Unit 4: The Constitution
advertisement

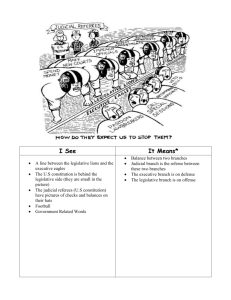
Read through the information on the structure of the articles of Confederation. As you read do the following: * Highlight or underline the main ideas in #’s 2-13. * On the back write down some ideas that you have about this government’s strengths and weaknesses. Read pages 132-137. Create a list of features of our first government that were good and those that were not so good. I. Articles of Confederation (1777-1789) A. First constitution of USA B. Written during the Revolutionary War (1777) C. Created a “firm league of friendship” among states II. Government under the Confederation A. Each state has ONE vote in Congress B. Congress choose a presiding officer- 1 yr term C. Congress has limited power 1. no power to enforce its own laws 2. no power to regulate trade 3. cannot collect taxes 4. no national court system 5. no army or navy Confederation diagram 1. People Vote for State Reps. 2. States make laws and choose National Reps. 3. National makes unofficial group decisions III. Problems under the Confederation A. Territorial Expansion 1. How to organize land in west? 2. Northwest Ordinance (1785 & 1787) a. divided land that later became OH, IN, IL, MI & WI b. set up a government for these territories 3. Most important act under Articles of Confederation Indian Land Cessions: 1768-1799 State Claims to Western Lands Northwest Ordinance of 1787 The United States in 1787 B. Economic problems 1. dispute over the value of money from different states 2. nation hit by an economic depression 3. farmers begin to lose land a. shay’s rebellion—MA farmers try to attack arsenal b. Can the new government respond? Shays’ Rebellion: 1786-7 There could be no stronger evidence of the want of energy in our governments than these disorders. -- George Washington IV. Constitutional Convention A. Philadelphia- May 1787 B. 55 delegates from 12 states (RI—none) C. GW presides over the meeting D. Sessions held in secret E. James Madison (VA) keeps detailed notes & has many ideas “Father of the Constitution” Independence Hall Philadelphia Ben Franklin John Hancock You will be divided into 4 groups and be assigned a topic to research using your book. (Your group will only have 10 minutes to read and develop an answer.) Your group will then present this information to the rest of the class. Pages 141-143 The topics are: 1) Virginia Plan 2) New Jersey Plan 3) The Great Compromise 4) The 3/5 Compromise V. How much power should the national government have? A. Two sides 1. strong National Government (Virginia Plan) 2. strong STATE government (New Jersey Plan) VIRGINIA PLAN James Madison (author) 3 branches Executive Judicial Legislative (Congress) Congress Divided into two houses Representation based on population NEW JERSEY PLAN William Paterson (author) 3 branches Executive Judicial Legislative (Congress) Congress One house; equal representation for states Connecticut Compromise Roger Sherman (author) 3 Branches Executive Judicial Legislative (2 houses) Congress Senate; 2 representatives per state House of Representatives; based on population (at least 1 per state) B. Solution 1. strong central government 2. states retain some power 3. power in government divided among three branches a. Executive b. Legislative (2 house Congress) c. Judicial federation diagram 1. People Vote for State and National Reps. 2. States make state laws and follows National laws 3. Nation makes official Laws and policies to be followed by all citizens VI. How should the states be represented in the new Congress? A. Two sides; 1. large states—base on population! 