File - Beechen Cliff School Humanities Faculty
advertisement
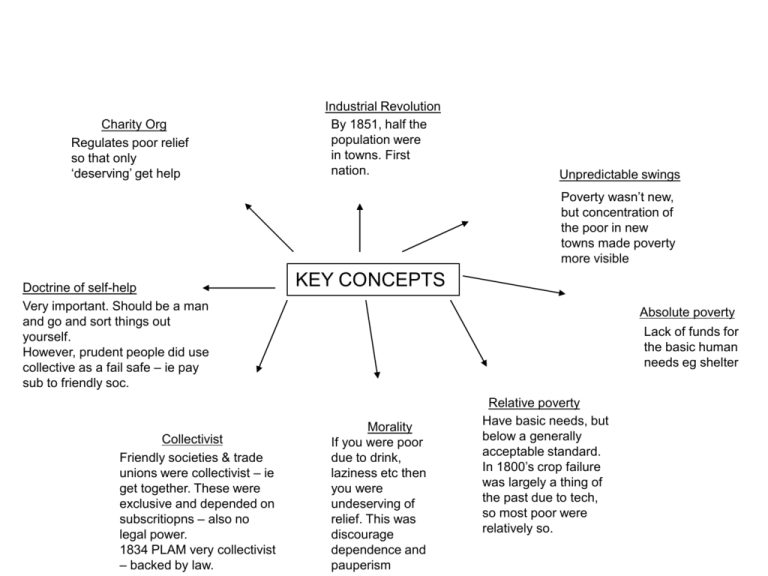
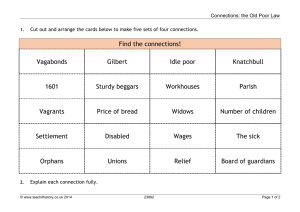
Charity Org Regulates poor relief so that only ‘deserving’ get help Industrial Revolution By 1851, half the population were in towns. First nation. Unpredictable swings Poverty wasn’t new, but concentration of the poor in new towns made poverty more visible Doctrine of self-help Very important. Should be a man and go and sort things out yourself. However, prudent people did use collective as a fail safe – ie pay sub to friendly soc. Collectivist Friendly societies & trade unions were collectivist – ie get together. These were exclusive and depended on subscritiopns – also no legal power. 1834 PLAM very collectivist – backed by law. KEY CONCEPTS Absolute poverty Lack of funds for the basic human needs eg shelter Morality If you were poor due to drink, laziness etc then you were undeserving of relief. This was discourage dependence and pauperism Relative poverty Have basic needs, but below a generally acceptable standard. In 1800’s crop failure was largely a thing of the past due to tech, so most poor were relatively so. Why categorise? They wanted to categorise poor so could then do something about it in order to push them into labour – good for economy Vagrants 40-100000 men and boys were vagrants. They begged despite the Elizabethan poor law stating they shouldn’t. Diets Price of bread always fluctuating. Made artificially high by Corn Laws. Lots of broths, stews etc. Took ingenuity – especially as standard of food being sold was very poor. New working class? Proletariat were poor relative to rest of nation. Some argue that I.R created a new, SINGLE working class – too simplistic? 1% of pop has 67% wealth - fear BEING POOR Survival £1 = 20s 1s = 12p 1p = ½ p and 2 farthings Inflation remained fairly negligible during 19th cent so needed £1 per week per family. No room at all for any extravagance – transport, beer, letters, stamps etc. Respectable ‘Respectable’ workers lived away from the slums and deemed themselves superior to inner circle. W.Booth (Salvos 1865). 3 circles of poverty. Outer is labour aristoc eg handloom. Inner = ‘darkest England”. Chadwick 1842 Report on San.cond of lab.pop of GB ‘ unknown country’ Paine – higher tax on landowners. Basic social welfare – inc ed allowances and OAP. 1792 Rights of Man. Came up with radical notion of workhouse. Liked v much. Owen – Socialist, factory owner. Glasgow – community based on co-op. Govt should follow suit. Too revolutionary. Ricardo – Inf by M and Adam Smith. 1817 ‘principles of pol economcy and taxation’. Abol poor law cos encouraged laziness and kids. Have a free market economy. 1601. For humane & order reasons. 15000 parishes resp for orphans, sick and elderly Poorhouses for indigent / deserving. Work provided and if none, then cash or food relief. Financed – poor rates based on property value. Each parish had overseer and vestry acc to local mag. 17th Cent – laws of settlement. Born / 3yrs settlement. 1782 Gilberts Act – parishes can unite to form auths and share poorhouse and costs. OLD POOR LAW Malthus – econ writer. Pop geometrical, ag arithmetical. Pop would outstrip food. Abol poor law cos diminished will of poor to save and landowners would pay higher wages cos no rates. Also, no incentive to have kids. Nat Char Org did have good features – central admin, universal standards. But B showed lack of respect for poor’s dignity, rights or emotional needs. Would make totally dep. Chadwick followed B Wasn’t first welfare system but genuine and patriarchal motives. Some workers even demanded patriarchy as a right. Bentham – doc of utilitarianism. Greatest hapiness to greatest number. 1798 ‘pauper man improved’. Entire resp to Nat Char Org. 250 indus houses (half mill pop) rising to 500. Abol outdoor relief. Deliberately tough. Those born stay til early 20s. Profit. 