pictorial stimuli that are both concrete and abstract or without meaningful referents Directions: “See this picture? Look carefully.” (Allow 5 seconds.) “Point to the picture you saw.” Nonverbal Memory (NVM) Nonverbal Memory (NVM) Example of a Completed First Page of the RIAS Record Form Example of Completed Profile Graphs From the RIAS Record Form Sample Case: ADHD Combined Type and Reading Disability 8-year-old boy in special education for three periods per day and daily after-school tutoring Dx of ADHD in 2002; currently taking Concerta (36 mg QD) Poor academic motivation Hx of cardiac arrest and anoxia at birth RIAS Results Verbal Intelligence Index (VIX) 85 Nonverbal Intelligence Index (NIX) 85 Composite Intelligence Index (CIX) 89 Composite Memory Index (CMX) 84 Other Results and Disposition Total reading is 70 on one measure and 69 on another Mother ratings are: Hyperactivity (89), Conduct Problems (79), Atypicality (80), Attention Problems (84), Aggression (73), and Depression (72) Regular education teacher ratings are: Hyperactivity (76), Attention Problems (71), Learning Problems (80) and Atypicality (96) Special education teacher rating is: Hyperactivity (72) Composite intelligence test score in 2002 was 89 Special education participation was increased RIAS Scheme of Verbal Descriptors of Intelligence Test Performance Interpretation Steps Collect collateral information List all scores that may indicate functional impairment or strength Integrate information and draw conclusions consistent with scientific knowledge Test rival hypotheses Sample Case: Academic Underachievement and Dysphoria 7-year-old second grader referred for suspected LD and severe emotional outbursts that occur daily at home Stanford-Binet composite in 2000 was 84; achievement scores ranged from 61 in math to 76 in reading Hx of depression for maternal grandmother, great grandmother, several aunts and uncles, and older sister; one aunt diagnosed with bipolar disorder Behavior during testing was optimal RIAS Results Verbal Intelligence Index (VIX) 96 Nonverbal Intelligence Index (NIX) 115 Composite Intelligence Index (CIX) 104 Composite Memory Index (CMX) 111 Other Results and Disposition Achievement scores ranged from 89 in mathematics to 94 in spelling Examinee over-controls emotions and has low self-esteem as indicated on Rorschach Mother ratings are: Somatization (73), Withdrawal (73), Atypicality (92), Attention Problems (71), Aggression (69), and Depression (69) Teacher ratings are: Anxiety (69) and Somatization (64) Psychotherapy and monitoring for learning disability and depression recommended Sample Case: Seizure Disorder, Adult Onset 40-year-old male high school graduate has worked in saw blade manufacturing for 22 years; factory uses acetylene to harden saw blades Chronic headaches for past 3 years Progressive symptoms of extreme fatigue, anxiety, agitation, anger outbursts, sweating, confusion Hard neurological signs, four focal lesions, noted on MRI Diagnosed with absence and complex partial seizure disorder, sleep apnea, possible early Parkinson’s disease Unable to work, receiving disability, and in litigation against former employer RIAS Results GWH 30 OIO VRZ 20 25 WHM 54 VRM 48 NVM 33 VIX/NIX/CMX CIX 66 81 70 84 Evaluation of Reliability and Validity Evidence for the RIAS Indexes and Subtests Demographic Characteristics of the U.S. Population and of the RIAS Standardization Sample: Percentages by Age and Ethnicity Demographic Characteristics of the U.S. Population and of the RIAS Standardization Sample: Percentages by Age and Educational Attainment Reliability Coefficients of the RIAS Subtests by Age Group Reliability Estimates of the RIAS Indexes by Age Group Standard Errors of Measurement of the RIAS Indexes by Age Group Stability Coefficients of Scores for the RIAS Subtests and Indexes for the Total Test-Retest Sample Stability Coefficients of Scores for the RIAS Subtests and Indexes for the 3- to 4-Year-Old Test-Retest Subsample Sample Case: ADHD Combined Type 11-year-old male fifth grader who has been taking Ritalin (now 20 mg SR) for past 6 years Adopted child with history of neglect, exposure to family violence, and multiple foster home placements Classified as “other health impaired” and receiving special education for 7 years Expresses dislike for school but is obtaining satisfactory grades Composite IQs were 84 at age 5 years, 77 at age 7 years, and 83 at age 9 years Nonverbal scores were always lowest (72 at age 5 years, 70 at age 7 years, and 