2. small states—equal per state B. Solution-The Great Compromise 1. Senate—each state 2 reps. 2. House of Representatives--# based on population (min. of 1 rep) VII. Problem #2– How should slaves be counted? A. Two sides 1. Southern states—count all slaves 2. Northern states—do not count ANY B. Solution—3/5 COMPROMISE 3/5 of slaves would count to determine eaCh state’s representatives 1790 Census Information on Population Delaware 59,096 8,887 % of Total Population 15.04% Rhode Island 68,825 948 1.38% Georgia 82,548 29,264 35.45% New Hampshire 141,885 158 0.11% New Jersey 184,139 11,423 6.20% Connecticut 237,946 2,764 1.16% South Carolina 249,073 107,094 43% Maryland 319,728 103,036 32.23% New York 340,120 21,324 6.27% Massachusetts 378,787 0 0% North Carolina 393,751 100,572 25.54% Pennsylvania 434,373 3,737 0.86% Virginia 691,737 292,627 42.3% Total for USA 3,582,008 681,834 19.04% State Slave Total Population Population Preamble and Article 1: 1) 2.2 2) 3.3 3) 3.4 4) 6.1 5) 6.2 6) 5.2 7) 7.3 8) 9.3 9) 10.2 10)5.1 11)7.2 12)10.3 Articles 4-7: 1) 4.1 2) 4.2.2 3) 4.3.1 4) 4.4 5) 5 6) 5 7) 6.2 8) 6.3 9) 6.3 10) 7 11) 7 VIII. How can the power of the government be limited? A. Give each of the three branches a different function 1. Executive Branch – carry out laws 2. Judicial Branch – interprets laws 3. Legislative Branch – makes laws SEPARATION OF POWERS Delivery Roads Crime Health Branches of U.S. Constitution Executive Judicial Legislative President Supreme Court Congress Enforce the Laws Agriculture Commerce Defense Education Energy Health & Human Services Homeland Security Housing and Urban Development Interior Justice Labor State Transportation Treasury Veteran’s Affairs Interprets the Laws Lower Federal Courts Make the Laws House Of Representatives Senate B. Set up a system of CHECKS AND BALANCES so that each branch can control what the other two branches do Checks and Balances of the Constitution Executive Branch Checks on Judicial Grant Pardons Appoint Judges Checks on Legislative Veto Bills Propose Bills Negotiate Treaties Nominate Officials Checks and Balances of the Constitution Legislative Branch Checks on Judicial Impeach Judges Make Amendments Approve Judge Nominees Change # of Supreme Court Judges Checks on Executive Impeach President Over Ride Veto Reject Treaties Reject Nominees Appropriate Money Checks and Balances of the Constitution Judicial Branch Checks on Executive Interpret Laws and Treaties Declare Acts and Laws Unconstitutional Checks on Legislative Interpret Laws and Treaties Declare Acts and Laws Unconstitutional How a Law Gets Made 2 1 3 Requirements/Terms of Office House of Representatives Senate President Minimum Age 25 30 35 Length of Term 2 Years 6 Years 4 Years Maximum number of terms Unlimited Unlimited 2 Terms Number per state Min. 1 per State: Pop. Based 2 Not applicable Total number 435 100 1 You need to search the internet or newspapers for an article dealing with one of the branches of the National Government. You need to cut out the article or post the web address into your edmodo assignment, summarize the article in 1-2 sentences, tell what branch it deals with, and why you think that. Due Date: 3-25-11 Preamble: We the people of the United States , in order to form a more perfect Union, establish justice, insure domestic tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote the general welfare, and secure the blessings of liberty to ourselves and our prosperity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America. IX. Ratifying the Constitution A. Nine of the 13 states had to approve before the Constitution could go into effect B. Federalists – support the Constitution 1. a strong government is needed to protect the people 2. James Madison & Alexander hamilton write “the federalist papers” to defend the Constitution C. Anti-Federalists – oppose the Constitution 1. a strong government is a threat to the people 2. Bill of Rights needed to protect individual rights Federalist vs. Anti-federalist D. Constitution is ratified by all thirteen states Ratification of The Constitution State Date Ratified votes votes % in for against favor Delaware Dec 7, 1787 30 0 100% Pennsylvania Dec 12, 1787 46 23 67% New Jersey Dec 18, 1787 38 0 100% Georgia Jan 2, 1788 26 0 100% Connecticut Jan 9, 1788 128 40 76% Massachusetts Feb 6, 1788 187 168 53% Maryland Apr 28, 1788 63 11 85% South Carolina May 23, 1788 149 73 67% New Hampshire June 21, 1788 57 47 55% Virginia June 25, 1788 89 79 53% New York July 26, 1788 30 27 53% North Carolina Nov 21, 1789 194 77 72% Rhode Island May 29, 1790 34 32 52% E. The Bill of Rights (first ten amendments to the Constitution) is added quickly What does The Bill of Rights protect? Open you textbooks to pages 166-167.