1795 Speenhamland System. Mags, Berks cos of French Rev and econ downturn. Pay ag labs according to number of kids and price of bread. Ie paying those who are working and poor. Variations – Roundsman system – send unemp round farms and allowance to farmer. Labour rate system – farmers exempt from rate if took on unemp. Suggestions – Greater distinction between poor labourer and pauper. Impressed by Southwell (notts) where they already had a deterrent workhouse and had stopped outdoor relief. New central auth needed. Stop Findings – saw ‘demoralisation’ outdoor rel. Less eligibility. of working class.’system which aims its allurements at the weakest parts of our nature – which offers marriage to the young, security to the anxious, ease to the lazy and impunity to the profligate’. Why – Corn Laws to help econ. No imort until 80s a quarter. Riots cos kept price of bread artificially high and couldn’t see the logic. Riots 1817-9 returning soliders. 1832 ROYAL COM 400 Pages – 15000 copies. First part attacked old poor law. Second gave recommendations. Criticised – only 10% of parishes invest. Confusing q’s to semiliterate overseers. Used to back up predetermined conclusions. 9 members – Nass Senior – prof of political econ at Oxford. Chadwick (B;s sec). 26 ass comms – interviewed, questionnaires, attended vestry meetings. Riots meant susp of Habeus Corpus (now imprisoned in secret and without trial). New Seditious Meetings Bill, 6 Acts (50 people, publications etc). Seemed to confirm policy of repression following end of Napolean. Urban riots matched in rural areas in late 20s. Eg Swing riots – burnt machines and effiges of Poor Law Comms. 1830s again – Fra – political turmoil. Corruption – poor law work given to local tradespeople. H of C investigated. 1819 Act set up select vestries. But even these became corrupt – eg Morpeth Sel V – 11/20 in ale indus and most relief payments ended up there. 1852 Outdoor Relief Regulation Order – withdrew compulsory labour from 1842 act. Also, most unions allowed to replace workhouses by outside labour. (therefore must softer). By 1871, only 1 in 6 unions abiding by the 1844 order. But workhouses seen as symbol of new system and housed over 150,000 by 1870. Easily passed parl – but local identity stronger then national as v rural. Thus compromises in imp centrality. Powers of persuasion needed with recalcitrant localities. Indus towns – cont to give outdoor rel cos periodic trade dep meant 1000s and little other humane choice. Not big enough or numerous enough. Labour Test orders Act 1842 – if outdoor must be given, then must do some parish work – eg stone breaking, but many ignored this. Generally good – by 180 14000 parishes into unions. !2 mill pop. Only 800 parishes not in. Most of 350 new workhouses built by 1839 were in Rural South – big success here. North, not so – W. Ridings and Lancs stern resistance. Hardly any built. (also, Cornwall) Limited success – delayed workhouse building meant cont outdoor relief. 1844 Comm did ‘outdoor rel prohib order’ to every union and hoped ¾ would stop. Many didn’t. Rules open to interp eg no outdoor ‘except in accident or emerg – therefore Guardians did what they felt like. IMPLEMENTATION Enforcement - Not many ass comms. Close sup impossible. Accumulated masses of results and stats but imposs for Somerset House to deal with it – unpaid office clerks. Admin probs ignored as H of C desired to play down failures. First job was unions – lots of pub meetings. Local interest groups didn’t like the union=30 parishes pattern cos can loose contracts and higher costs. Time pressure – had to be registering births, deaths and marriages by 1837. Also contend with Gilberts unions and the 20% of parishes who had select vestries – clash. Commissioners didn’t have to report to parl. Initially only for 5 years and then renewed annually after 1839. 1847 turned into Poor Law Board – more direct control after workhouse atrocities – report to parl. Ass Comms had power to alter exiting workhouses but had to get Guardians to approve for building of new ones. Some ass c had big political skill here, some didn’t. 1836 9 ass comms upto 21. All agree its big significance and the fact that the poor hated it Broadly reflected commissions recc: estab central auth, parishes into unions, stopped outdoor, less eligib, workhouse test – ie if leave, no relief. Central – PLC 3 comms in London. Chadwick Secretary (upset). 