64 at age 9 years) RIAS Results Verbal Intelligence Index (VIX) 92 Nonverbal Intelligence Index (NIX) 104 Composite Intelligence Index (CIX) 98 Composite Memory Index (CMX) 80 Other Results and Disposition Achievement scores ranged from 84 in mathematics to 114 in spelling Adoptive mother ratings are: Hyperactivity (73) and Attention Problems (68) Teacher ratings are: Anxiety (79) and Learning Problems (71) Continue special education with additional strategies to help him stay organized and productive Demographic Characteristics for the RIAS and WISC-III Correlations Sample Correlations Between the RIAS Indexes and the WISC-III IQs Correlations Between the RIAS Subtests and the WISC-III Subtests Demographic Characteristics for the RIAS and WAIS-III Correlations Sample Correlations Between the RIAS Indexes and the WAIS-III IQs Correlations Between the RIAS Subtests and the WAIS-III Subtests Demographic Characteristics for the RIAS and WIAT Correlations Sample Correlations Between the RIAS Indexes and the WIAT Composites Correlations Between the RIAS Subtests and the WIAT Subtests RIAS Scores for Various Clinical Groups RIAS Scores for Children and Adults With Learning Disabilities or AttentionDeficit/Hyperactivity Disorder RIAS Scores for Five Groups With Psychiatric Disorders Example of a Completed Score Summary and Profile Graphs From the RIST Record Form Standard Errors of Measurement and Reliability Coefficients of the RIST by Age, Gender, and Ethnicity Stability Coefficients of the RIST Correlations Between the RIST and Other Measures of Intelligence and Achievement RIST Scores for Various Clinical Groups Correlations Between the RIAS Subtest T Scores and Indexes and the RIST Index by Age Group Cumulative Percentages of RIAS Subtest Score Discrepancies for Ages 6 to 11 Years RIAS Measure of g: Four Subtests RIAS Intelligence Subtest Loadings From a Principal Factors Solution by Age Group RIAS Measure of g: Six Subtests RIAS Intelligence and Memory Subtest Loadings From a Principal Factors Solution by Age Group Verbal and Nonverbal Components: Four Subtests Verbal and Nonverbal Components: Six Subtests Verbal, Nonverbal, and Memory Components Goodness of Fit Statistics for Confirmatory Factor Analyses of Competing Models for the RIAS in 3- to 5-Year-Olds Goodness of Fit Statistics for Confirmatory Factor Analyses of Competing Models for the RIAS in 6- to 11-Year-Olds Goodness of Fit Statistics for Confirmatory Factor Analyses of Competing Models for the RIAS in 12to 18-Year-Olds Goodness of Fit Statistics for Confirmatory Factor Analyses of Competing Models for the RIAS in 19to 54-Year-Olds Goodness of Fit Statistics for Confirmatory Factor Analyses of Competing Models for the RIAS in 55to 94-Year-Olds Cumulative Percentages of RIAS Subtest Score Discrepancies for Ages 19 to 94 Years Smoothed Mean Raw Scores for the Guess What Subtest for Males by Age Smoothed Mean Raw Scores for the Guess What Subtest for Females by Age Sample Case: Lacunar Infarct Age 52, seen for infarct in the posterior limb of the left internal capsule Symptoms include right unilateral deficits in motor strength and speed, impaired attention, impaired visual-motor integration, and diminished short-term memory, although memory improved 1 year postincident Depression and anxiety have worsened to include suicidal ideation and taking 4 or more hours to fall asleep K-BIT was 92 in 2001 and 88 in 2002 MMPI-2 Results Hypochondriasis 80 Depression 96 Hysteria 75 Psychopathic Deviate 63 M/F 65 Paranoia 92 Psychasthenia 88 Schizophrenia 91 Hypomania 49 Social Introversion 86 RIAS Results GWH 41 OIO VRZ 44 42 WHM 39 VRM 51 NVM 41 VIX/NIX/CMX CIX 89 88 87 94 Diagnoses Axis I 294.9 Cognitive Disorder due to CVA 316 Stress-Related Physiological Response Affecting Medical Condition 296.23 Major Depressive Disorder, Severe Without Psychotic Features Axis II V71.09 No diagnosis Axis III Status post CVA in 2000 Hypertension, migraines Axis IV Occupational problems (unemployment), problems with primary support group (conflicts with live-in boyfriend), economic problems Axis V Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF) = 30 Resources PAR: www.parinc.com Kamphaus, R. W. (2005). Clinical assessment of child and adolescent intelligence (2nd ed.). New York: Springer. Available at www.springer.com. Frick, P. J., Barry, C., & Kamphaus, R. W. (2009). Clinical assessment of child and adolescent personality and behavior (3rd ed.). New York: Springer. Available at www.springer.com. rkamp@uga.edu