CJ-1 Vocabulary
advertisement
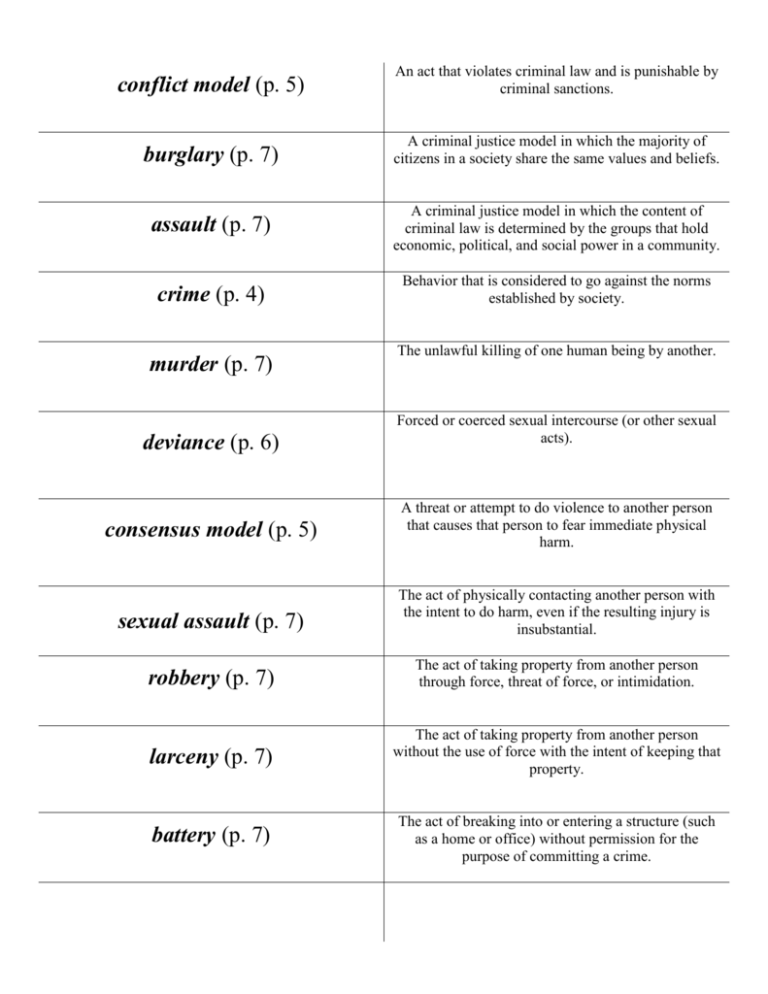
conflict model (p. 5) An act that violates criminal law and is punishable by criminal sanctions. burglary (p. 7) A criminal justice model in which the majority of citizens in a society share the same values and beliefs. assault (p. 7) A criminal justice model in which the content of criminal law is determined by the groups that hold economic, political, and social power in a community. crime (p. 4) Behavior that is considered to go against the norms established by society. murder (p. 7) deviance (p. 6) consensus model (p. 5) The unlawful killing of one human being by another. Forced or coerced sexual intercourse (or other sexual acts). A threat or attempt to do violence to another person that causes that person to fear immediate physical harm. sexual assault (p. 7) The act of physically contacting another person with the intent to do harm, even if the resulting injury is insubstantial. robbery (p. 7) The act of taking property from another person through force, threat of force, or intimidation. larceny (p. 7) The act of taking property from another person without the use of force with the intent of keeping that property. battery (p. 7) The act of breaking into or entering a structure (such as a home or office) without permission for the purpose of committing a crime. Behavior that has been labeled criminal because it is contrary to shared social values, customs, and norms. public order crime (p.7) white-collar crime (p.8) organized crime (p. 8) criminal justice system (p. 9) Nonviolent crimes committed by business entities or individuals to gain a personal or business advantage. Illegal acts carried out by illegal organizations engaged in the market for illegal goods or services. The interlocking network of law enforcement agencies, courts, and corrections institutions designed to enforce criminal laws. federalism (p. 10) A form of government in which a written constitution provides for a division of powers between a central government and several regional governments discretion (p. 14) The ability of individuals in the criminal justice system to make operational decisions based on personal judgment instead of formal rules. “wedding cake” model (p. 15) civil rights (p. 17) crime control model (p. 17) due process model (p. 17) A wedding cake-shaped model that explains how different cases receive different treatment in the criminal justice system. The personal rights and protections guaranteed by the Constitution, particularly the Bill of Rights. A criminal justice model that places primary emphasis on the right of society to be protected from crime and violent criminals. A criminal justice model that places primary emphasis on the right of the individual to be protected from the power of the government. The use or threat of violence to achieve political objectives. terrorism (p. 19) homeland security (p. 19) A concerted national effort to prevent terrorist attacks within the United States and reduce the country’s vulnerability to terrorism.