1 union=30 parishes. Board of Guardians to be elected to strictly run workhouses. PLAM 1834 Some critics fuse both. A new free market philosophy gained hegemony without displacing control of landed aristocracy. Eg MJ Daunton (Revisionist) Other critics – Actually maintained powers of landed class. New system gives more control over turbulent, disaffected peasantry. After all, 1832 comm had been appointed by aristocratic H of C. Also landowners on board of Guardians. Eg Anthony Brundage (traditionalist) Critics – It’s class legislation by newly enfranchised mid class. Done to reduce rate burden and force workers to accept lower wages in fear. Workers forced to accept principles of free market economy / capitalism – eg Mitchell Dean (Marxist) Elsewhere, relative ease. NE v easy and London too. Midlands no one took direct action against trade slumps (eg found in Nott stocking trade) Todmorden 1838 – John Fielden, Radical MP. Closed down factory and stopped paying rates in protest at elected Board of Guardians. Workers attacked homes of Guardians. Overall – only anti poor law movt was in W Ridings and Lancs. No national coherence and ad hoc. Too broad alliance eg evangelical Tories and working class radicals. Late 1830s turned to chartism – ie reform would come by having parl elec by working men. Poor – patriarchal rights gone, symbolised new harsh auth, punishment for being poor, prison-like. Often wh a distance from home thus impersonal and threatening. Fuelled rumours of killing poor – following Malthus’ views on pop. Eg book of murder. 2 anonymous propaganda pamphlets talked about gassing kids. No distinction between deserving and undeserving. Hard working thrown in with criminals and treated the same. OPPOSITION Severe trouble in N – PLAM added to env of ’10 hour movt’ – camp for 10hr day. Comm tried in 1837+8 to intro unions (chadwich had advised to do it 3 yrs earlier when econ better) in Lancs and W Ridings. Mobs oftern formed upton 5000. Bradford 1837 and Dewsbury 1838 attacked workhouse buildings. Troops needed. Rioting – Kent 1835 and Amersham Union, Berks. Mob tried to stop paupers biegn moved to new workhouse in Amersham. Police and mags read riot act and armed yeomanry. Centralisation – John Walter of Times – a berks mag did not like it. Locality should run itself. Indep of local parish deemed cornerstone of English liberty. Campaigners said forced workers to accept lower wages. Highlighted lashes between old poor law guardians and vestrymen who bel they were doing well. Whouses in towns not enough for bad times, a useless drain on resources when times were good. Ratepayers – recognised indoor rel cost twice that of outdoor relief and feared breaking of patriarchal ties weakened social control. Abuse – many instances. March 1846 select HofC committee invest Andover, Hamps. Systematically underfed, watered milk, eating marrow off bones set to crush. Drunk bully master, cheap and undignified burials, sexual assault by master and son. Only forced to resign, that’s all. Centralised standards said to protect. Ie cant beat adults or girls, minimum food standards. Confinement cells. But some rules were tyrannical – eg if in wrong part of workhouse, not asking permission, too much noise etc then in trouble. Food – guardians to choose from 6 dietaries. Eg no2 was almost entirely bread and cheese for 3 meals. Meat only on Sunday. Variable quality. No cutlery. Unpleasant tasks – oakum picking, untwist ropes, stone breaking, crush animal bones for fert (stopped 1840s) Debate – Andover atypical, other atrocities were exag and invented. Also, centralisation provides prot. But if system designed to be harsh, people will inevitably push the boundaries. WORKHOUSES Uniform – segregation even if married – v bad cos of Victorian family values. For deterrent so wouldn’t spend ages in there like old system. Monotonous – Up 5, Brek 6-7. Lunch 12-1. Supper6-7, Bed 8. Compuls prayers. Design – Sampson Kempthorne. Y shaped, two or 3 stories. Main had workhouses. One wing had kitchen/dining/chapel. Other had dorms/day rooms. Masters yard in middle. Also, cruciform – two stories. Wall held workrooms and 4 work / ex yards. Each arm of cross had dining/dorm/chapel/schoolrooms. 200-500 paupers. Less elig – v strict but didn’t want cruelty. Said that they were protecting them from old poor law by having standards. Winter 1836 – 209 applied for relief in Uckfield, Sussex. Only 11 accepted workhouse. Rest had nothing as a result (cos heard workhouse so bad)